By 2025, Google’s own documentation confirmed that each language version of a website is indexed and ranked independently, and content freshness is evaluated per language, not at the domain level.
This changes how global SEO works.
When translated pages lag behind the source site, search engines treat them as outdated, incomplete, or low-value content. Over time, this leads to indexing gaps, ranking loss, and uneven visibility across regions, even if the primary language performs well.
By 2026, AI website translation has become critical not because it replaces human translators, but because it enables search-speed multilingual publishing. AI allows content updates, technical SEO elements, and on-page signals to propagate across languages in near real time, preserving parity across markets.
In this context, AI website translation for global SEO 2026 is no longer about efficiency. It is about maintaining ranking consistency, index coverage, and search visibility as websites scale across languages and regions.
Key Takeaways
- AI website translation for global SEO 2026 is an SEO system, not a language task. Search engines rank each language independently, so consistency and freshness matter by language.
- Speed alone does not protect rankings. Translation must stay aligned with SEO structure, intent, and updates across every page element.
- Full-page coverage is non-negotiable. Metadata, internal links, UI text, structured data, and alt text impact visibility as much as body copy.
- Risk-based automation wins. High-impact pages need control and review, while low-risk content can scale fully automated.
- Measurement must be language-specific. Rankings, index coverage, engagement, and update latency reveal whether AI translation is helping or hurting SEO.
- Infrastructure beats tools. Platforms built for continuous, governed translation enable safe global SEO scale in 2026.
How Search Engines Evaluate Multilingual Content in 2026
Search engines do not evaluate multilingual websites as a single entity. Each language version is indexed, ranked, and judged independently. According to Google Search Central, translated pages are assessed on their own merit, and strong performance in one language does not automatically benefit others.
In 2026, three evaluation factors are critical:
1. Language relevance and search intent: Search engines assess whether content truly matches the user’s language and intent. Literal translations weaken relevance signals, generic phrasing limits ranking potential, and poor language fit increases bounce rates.
2. Content parity and freshness: Each language version is evaluated for completeness against the source. Missing sections reduce crawl priority, delayed updates signal lower quality, and outdated metadata directly impacts visibility.
3. Structural and technical consistency: Search engines rely on structure to interpret multilingual relationships. Clear language-specific URL patterns, correct hreflang implementation, and consistent internal linking and metadata are essential. Structural inconsistencies fragment SEO value and slow indexing.
