In 2026, voice data has become too valuable to ignore. Customer calls, IVR interactions, voice searches, and spoken commands contain insights that can improve service quality, automate workflows, and expand reach across regional language users. But as voice adoption grows, organisations need a reliable way to convert large volumes of audio into accurate, usable text without slowing down product teams or delaying launches.
This is where speech-to-text APIs play a critical role. They enable businesses to transform live and recorded audio into structured text that can be searched, analysed, localised, and integrated into existing systems. The challenge, however, is getting started.
This Speech-to-Text API Qwik Start guide aims to help teams get started quickly, test real-world audio, and validate transcription accuracy before scaling to production.
At a Glance
- Speech-to-Text APIs convert spoken audio into structured text using Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR), enabling businesses to analyse voice data, automate workflows, and support multilingual customer interactions.
- India’s linguistic diversity, regional accents, code-switching, and noisy telephony audio make transcription challenging. Accurate STT requires models trained on real-world Indian speech patterns and dialects.
- Generic APIs often fail with mixed-language speech, telephony-grade audio, and regional accents, making them unreliable for production workflows in India’s enterprise and call-center environments.
- Reverie’s RevUp platform allows rapid evaluation of STT capabilities via interactive playgrounds, file-based uploads, and real-time streaming, supporting Indian languages, code-switched speech, and telephony-quality audio.
- After initial testing, businesses can integrate Reverie’s STT API into apps, IVR systems, or analytics platforms, customise domain vocabulary, deploy at scale (cloud or on-premise), and leverage dashboards for monitoring and optimisation.
What Is a Speech-to-Text API?
A Speech-to-Text API is a software interface that converts spoken audio into written text using Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR). In practical terms, it allows applications to listen to, understand, and transcribe what users say, whether the audio comes from a phone call, a mobile app, an IVR system, a meeting recording, or a voice note.
For businesses, a strong Speech-to-Text API acts as the underlying engine that powers voice-driven workflows at scale. It enables multilingual customer interactions, automates voice-heavy operations, and turns unstructured audio into data that can be analysed and acted upon.
In the Indian context, this means supporting real conversations across languages such as Hindi, Tamil, Telugu, Bengali, Kannada, Marathi, and more, often within the same interaction.
Behind the scenes, the API processes raw audio signals, applies acoustic and language models trained on regional speech patterns, identifies speakers, adds punctuation, and returns clean, structured text. This output can then flow directly into CRMs, analytics platforms, chatbots, quality-assurance systems, or automation pipelines.
Speech-to-text APIs are used across industries wherever voice needs to be converted into reliable, actionable text:
- Multilingual customer support and call centers: Transcribing real customer calls in regional and mixed languages for quality monitoring, compliance, and analytics.
- IVR systems: Understanding natural caller responses instead of relying on rigid, scripted inputs.
- Voice search and in-app commands: Enabling users to search products, navigate apps, or trigger actions using spoken queries in their preferred language.
- Automated call analytics and compliance monitoring: Converting large volumes of call recordings into searchable text for audits, insights, and reporting.
- Healthcare, legal, and BFSI workflows: Creating accurate documentation from doctor-patient conversations, legal proceedings, or financial calls.
- Voice bots and conversational AI: Powering real-time transcription for automated agents that operate in regional languages.
This foundation makes speech-to-text APIs a critical building block for businesses looking to operationalise voice data rather than treat it as unstructured, unused input.
