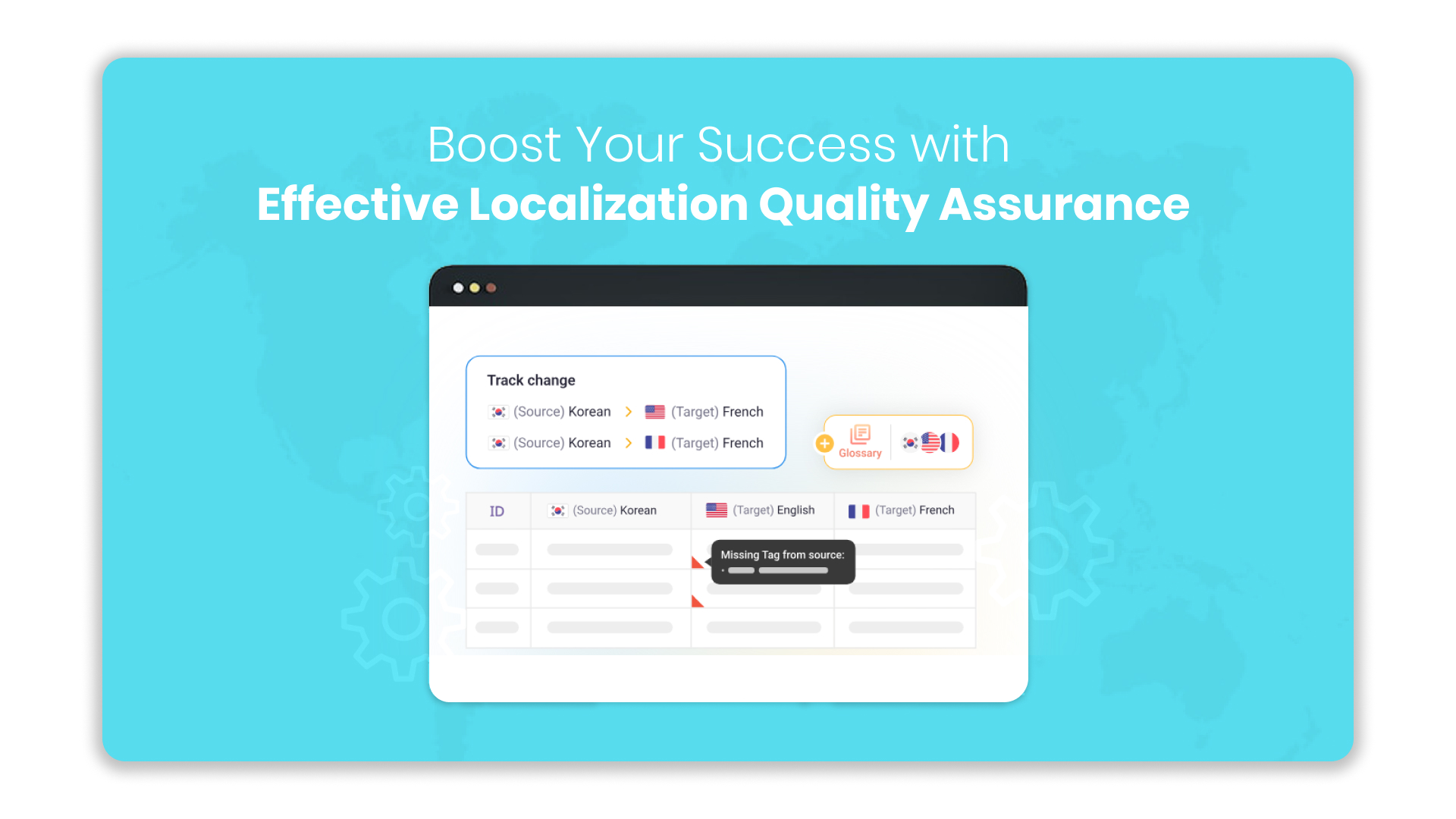
Are your localised product releases getting delayed because quality checks keep breaking your workflow?