In 2026, global SEO success depends less on the number of languages supported and more on how consistently each language version meets search engine expectations. AI website translation supports this consistency by keeping content, structure, and updates aligned at scale.
What Makes AI Website Translation SEO-Effective
In 2026, AI website translation is SEO-effective only when it fits naturally into how global SEO teams plan, publish, and optimise content. Effectiveness comes from precision and control, not speed alone.
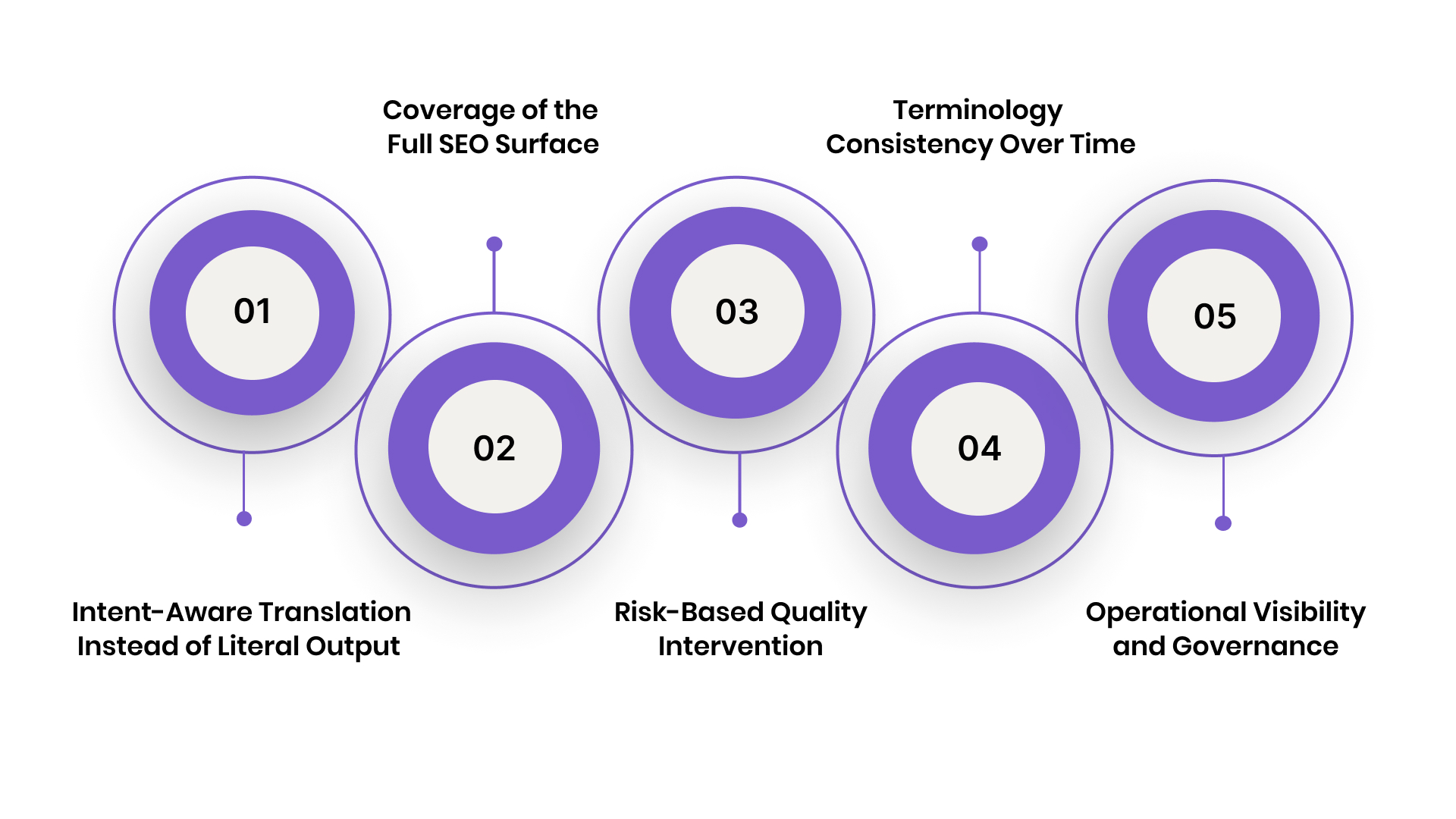
1. Intent-aware translation instead of literal output: Search queries vary by language in phrasing, tone, and intent. AI systems must adapt headings, CTAs, and copy to match local search behaviour, not mirror source-language wording. This directly affects engagement and ranking signals.
2. Coverage of the full SEO surface: SEO impact extends beyond body text. Navigation labels, breadcrumbs, alt text, and structured data all influence crawl behaviour and relevance. AI translation must handle every searchable and interactive element consistently.
3. Risk-based quality intervention: Pages do not carry equal SEO value. High-traffic, conversion-focused, or competitive pages require stricter validation, while low-impact pages can remain automated. This allows scale without introducing ranking instability.
4. Terminology consistency over time: Frequent updates expose SEO risk when terminology drifts. Stable, controlled language improves topical authority and reduces confusion for both users and search engines, especially in regulated or trust-sensitive industries.
5. Operational visibility and governance: SEO teams need transparency into translation changes, version history, and rollback options. Clear ownership across content, SEO, and localisation prevents silent regressions and ranking volatility.
In 2026, AI website translation supports SEO growth when it is intent-aware, governed, and embedded into real workflows. When those conditions are met, AI strengthens search performance instead of destabilising it.
SEO-Critical Components That Must Be Translated
For AI website translation to support global SEO in 2026, translation must go beyond visible page copy. Several high-impact components directly affect crawl depth, relevance signals, and user interaction, yet are often overlooked.
1. Page titles and meta descriptions: These elements shape search visibility and click-through rates. Titles should follow local phrasing conventions, while meta descriptions influence engagement. Reusing source-language metadata weakens SERP performance.
2. Headings and information hierarchy: Search engines use headings to understand structure and topical relevance. H1s and H2s must remain semantically aligned, and heading order should stay intact after translation to avoid confusing crawlers and users.
3. Internal link anchors: Anchor text carries contextual relevance. Translated anchors should match local query language, as generic or inconsistent anchors dilute topical signals and weaken internal linking strategies.
4. Navigation and interface text: Menus, filters, and facets influence crawl paths and page discovery. Untranslated or poorly translated UI elements disrupt continuity and limit index depth.