Also Read: What is Language Translation and How Does It Work
Why Speech-to-Text Is Harder for Indian Languages
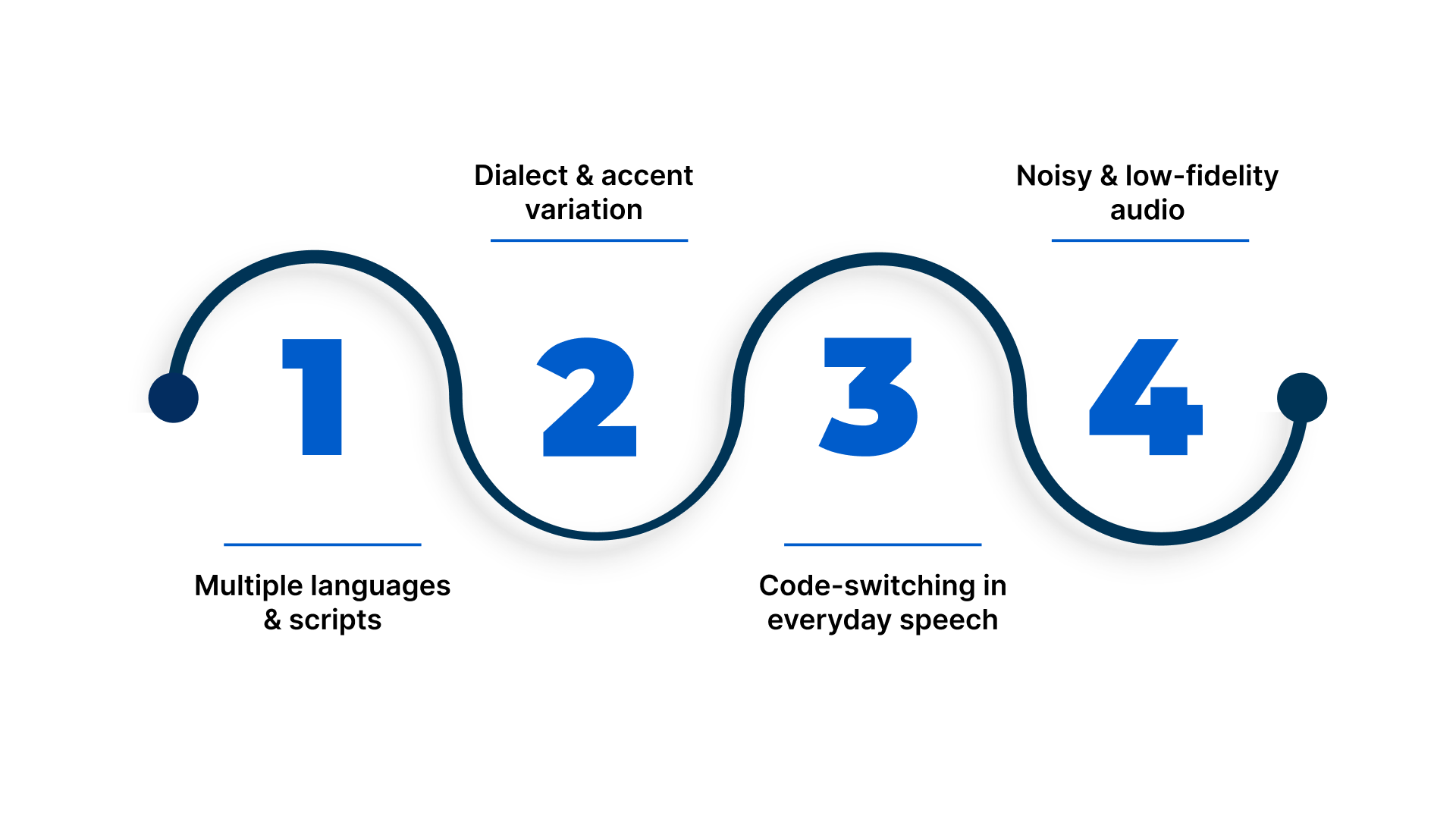
Speech-to-text systems perform best when they are trained on speech patterns that closely reflect real-world usage. In India, this is inherently more complex due to the country’s linguistic diversity, speaking styles, and audio conditions commonly found in enterprise environments.
Key challenges include:
- Multiple languages and scripts: India has many widely used languages, each with its own script, grammar, and phonetics. A speech-to-text system must correctly identify and process different languages without relying on a single linguistic structure.
- Dialect and accent variation: Pronunciation, intonation, and word usage vary significantly across regions. Even within the same language, regional accents can affect recognition accuracy if models are not trained on diverse speech samples.
- Code-switching in everyday speech: Indian speakers frequently mix languages within the same sentence, such as Hindi–English or Tamil–English, especially during customer calls or IVR interactions. Accurately handling this requires models that can switch languages seamlessly in real time.
- Noisy and low-fidelity audio: Many business conversations occur over telephony networks or IVR systems, where audio is compressed, noisy, or affected by background sounds and overlapping speech.
These conditions significantly degrade performance for speech-to-text systems that are tuned primarily for clean, high-quality audio.