For Product Managers and Marketing Leaders, ensuring localisation accuracy is not just a language task. It affects user trust, regulatory compliance, and the success of every digital experience you deliver across regions. Whether you manage eCommerce or enterprise applications, quality assurance is crucial for delivering reliable multilingual experiences.
Are you also facing challenges like inconsistent terminology, unclear review ownership, or quality checks that slow down your release cycles? This blog explores the best practices for localisation quality assurance, helping you build reliable, scalable, and high-quality multilingual experiences across your digital platform.
TL;DR
- Localisation Quality Assurance (LQA) ensures every language version of your digital platform is accurate, compliant, and user-ready across all regions.
- A strong LQA process includes clear quality standards, consistent terminology, structured workflows, and multi-level linguistic, functional, visual, and performance checks.
- LQA is essential for protecting user trust, meeting regulatory requirements, maintaining brand consistency, and reducing rework in large-scale multilingual operations.
- Effective localisation workflows depend on steps like preparing standards, testing across contexts, running pilot reviews, monitoring performance, and improving with each release.
- Best practices include using a centralised glossary, validating meaning and context, reviewing cultural suitability, using automation with human checks, involving native experts, and tracking quality KPIs.
What is Localisation Quality Assurance (LQA)?
Localisation Quality Assurance (LQA) is the process you use to verify that every translated version of your digital platform is accurate, consistent, and suitable for your users across regions. It verifies language quality, interface alignment, and cultural relevance so your platforms work smoothly in every market you serve.
For medium to large enterprises, LQA ensures that your content meets regulatory standards, supports accessibility needs, and protects user trust. A strong LQA process depends on several core elements. Here are some of the essential components you should include to maintain quality across all languages:
- Clear quality standards that define accuracy, tone, and compliance expectations.
- A centralised glossary and style guide to maintain consistent terminology and branding.
- Prepared source content that is structured, clear, and easy to translate.
- Multi-level review workflows covering linguistic, functional, visual, cultural, and compliance checks.
- Clear ownership across product, marketing, localisation, and regulatory teams.
- Automated testing tools to speed up checks and reduce manual workload.
- Real-device and real-market testing to validate behaviour across platforms and regional conditions.
- Continuous feedback loops to improve your localisation quality over time.
Once you know what LQA is, the real question is why it matters for your digital platforms across regions.
Also Read: 5 Inspiring Website Localisation Examples That Transformed User Engagement
What’s the difference between localisation QA and proofreading?
Localisation QA and proofreading may look similar, but they serve very different purposes in your multilingual workflow. Proofreading focuses only on correcting grammar, spelling, and language flow in translated content. It ensures that the text reads well, but it does not check how that content behaves.
Localisation QA goes much deeper. It checks whether the translated content is accurate, culturally suitable, and fully functional within your website, app, or digital platform. This includes reviewing UI alignment, layout issues, broken strings, formatting, compliance terms, and overall user experience across languages.
For enterprises operating at scale, proofreading alone is not enough. You need localisation QA to ensure your multilingual platforms work correctly, remain compliant, and deliver a smooth, trustworthy experience to users in every region.