5. Image alt text and media labels: Media supports both accessibility and search visibility. Alt text must match the page language, as language mismatches reduce relevance signals and affect assistive technologies.
6. Structured data values: Search engines interpret structured fields literally. Schema values must align with the page language, since mixed-language markup creates ambiguity and can affect rich result eligibility.
7. Transactional and trust content: Forms, error messages, confirmations, and disclaimers influence conversion signals. Poor translation reduces clarity, weakens trust, and increases abandonment.
In 2026, SEO performance depends on whether every discoverable and interactive element of a page communicates clearly in the target language. AI website translation becomes SEO-ready only when it covers the full page surface, not just the visible copy.
How Enterprises Implement AI Website Translation Without Hurting SEO
By 2026, the primary risk in AI website translation is no longer translation quality. It is execution discipline. Even accurate AI output can weaken global SEO if translation operates outside core publishing, release, and optimisation workflows.
High-performing enterprises implement AI translation as a controlled, event-driven system that stays aligned with how content and SEO actually move.
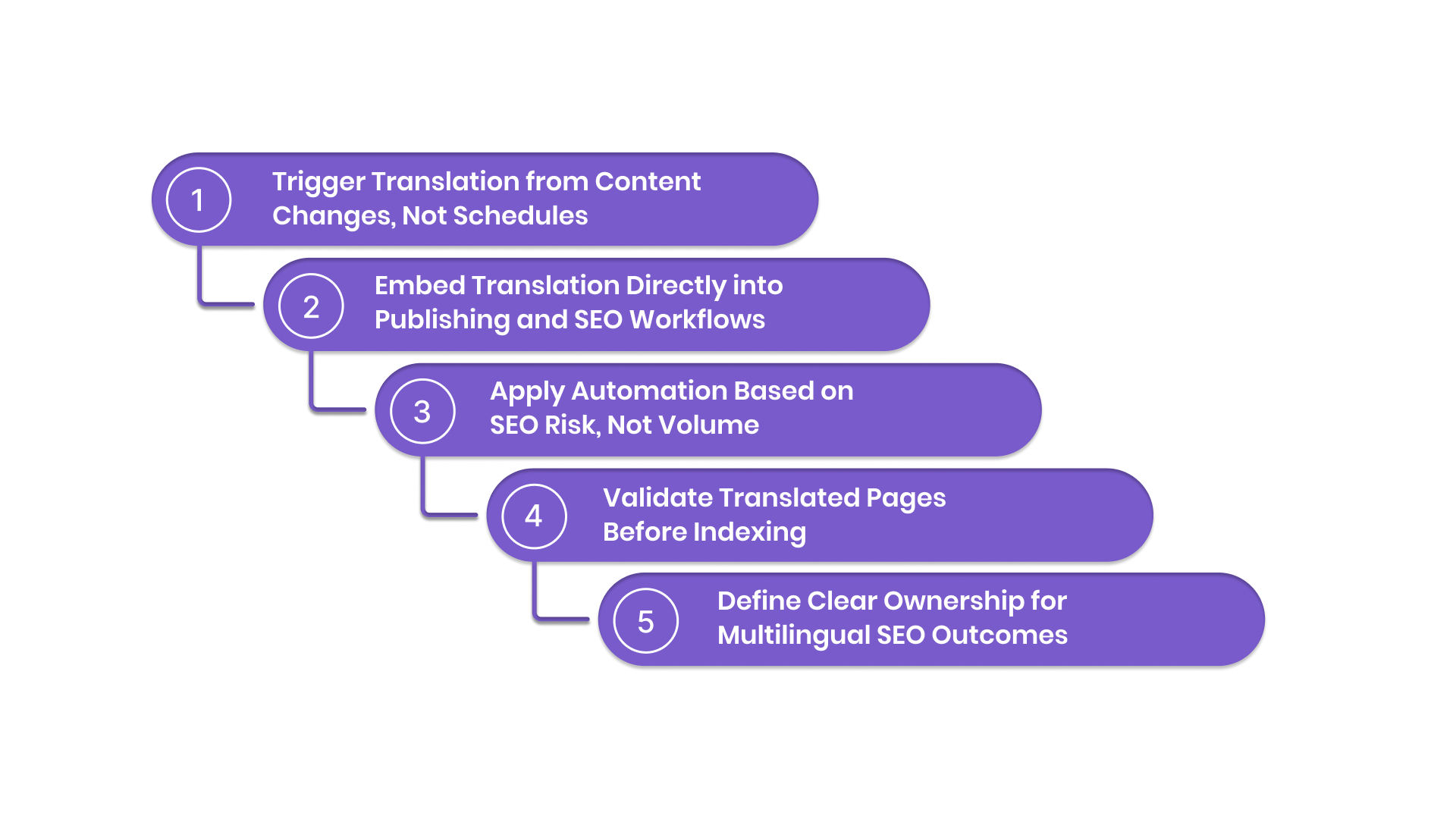
- Trigger Translation from Content Changes, Not Schedules: AI translation must respond to real content updates, not calendar-based batches. Whenever source content changes, translation and associated SEO elements should update in the same release cycle. Scheduled or manual translation creates silent freshness gaps that search engines interpret as quality decay.