Also Read: 8 Benefits of a Multi-Language Website
Why Generic STT APIs Often Fall Short in India
Many generic speech-to-text APIs are built using English-first training data and later extended to support additional languages. While this approach works in controlled environments, it often breaks down in real Indian use cases.
Common limitations include:
- Limited support for mixed-language speech, leading to incorrect word recognition when languages are combined in a single utterance.
- Higher error rates on telephony-grade audio, which is common in call centers, IVR systems, and customer support workflows.
- Inconsistent accuracy across regions and accents, making it difficult to deploy the same solution reliably across the country.
These constraints make it challenging to use generic STT APIs for production workloads in India.
For businesses operating at scale, an Indian-language-first speech-to-text approach like that of Reverie’s Speech-to-Text API, trained on regional speech, dialects, and real call environments, is essential to achieve reliable and consistent transcription outcomes.
Through Qwik Start via Reverie’s RevUp platform, teams can rapidly test Indian-language transcription on real audio, validating accuracy, mixed-language handling, and telephony-grade performance before moving to full-scale production.
Speech‑to‑Text API: Qwik Start Guide
Reverie’s Speech‑to‑Text API enables businesses to convert spoken language into written text across 11+ Indian languages with high accuracy, making voice data usable for search, analytics, automation, and customer workflows.
With support for real‑time streaming and file‑based transcription, broad language coverage, and developer‑friendly onboarding via the RevUp platform, teams can evaluate and begin using speech‑to‑text in minutes rather than weeks.
The self‑serve RevUp portal provides free credits, API keys, and an interactive playground, all designed to help you rapidly prototype, validate, and integrate automatic speech recognition into enterprise systems without upfront integration overhead.
Here’s a step-by-step guide you can follow:
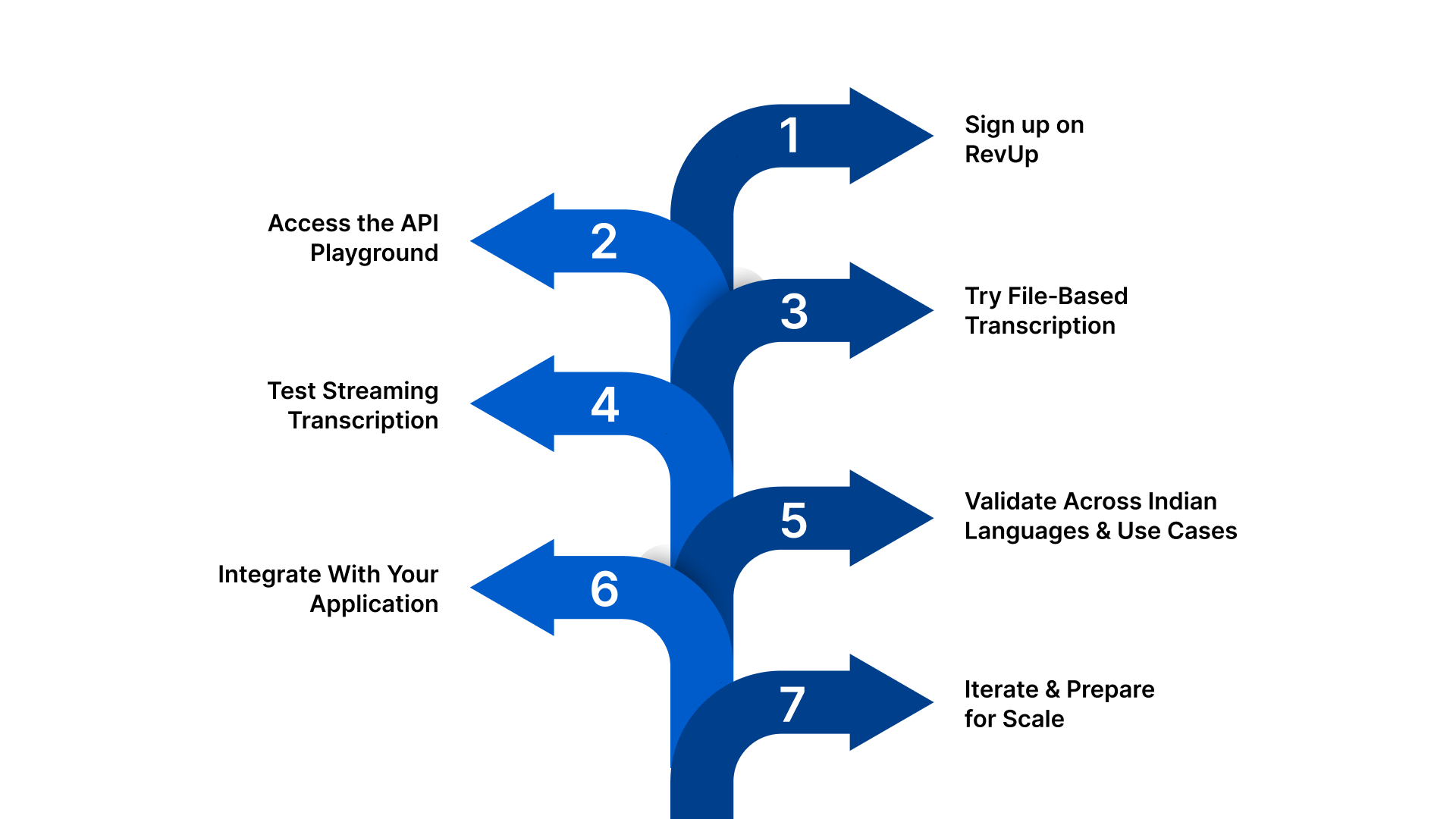
Step 1: Sign up on RevUp
Quick setup: Create a RevUp account, access your dashboard, and get credentials.
- Register on the RevUp developer portal, which offers free API credits to evaluate speech‑to‑text and other language APIs immediately.
- Your API credentials (REV‑API‑KEY and REV‑APP‑ID) are generated instantly and required for all API calls.
This step ensures you are ready to interact with the API and test real audio without waiting for manual provisioning or sales engagement.
Step 2: Access the API Playground
Interactive testing: Try STT features live with minimal setup, right in your browser.