Why Localisation Quality Assurance Matters
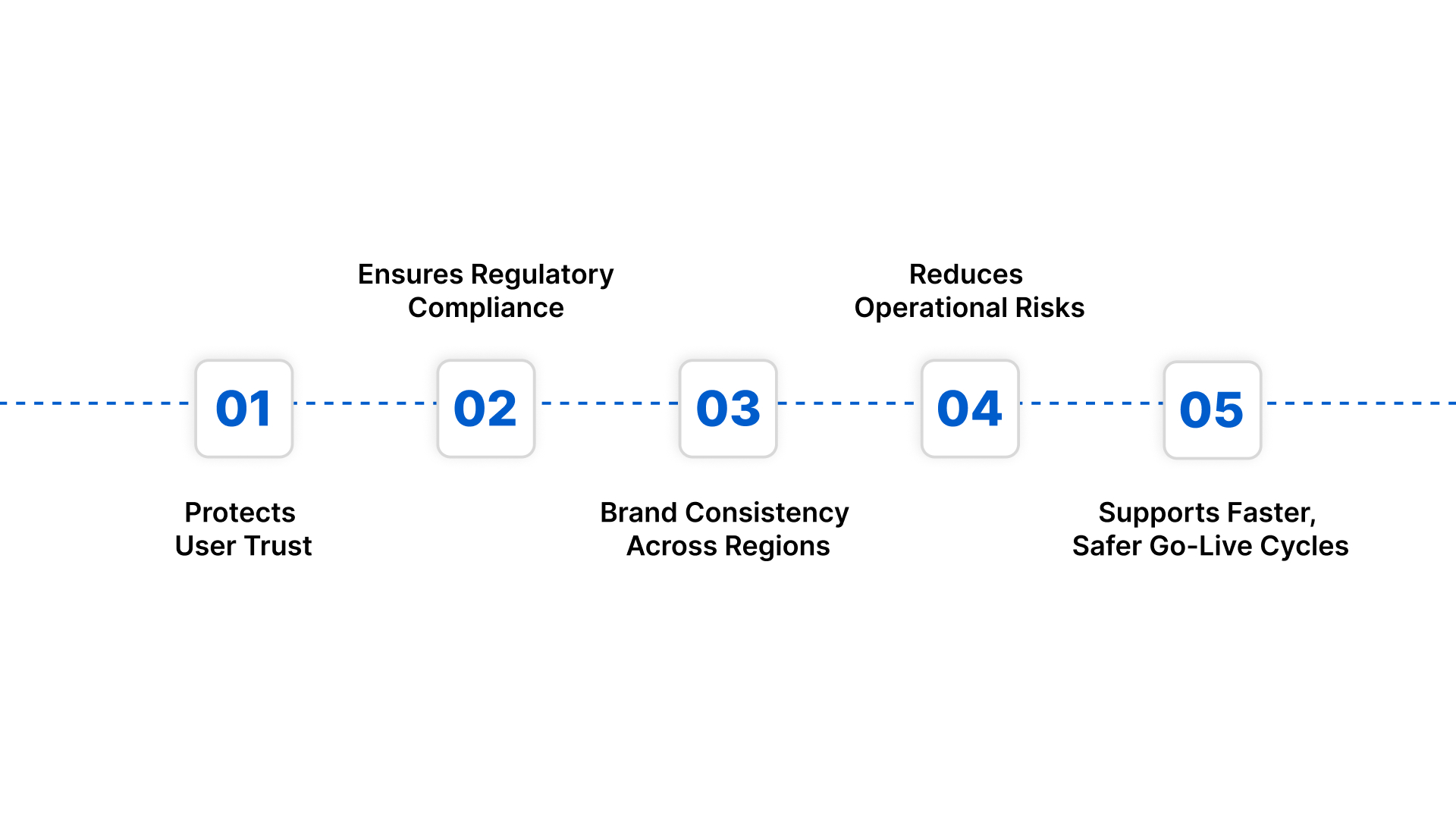
Localisation Quality Assurance (LQA) helps you deliver accurate, consistent, and trustworthy multilingual experiences across every digital platform you manage. Here are the key reasons why LQA is essential for your business:
1. Protects User Trust
Your users expect clear and error-free communication in their own language. LQA helps you avoid translation mistakes, confusing UI elements, or cultural mismatches that can weaken trust.
2. Ensures Regulatory Compliance
Industries such as banking, insurance, healthcare, and public services require accurate and compliant multilingual content. LQA helps you validate critical terms, disclosures, and instructions to ensure compliance with legal and accessibility standards.
3. Maintains Brand Consistency Across Regions
When multiple teams work on multilingual expansion, brand voice and terminology can easily become inconsistent. LQA ensures your messaging stays uniform across all languages, platforms, and markets.
4. Reduces Operational Risks
Poor localisation can lead to customer complaints, product failures, and rework. LQA helps you identify issues early, reducing the risk of costly fixes or reputation damage after launch.
5. Supports Faster, Safer Go-Live Cycles
With proper LQA checks, your teams can release multilingual content more confidently. This prevents last-minute errors that delay app launches or updates.
If you want to maintain this level of consistency across languages, a multilingual platform such as Anuvadak helps your teams manage updates, track translation progress, and ensure every language version meets the same quality and compliance expectations.
To apply LQA effectively, you need to know the key types involved.