- Embed Translation Directly into Publishing and SEO Workflows: Translation should run inside CMS, CI/CD, or deployment pipelines, not as a post-publish task. SEO and localisation checks happen before pages go live, ensuring translated versions never lag behind the primary site or bypass optimisation controls.
- Apply Automation Based on SEO Risk, Not Volume: Not all pages require the same level of oversight. High-traffic, revenue-driving, or competitive pages receive stricter validation, while low-impact or long-tail pages remain fully automated. Review depth is determined by SEO risk, not content quantity.
- Validate Translated Pages Before Indexing: SEO-safe implementation includes automated pre-index checks. Missing metadata, broken layouts, schema errors, or language mismatches are flagged before search engines crawl the page. This prevents weak signals from entering the index and protects overall domain trust.
- Define Clear Ownership for Multilingual SEO Outcomes: Successful enterprises assign responsibility by outcome, not task. SEO teams own performance by language, localisation teams ensure parity and completeness, and clear escalation paths exist when rankings diverge across regions. Without ownership, issues surface too late to correct.
When AI website translation is implemented as an event-driven, governed system, enterprises can scale languages without sacrificing rankings, consistency, or visibility. This is what separates SEO-safe AI translation from operational risk at scale.
How to Measure the SEO Impact of AI Website Translation
Once AI website translation is in place, the challenge shifts from execution to validation. In 2026, SEO leaders assess AI translation through search performance and business impact, not linguistic metrics.
- Track performance by language, not by domain: Measure impressions, clicks, and rankings for each language separately. Treat every language as an independent SEO market and identify where growth stalls despite strong source-language performance.
- Compare ranking parity across languages: Healthy multilingual SEO shows alignment across equivalent intent pages. Large ranking gaps often indicate issues with intent fit, terminology, or structure. Reducing these gaps over time signals effective AI translation.
- Measure crawl and index coverage by language: Track indexed URLs against expected page counts for each language. Identify orphaned or slow-to-index pages, which usually point to workflow or structural problems rather than translation quality.
- Monitor engagement signals as SEO health indicators: Review bounce rate, dwell time, and navigation depth by language. Drop-offs in key journeys often reveal intent mismatch or terminology instability introduced during translation.
- Track update latency as a core SEO metric: Measure the time between source updates and translated updates. Languages that consistently lag are more likely to experience ranking or traffic loss. Low latency is a strong indicator of SEO-safe AI translation.
- Tie translation performance to business outcomes: Connect SEO visibility to conversions, assisted revenue, and cost efficiency versus manual localisation. This links AI translation directly to measurable business value.
In 2026, organisations succeed when AI website translation is measured as an SEO system. Focusing on visibility, parity, engagement, and speed turns AI translation into a predictable growth lever rather than a scaling risk.
Common AI Website Translation Mistakes That Break Global SEO
In 2026, most SEO failures linked to AI website translation are not caused by poor language quality. They are caused by system-level execution failures. These issues quietly undermine rankings even when translated content appears accurate.