- The API Playground in RevUp lets you upload audio or run tests without writing code, perfect for early evaluation.
- You can experiment with different languages, file types, and real‑time scenarios to gauge baseline performance before deeper integration.
This interactive space helps teams quickly compare outcomes across use cases without setting up SDKs or environments.
Step 3: Try File‑Based Transcription
Asynchronous testing: Upload recorded audio to see how accurately the API converts speech to text.
- Upload a file and specify language codes like hi for Hindi or bn for Bengali to see transcription results.
- The API returns structured text along with confidence scores, helping you assess output quality and formatting needs.
This step lets you evaluate how the system handles noise, telephony‑grade audio, and mixed dialect inputs before integrating it into your production pipeline.
Step 4: Test Streaming (Real‑Time) Transcription
Live audio workflows: Validate live speech conversion for voice UIs and interactive systems.
- Streaming APIs let you send audio in real time and receive partial and final transcripts as the audio flows in.
- Real‑time testing is essential for use cases like IVR, live meeting captioning, or voice interfaces embedded in products.
This gives a clear sense of how the API performs under latency‑sensitive and continuous speech scenarios.
Step 5: Validate Across Indian Languages & Use Cases
Qualitative checks: Compare transcription quality across languages and conditions relevant to your business.
- Test Indian languages like Hindi, Tamil, Kannada, Malayalam, and others supported by the API.
- Evaluate mixed‑language speech and code‑switching patterns (e.g., Hindi‑English) to confirm robustness.
This helps you assess linguistic coverage, noise resilience, and real‑world applicability early in the evaluation cycle.
Step 6: Integrate With Your Application
Engineering integration: Move from evaluation to embedding speech‑to‑text capabilities.
- Use documented SDKs or REST calls to call the Speech‑to‑Text API from your codebase.
- Integrate audio capture from your systems (e.g., apps, call logs, voice interfaces) and handle responses for downstream use (search, analytics, automation).
This step positions your solution toward production readiness while preserving flexibility.
Step 7: Iterate & Prepare for Scale
Enterprise readiness: Plan for performance, custom vocabularies, and deployment constraints.
- Expand testing across diverse audio sources and languages to refine model fit.
- Consider domain customisation for specialised terminology if needed.
- Plan your deployment strategy (cloud or on‑premise) according to compliance and operational needs.
This final phase ensures you’re ready to move beyond prototypes to large‑scale usage.