Types of Localisation Quality Assurance
Localisation Quality Assurance (LQA) covers different checks that help you confirm whether your multilingual content is accurate, consistent, and ready for release. Each type focuses on a specific quality element, enabling you to manage risk, maintain compliance, and deliver a smooth user experience across regions.
Here are the main types of LQA:
1. Linguistic Quality Assurance
Linguistic LQA ensures that your translated content is accurate, consistent, and aligned with the intent of the source content. It helps you maintain brand voice, follow terminology rules, and avoid errors that may confuse users or raise compliance issues in regulated sectors like BFSI, healthcare, or government services.
What you check here:
- Correct meaning and context.
- Terminology and glossary adherence.
- Grammar, punctuation, and spelling.
- Tone and brand consistency.
2. Functional Quality Assurance
Functional LQA checks whether the translated content works properly inside your digital product. You confirm that the user interface, buttons, forms, and workflows behave as expected across all language versions. This is critical when you manage mobile apps, portals, or enterprise platforms at scale.
What you check here:
- UI alignment and layout issues.
- Text expansion or truncation.
- Navigation and button behaviour.
- Form inputs and error messages.
3. Visual Quality Assurance
Visual LQA ensures that your multilingual content looks clear, accessible, and readable for all users. It helps your teams identify design issues early, especially when scripts like Hindi, Tamil, Bengali, or Urdu require additional spacing or font adjustments.
What you check here:
- Font compatibility across languages.
- Readability and clarity.
- Image–text balance.
- Icon and symbol relevance.
4. Performance Quality Assurance
Performance LQA focuses on how your multilingual content affects the speed and stability of your digital product. Different scripts, longer text, or additional language files can affect load times, especially on high-traffic websites.
What you check here:
- Page load time across languages.
- Rendering speed for different scripts.
- API response time for language content.
- Overall app or website performance after localisation.
The next step is to understand key aspects of the process from start to finish.
Key aspects of the Localisation Quality Assurance Process?
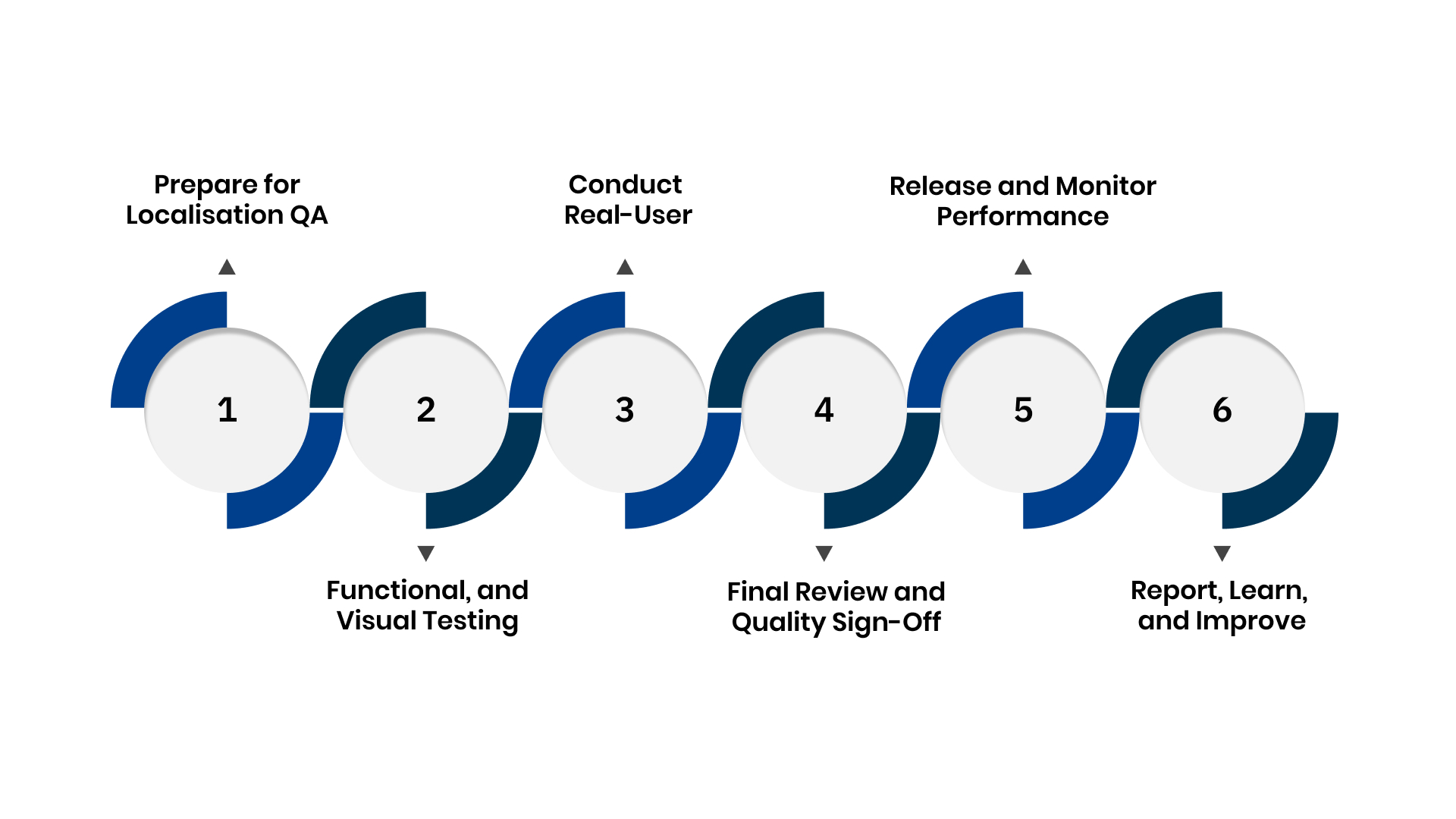
A good localisation QA process helps you manage quality at every stage of translation and product development. Here are the key aspects to focus on in your localisation QA workflow:
1. Prepare for Localisation QA