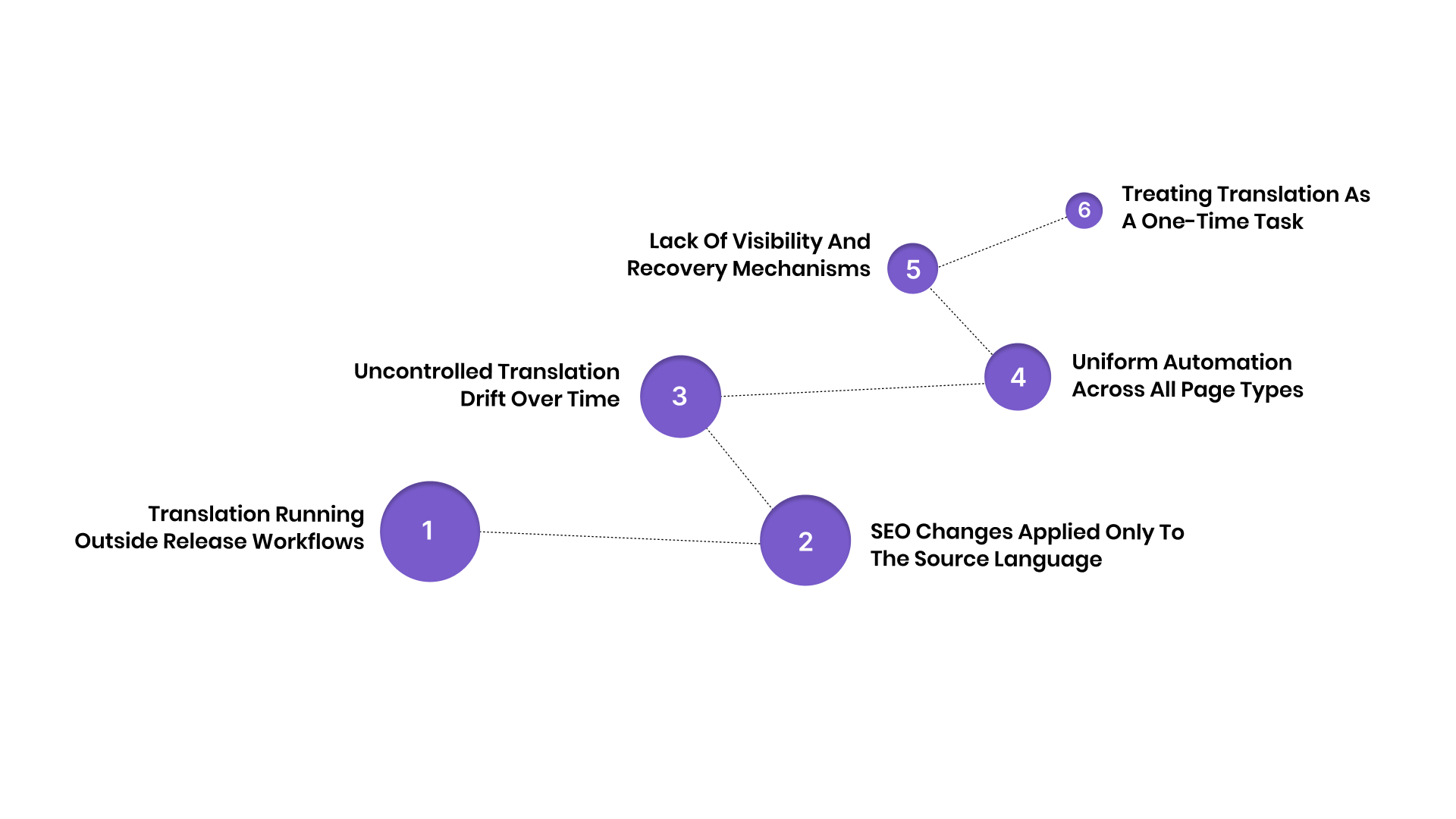
- Translation Running Outside Release Workflows: When translation updates trail source releases by hours or days, search engines encounter inconsistent signals across languages. These delays compound over time and steadily erode visibility, especially on frequently updated sites.
- SEO Changes Applied Only to the Source Language: Global SEO teams often optimise internal links, headings, templates, or page structure in one language only. When these changes do not propagate automatically, SEO equity fragments across markets without obvious warnings.
- Uncontrolled Translation Drift Over Time: Without enforced terminology and version control, AI output evolves inconsistently across updates. This weakens topical authority, creates semantic noise, and confuses search engines on high-frequency content.
- Uniform Automation Across All Page Types: Applying the same automation rules to pricing pages, legal disclosures, trust content, and long-tail blog posts introduces unnecessary risk. Some content types amplify small inconsistencies into ranking or conversion losses.
- Lack of Visibility and Recovery Mechanisms: Teams often notice traffic drops without knowing what changed, when it changed, or why. Without version history, audit trails, or rollback options, recovery becomes slow and reactive.