By following this Qwik Start guide, teams can go from initial sign‑up to actionable transcription results in a short time, enabling evaluation of Indian‑language performance, real‑time and batch workflows, and integration prototypes that inform production‑ready decisions.
Also Read: Medical Transcription: Revolutionising Healthcare Through Precision, Technology, and Efficiency
When to Use Speech‑to‑Text API Qwik Start
The Qwik Start approach is ideal when teams need a fast, low‑friction path to evaluating speech‑to‑text capabilities and building confidence before deeper integration or production rollout.
Here are the key scenarios where it makes sense to use this quick‑start approach:
- Building a quick proof of concept: When you want to validate a voice‑enabled idea, such as transcribing customer calls, enabling voice search, or automating meeting notes, the Qwik Start approach helps you verify feasibility with minimal setup. You can use free speech‑to‑text credits and the API Playground to test real audio samples before writing any production code.
- Testing Indian language accuracy: If your use case involves transcribing speech in Hindi, Bengali, Tamil, Kannada, or other major Indian languages, the Qwik Start approach gives you immediate access to Reverie’s multilingual ASR models. This enables you to assess how well the system handles regional speech, code‑switched input (e.g., Hinglish), and diverse accents in real conditions.
- Evaluating real‑time vs batch transcription needs: Different products require different transcription modes. Real‑time streaming for live voice interfaces, IVR systems, or voice bots. Batch/file‑based transcription for archived call recordings or meeting content. The Qwik Start approach lets you test both workflows quickly using the API Playground or sample API calls, so you can decide which mode fits your architecture.
Before committing to a vendor, you can use the Qwik Start approach to benchmark relative performance, including accuracy, noise resilience, multilingual handling, timestamps, and formatting across multiple APIs. This early evaluation reduces risk and speeds up decision making.
Real‑World Indian Use Cases You Can Validate in Minutes
Reverie’s Speech‑to‑Text APIs support 11–12 Indian languages, code‑switching patterns (like Hinglish), and both batch and real‑time scenarios, making them suitable for a variety of voice‑centric workflows across sectors.
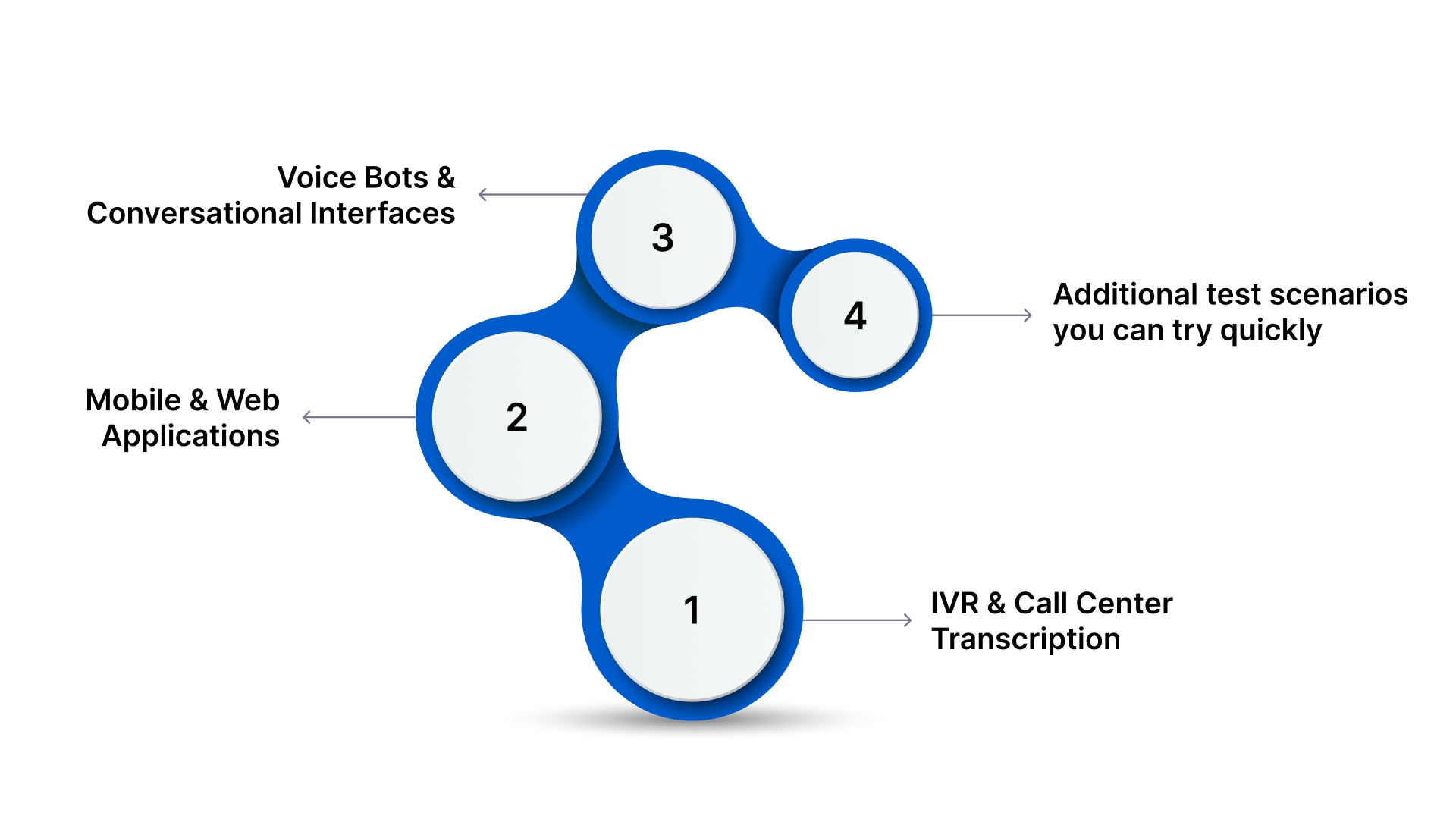