Start by creating a clear foundation for quality. You need defined quality standards, glossaries, and style guidelines so that every team works with the same rules. Choose the right tools for translation, QA, and collaboration. Also, decide which content needs priority review.
2. Execute Linguistic, Functional, and Visual Testing
Carry out detailed linguistic checks to ensure meaning, tone, terminology, and cultural relevance. Then, validate functional behaviour to confirm that layouts, buttons, navigation, forms, and error messages work correctly after translation.
Finally, review the visual experience to ensure fonts, spacing, directionality, and UI elements display cleanly across languages.
3. Conduct Real-User or Pilot Testing
Before you release widely, run a small pilot with users or internal reviewers who represent your target regions. This helps you identify issues that may only appear under real-world conditions, such as device variation, network behaviour, or local user expectations.
4. Final Review and Quality Sign-Off
After resolving all earlier issues, perform a final end-to-end check. Validate the complete experience language accuracy, UI stability, content flow, compliance requirements, and accessibility. Only sign off when all teams agree that the content meets the defined quality standards.
5. Release and Monitor Performance
Once your multilingual version goes live, monitor user feedback, error reports, and performance metrics. This helps you identify any issues that appear at scale or during live usage.
6. Report, Learn, and Improve
Document all findings, challenges, and improvements from the QA cycle. Use these insights to refine your localisation processes, update your guidelines, and strengthen your next release. Continuous improvement helps you scale multilingual content confidently and consistently.
Tools such as Anuvadak simplify several of these steps by offering automated updates, structured review workflows, and real-time progress tracking. This helps your teams maintain content quality while reducing the time spent on manual coordination.
Even with a strong QA process, you may still face recurring localisation issues. Understanding these challenges helps you address them early.
Also Read: E-commerce Localisation: A Comprehensive Guide for Seamless Expansion
Common Localisation Quality Challenges (and How to Solve Them)
Managing multilingual content at scale often brings issues that slow down delivery, affect accuracy, or create compliance risks. Identifying these challenges early helps you maintain consistency, reduce rework, and deliver reliable experiences across regions.