- Treating Translation as a One-Time Task: AI translation fails when it is executed as a batch project rather than a continuous system. Static translations fall behind dynamic websites, creating freshness gaps that search engines penalise.
These failures occur not because AI is inaccurate, but because translation is ungoverned. Avoiding them requires treating AI translation as part of SEO infrastructure, not as an isolated localisation step.
Where Human Review Still Matters in AI Website Translation
By 2026, AI handles the majority of website translation at scale. Human review remains essential, not as a default layer, but as targeted exception handling where SEO risk and business impact are highest.
- High-Impact SEO Pages: Pages that drive significant traffic, revenue, or brand visibility require intent validation and precision. Human review ensures these pages align with competitive search behaviour and ranking expectations.
- Regulated and Compliance-Sensitive Content: Financial, healthcare, legal, and policy content demands consistency and accuracy across updates. Human oversight reduces regulatory, trust, and reputational risk where errors carry real consequences.
- Search-Intent-Sensitive Content: Competitive keywords often depend on nuance, phrasing, and contextual relevance. Human judgement helps refine AI output where small wording shifts affect rankings.
- Brand and Conversion-Critical Messaging: Value propositions, CTAs, onboarding flows, and trust messaging influence user confidence and conversion. Human review ensures tone, clarity, and positioning remain consistent across markets.
- Exception Handling and Quality Escalation: Humans play a critical role in reviewing flagged anomalies, resolving edge cases, and approving changes on pages identified as high SEO risk.
The winning model is risk-based human review, not blanket manual processes. This preserves speed and scale while protecting SEO performance, trust, and conversion outcomes.
How High-Performing Teams Scale Global SEO with AI Translation Platforms
By 2026, high-performing SEO teams are defined by how reliably every language stays search-ready, not by how many languages they support. The difference is operating discipline.
These teams treat AI website translation as a continuous system, not a content task.
What they do differently:
- Translation triggers automatically from CMS updates or deployments
- SEO, content, and localisation workflows run in parallel
- Pages are reviewed based on SEO risk, not volume
- Performance is tracked by language for parity, index coverage, and latency
- Changes can be rolled back quickly without disrupting releases
This prevents the most common global SEO failure: language versions falling out of sync.
From Tools to Infrastructure
This model cannot be supported by standalone translation tools. It requires infrastructure embedded in publishing workflows, covering the full SEO surface, enforcing consistency, and providing governance at scale.
How Platforms Like Anuvadak Enable This Model
Platforms like Anuvadak act as a multilingual publishing infrastructure.
They enable:
- Always-on multilingual updates through direct CMS and deployment integration
- Full-page SEO coverage, including metadata, headings, internal links, UI text, schema, and accessibility labels
- Governed automation with terminology control, role-based review, and rollback
- Enterprise readiness with security, auditability, and compliance built in
Teams that treat AI translation as infrastructure maintain ranking parity, reduce SEO risk, and scale visibility without slowing content velocity.
This is how AI website translation becomes a long-term global SEO advantage, not just an efficiency gain.
Choosing an AI Website Translation Platform for Global SEO
By 2026, selecting an AI translation platform is fundamentally an SEO decision, not just a localisation one.
Key criteria to evaluate include:
- Full-page translation coverage: The platform must handle metadata, UI elements, structured data, and internal links; not just body content.
- Native workflow integration: Translation should integrate directly with CMS, release pipelines, and content updates to avoid lag.
- Governance and traceability: Teams need visibility into changes, approvals, version history, and rollback options.
- Terminology and consistency controls: Support for glossaries and domain-specific language is essential for long-term SEO stability.
- Scalability without risk: Automation should increase speed without amplifying errors or inconsistencies across languages.
The right platform ensures AI translation strengthens global SEO rather than undermining it as content velocity grows.
Conclusion: Turning AI Translation into a Global SEO Advantage
By 2026, global SEO is no longer won by publishing more content, but by keeping every language version accurate, current, and searchable. Search engines now judge performance at the language level, which means even small delays or inconsistencies can weaken visibility.
AI website translation matters because it allows multilingual content to move at the same pace as the source site. When translation is integrated into SEO and publishing workflows, teams can maintain alignment across markets without sacrificing control or quality.
Platforms like Anuvadak help organisations operationalise this approach, turning AI translation into dependable SEO infrastructure rather than a one-off tool.
If global rankings matter in 2026, continuous and governed AI website translation is no longer optional.