1. IVR and Call Center Transcription
Transcribe multilingual, telephony audio into text for analysis and automation.
- Convert inbound regional language calls into searchable text for quality and compliance workflows.
- Handle mixed Hindi‑English conversations commonly seen in Indian support calls.
- Process telephony‑grade audio (compressed, noisy call recordings) to extract insights without manual review.
This is especially useful in customer support and contact centers where understanding caller intent, sentiment, and issues fast can improve resolution times and customer satisfaction.
2. Mobile and Web Applications
Enable voice‑first interactions that enhance engagement and accessibility.
- Add voice search to your app or site, letting users speak queries in their preferred Indian language instead of typing.
- Improve regional accessibility by letting users interact with content through speech, helping bridge literacy or input‑barrier gaps.
Whether you’re building e‑commerce voice discovery, search bars, or form inputs, speech‑to‑text can reduce friction and boost engagement.
3. Voice Bots and Conversational Interfaces
Power voice‑driven user interactions with real‑time transcription and action triggers.
- Enable real‑time streaming of spoken input to text for voice assistants, chatbots, or virtual agents that respond immediately.
- Use transcription to fuel keyword detection and automated triggers, for example, identifying “refund” or “urgent” during a support call and routing appropriately.
This use case is ideal for multilingual voice bots that need to understand and act on speech in Indian languages, for customer service, lead capture, or interactive support.
4. Additional Example Scenarios You Can Test Quickly
While the above are core use cases, Reverie’s speech‑to‑text capabilities can also be validated in workflows such as:
- Voice‑enabled search in OTT or media apps, where spoken queries help users find content faster.
- Automated transcription for video content, aiding indexing and subtitles generation for regional audiences.
- Front‑line enterprise tools (e.g., sales calls, on‑field data capture) where spoken notes become searchable documentation.
By testing any of these scenarios with real audio in the RevUp API playground or via quick API calls, you can validate how well Reverie’s Speech‑to‑Text models handle Indian language nuances and production‑like conditions early in your evaluation.