Here are the common localisation quality challenges you may face and how you can solve them:
1. Inconsistent Terminology Across Languages
Across large teams, different reviewers or vendors may use different translations for the same term. This creates confusion and damages trust. You can solve this by maintaining a centralised glossary and style guide that all teams follow. This ensures that product names, regulatory terms, and service-specific phrases remain consistent across all languages.
2. Poor Context or Ambiguous Source Content
If the original text is unclear, translators cannot deliver accurate results. This leads to confusion across all language versions. The best way to address this is to improve the source content first. Write clear, simple, unambiguous text and provide screenshots, notes, and examples so translators understand the full intent. Better source content always leads to better translations.
3. Layout and UI Breakage After Translation
Translations can be longer, use different scripts, or require right-to-left formatting, which often breaks the interface. This affects readability and user experience. To solve this, always run visual and functional testing inside the product on real devices. Checking alignment, spacing, truncation, and font support ensures your content fits smoothly across all languages.
4. Cultural Insensitivity or Incorrect Tone
What sounds normal in one region may feel inappropriate or confusing in another. This is a major risk for customer communication, government services, healthcare updates, and financial guidance. You can prevent this by involving native reviewers who understand cultural nuance and can adjust tone, examples, and references to suit local expectations.
5. Limited Feedback from Real Users
Internal teams may miss issues that arise only in real-world use, such as unclear instructions or confusing navigation. You can solve this by running pilot tests or collecting feedback from actual users in your target regions. Real user insights help you refine clarity, usability, and tone before the full release.
Once you understand the common localisation challenges, the next step is to apply the right practices to prevent these issues and strengthen your QA process.
Best Practices for Localisation Quality Assurance
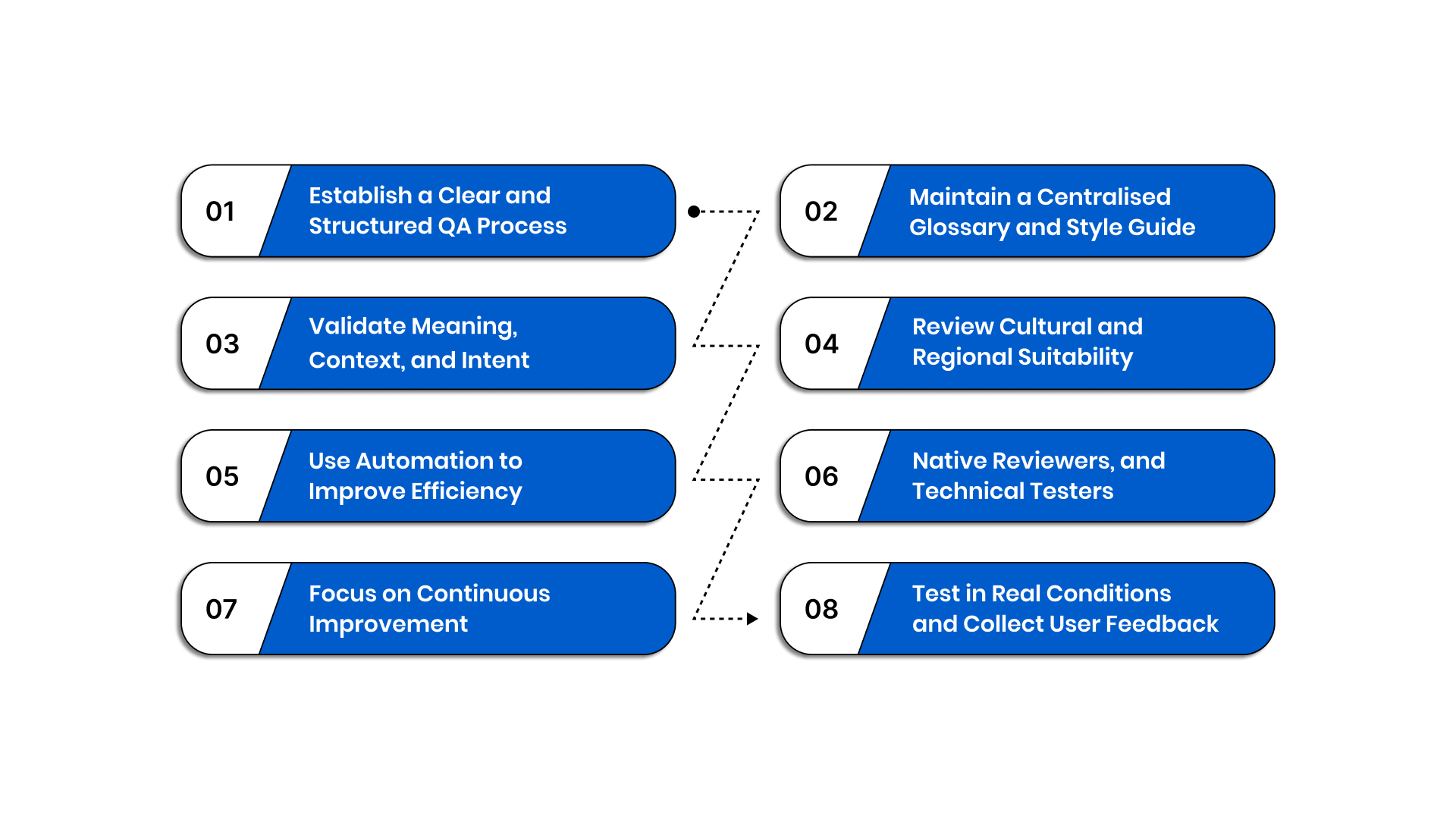
A strong Localisation QA process helps you deliver accurate, compliant, and user-friendly multilingual content across all your digital platforms. When you manage multiple languages at scale, following proven best practices ensures consistency, reduces risk, and keeps your releases on track:
1. Establish a Clear and Structured QA Process
A strong QA process starts with defined steps, clear ownership, and agreed quality standards. Each team should know who checks linguistic quality, who tests UI, who approves legal terminology, and who signs off the final version.
A structured workflow reduces delays, eliminates confusion, and ensures that every language version undergoes the same level of review before release.
2. Maintain a Centralised Glossary and Style Guide
A shared glossary helps you maintain consistency for product terms, financial terminology, medical language, policy instructions, or legal phrases across all languages.
Your style guide should set rules for tone, formatting, punctuation, brand voice, and examples. Together, these tools help your teams deliver consistent and compliant content at scale.
3. Validate Meaning, Context, and Intent
Always check whether the translated content accurately reflects the original message. A sentence can be grammatically correct yet still wrong in meaning if the context is misunderstood.
Pay close attention to instructions, policy text, UI messages, and any content where misunderstanding could create risk, confusion, or compliance issues.
4. Review Cultural and Regional Suitability
Cultural relevance is essential when serving users across India’s diverse languages and regions. Colours, symbols, examples, tone, and expressions must suit the local audience.
A cultural review ensures your content is respectful, clear, and aligned with local norms, especially important for citizen communication, financial guidance, or healthcare information.
5. Use Automation to Improve Efficiency
Automated QA tools help detect issues like inconsistent terminology, missing translations, incorrect placeholders, and formatting errors quickly.
Combine automation with human review for the best results. Translation memory, terminology databases, and integrated localisation platforms help you manage large volumes of multilingual content without losing quality.
6. Involve Local Experts, Native Reviewers, and Technical Testers
A strong LQA team requires expertise on multiple fronts:
- Native language proficiency to ensure accuracy.
- Cultural knowledge to avoid regional misunderstandings.
- Technical capability to test product behaviour.
This mix helps you validate language, meaning, and functionality across all language versions.
7. Track Quality Metrics and Focus on Continuous Improvement
Monitor quality KPIs such as:
- Error types and frequency.
- First-time accuracy.
- Reviewer feedback across regions.
- Terminology adherence.
- User satisfaction.
Analysing these metrics helps you identify recurring issues, refine your guidelines, and improve your localisation process over time. Continuous improvement ensures your multilingual experience remains consistent as your platform grows.
8. Test in Real Conditions and Collect User Feedback
Test your localised content with real users or small regional pilot groups before full release. They can identify issues that only appear under real-world usage, such as unclear wording, navigation problems, or tone mismatches.
This is especially important for mobile apps, eCommerce journeys, banking workflows, government portals, and healthcare information systems.
Also Read: Anuvadak – Website Localisation and Translation Tool
To apply these best practices effectively, you also need the right tools to support your localisation workflow.
Choosing the Right LQA Technology and Tools
Selecting the right localisation QA tools is essential when you manage multilingual content at scale. The right technology helps you reduce manual effort, maintain consistency, and speed up your review cycles across all languages.
Here are the key capabilities you should look for when choosing LQA tools:
1. Support for Multiple Languages and Scripts: Your tool should handle Indian languages, complex scripts, and right-to-left formatting without breaking your UI or introducing errors.
2. Built-in Terminology and Glossary Management: Look for tools that allow you to maintain a shared glossary, enforce terminology rules, and ensure consistency across large teams.
3. Automated QA Checks: Choose tools that can automatically detect missing translations, placeholders, formatting issues, and inconsistencies to reduce manual review time.
4. Real-Time Preview and UI Testing: A good LQA tool should let you preview how translated text appears in your actual product, helping you catch layout or truncation issues early.
5. Integration with Your CMS or Product: Seamless integration helps you automate updates, sync content faster, and reduce the risk of outdated or mismatched translations.
6. Analytics and Quality Reporting: Look for tools that provide dashboards, quality metrics, progress tracking, and error reports to help you monitor performance over time.
The next step is choosing a platform that can support these needs.
How Anuvadak Helps Improve Localisation Quality
Anuvadak is a unified multilingual website and app localisation platform that enables enterprises and government organisations to translate, manage, and deploy multilingual websites with minimal overhead and improve localisation quality. It supports Indian languages via a neural machine translation engine, automates content updates, and consolidates multilingual workflows on a single dashboard.
Here are the key benefits Anuvadak offers:
1. Faster and High-Quality Translation
Anuvadak uses an Indian-language specific neural machine translation engine that speeds up translation while improving accuracy for local languages. It also updates newly added English content automatically across all regional versions, ensuring users always receive the latest information in their preferred language.
2. Centralised Project and Content Management
Anuvadak consolidates your entire localisation workflow into one system, so you no longer need separate infrastructure, teams, or content management tools. You can easily add subdomains, manage settings, maintain version control, and oversee multilingual projects.
3. Powerful Analytics for Better Decision-Making
The analytics dashboard gives you clear visibility into localisation progress, user engagement, project performance, and page views. With insights into language-specific progress and site traffic, you can make data-driven decisions and optimise multilingual content based on real user behaviour.
4. End-to-End Automation for Higher Efficiency
Anuvadak automates most localisation tasks from string updates to page previews, reducing manual effort and speeding up deployment. Features like continuous localisation support and auto-updating of translated content ensure your website stays up to date across multiple Indian languages with minimal human intervention.
Conclusion
Localisation quality assurance plays a crucial role in delivering clear, consistent, and trustworthy multilingual experiences across your digital platforms. By following structured workflows, setting strong quality standards, involving native experts, and testing in real conditions, you can reduce errors, improve compliance, and enhance user trust across regions.
If you manage multilingual websites across regions and want a faster, more reliable way to maintain quality, Anuvadak gives you a complete localisation system designed for scale. This makes it ideal for enterprises in BFSI, eCommerce, healthcare, education, government, automotive, legal, and compliance sectors.
If you’re ready to simplify localisation and improve quality at scale, contact us to learn how Anuvadak can support your multilingual growth!
FAQs
1. Can automation or tools fully replace human review in LQA?
No. Automation helps catch technical issues such as missing translations, placeholders, and formatting errors, but human reviewers are essential for assessing tone, cultural relevance, context suitability, and natural language flow.
2. What common localisation problems does LQA help prevent?
LQA helps prevent language mistakes (typos, mistranslations), UI/UX issues (layout breakage, truncated text), cultural mis-references (wrong imagery or tone), regulatory or compliance errors, and functional glitches, all of which can degrade user trust or cause legal/brand risk.
3. Is LQA worth the investment for enterprises with many languages and high traffic?
Yes. For large-scale, multilingual platforms, proper LQA reduces rework, protects brand reputation, ensures regulatory compliance, improves user experience, and supports scalable global growth, making it a valuable investment.