From Qwik Start to Production‑Scale STT
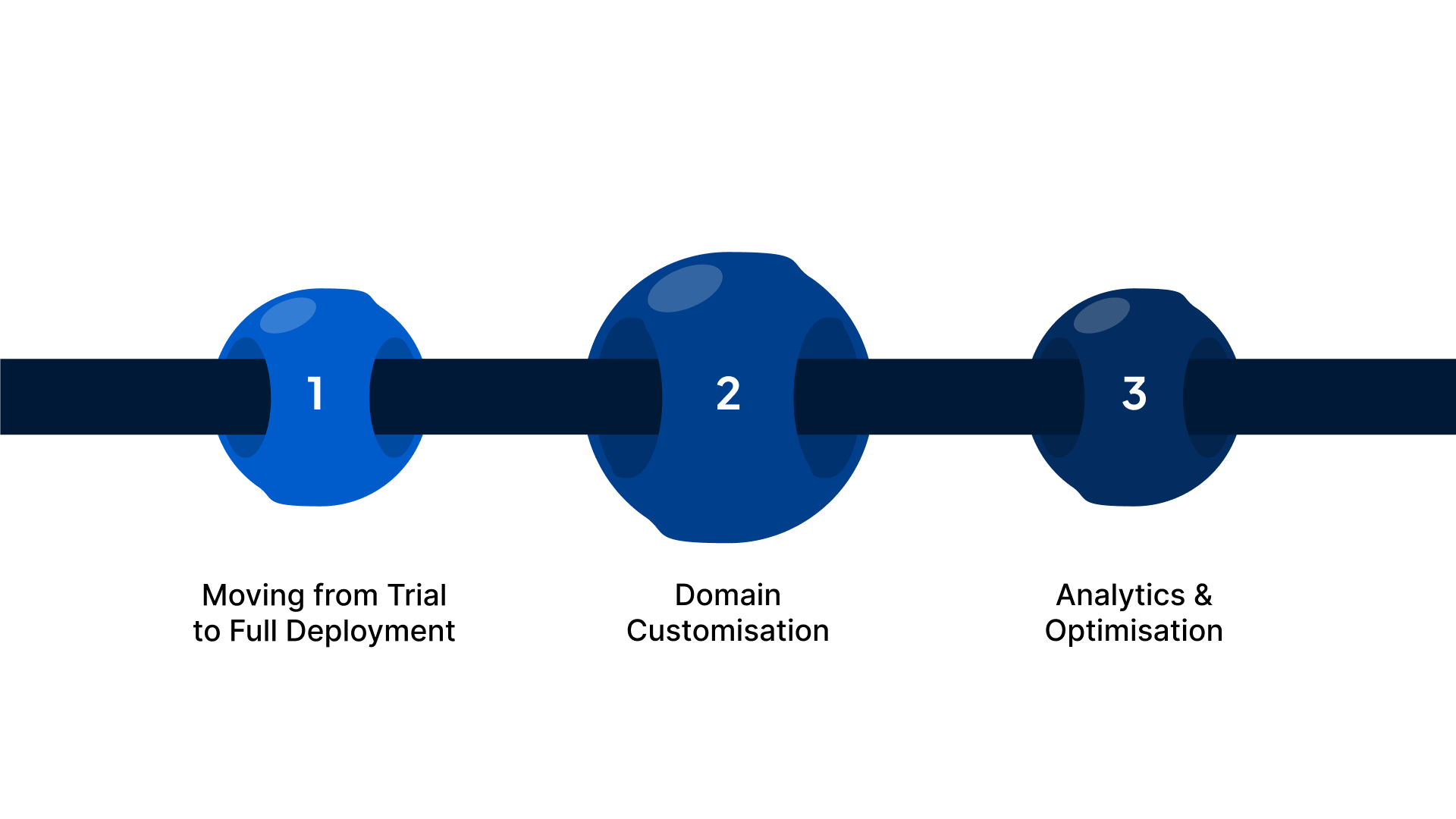
After validating basic capabilities with the Qwik Start approach, teams often need to transition toward production‑grade use of Reverie’s Speech‑to‑Text API.
The path from initial evaluation to scalable implementation typically involves the following phases:
- Moving from Trial to Full Deployment: Once your early tests confirm that Reverie’s STT meets your requirements, you can upgrade from the free RevUp trial credits to a paid usage tier that suits your expected volume. The documentation offers clear guidance on authenticated API integration for both streaming and file‑based use cases.
- Domain Customisation: Reverie supports customisable language models and domain vocabulary, which helps improve transcription accuracy for specialised contexts like legal terms, healthcare jargon, or financial expressions. Tailoring models to domain‑specific language increases relevance and precision for business workflows.
- Analytics and Optimisation: The RevUp dashboard provides usage analytics, real‑time API consumption insights, and logs that help engineering teams monitor performance and optimise usage patterns. These analytics tools are valuable as teams scale from prototype to production.
Reverie’s STT API supports both cloud‑based and on‑premise deployment options, giving enterprises flexibility to meet compliance, security, or data‑residency requirements. This flexibility ensures that high‑volume production workloads can be run where they make the most sense for your organisation.
Also Read: Voice AI in Consumer Electronics: Redefining Customer Experience
Why is Reverie Speech-to-Text API Best Suited for Indian Businesses
Reverie offers a unified voice API platform tailored for India’s multilingual and mixed-language environment. Its Speech-to-Text API accurately converts spoken audio into text across 11+ Indian languages, while the Text-to-Speech API generates natural-sounding voices from written content.
Designed specifically for Indian enterprises, startups, and public-sector organisations, Reverie enables businesses to unlock voice data for analytics, customer support, and digital engagement.
Key Reasons Indian Businesses Choose Reverie:
- Comprehensive Indian language support: Covers major languages including Hindi, Tamil, Telugu, Kannada, Bengali, Marathi and more, ensuring regional coverage for voice applications and customer interactions.
- Real-time and batch transcription: Processes live calls, IVR audio, meetings, and prerecorded files, helping businesses handle day-to-day operations efficiently.
- Flexible deployment options: Cloud or on-premise setups meet India’s regulatory, compliance, and data-residency requirements, critical for BFSI, government, and large enterprises.
- Custom vocabulary and formatting: Recognises domain-specific terminology and adds punctuation automatically, producing clean, actionable transcripts for workflows like customer support, compliance, or legal documentation.
- Integrated text-to-speech engine: Converts text into natural-sounding voices for IVR, voice assistants, accessibility solutions, and audio content creation, all optimised for Indian accents and regional pronunciation.
Reverie is ideal for Indian enterprises, startups, and public-sector organisations seeking reliable multilingual STT and TTS capabilities. Typical use cases include:
- Customer support & call centers: Regional language support and automated transcription for IVR and agent conversations.
- BFSI & government: Accurate transcription and TTS for multilingual documentation, citizen engagement, and regulatory compliance.
- E-commerce & apps: Voice search, voice commands, and interactive voice-first experiences for regional audiences.
- Education & healthcare: Transcribing lectures, patient consultations, or creating accessible content in multiple languages.
Reverie stands out for enabling Indian businesses to engage customers and internal teams in their preferred languages, turning speech into actionable insights while supporting scalable, enterprise-grade deployments.
Conclusion
Choosing the right Speech-to-Text API isn’t about picking the most popular platform, it’s about selecting one that aligns with your market, audio conditions, and enterprise workflows.
For businesses operating in India’s multilingual and high-volume environments, Reverie’s Speech-to-Text API delivers:
- Accurate transcription across Indian languages and mixed-language speech, including diverse accents and dialects
- Real-time streaming and batch processing for both live and recorded audio
- Custom vocabulary adaptation for industry-specific terms
- Flexible cloud or on-premise deployment to meet compliance and security requirements
With Reverie, teams can convert speech into actionable text at scale, enabling faster insights, better customer engagement, and seamless integration into existing workflows.
Get started today with RevUp and test it in minutes. Sign up today!
FAQs
1. Can Reverie’s Speech-to-Text API handle regional dialects within a language?
Yes. Beyond standard Indian languages, the API is trained to recognise common regional variations and accents, ensuring accurate transcription even when users speak in local dialects or mixed-language patterns.
2. How quickly can a business start testing the API in real-world scenarios?
Using the RevUp platform, teams can obtain API credentials, free credits, and access the interactive playground within minutes, making it possible to validate transcription accuracy and workflows immediately.
3. Does Reverie provide analytics for transcription performance?
Yes. The platform offers dashboards that track usage, transcription quality, and error patterns, helping teams monitor performance, optimise workflows, and make informed deployment decisions.
4. Can I integrate Reverie’s API with existing voice applications like IVR or call-recording systems?
Absolutely. The API supports both real-time streaming and batch file processing, making it compatible with IVR systems, voice bots, call recordings, and mobile/web apps without major code changes.
5. Is Reverie’s Speech-to-Text suitable for regulated industries like BFSI or healthcare?
Yes. With secure, enterprise-grade architecture and flexible deployment options (cloud or on-premise), Reverie meets data-residency, compliance, and privacy requirements necessary for BFSI, healthcare, and government use cases.


