Voice data across Indian enterprises is growing fast. However, much of it remains unusable, locked away in calls, IVR systems, bots, and voice apps, without structured text for analysis or automation. This challenge becomes harder in India, where multilingual inputs, dialects, and Hindi‑English code‑switching reduce transcription accuracy.
In fact, evaluations of Hinglish code‑switched speech show that ASR systems can experience a 30–50% higher word error rate than in monolingual speech. This highlights the difficulty of extracting useful text from mixed‑language audio.
In this blog, you’ll explore how Deepgram and Google Speech to Text compare on multilingual accuracy, enterprise reliability, integration readiness, and real-world deployment for Indian business platforms.
At a Glance
- Deepgram is optimised for India’s multilingual, code-switched speech, including Hinglish and regional dialects.
- Google Speech-to-Text excels in broad global coverage with 125+ languages, but is English-centric.
- Deepgram handles noisy, telephony-grade audio better for BFSI, education, and e-commerce workflows.
- Google provides reliable cloud-based APIs and extensive documentation, but is less focused on Indian mixed-language environments.
- Deepgram offers flexible integration with analytics dashboards, keyword spotting, profanity filtering, and interactive API playgrounds.
Deepgram STT in 2026: Platform Overview and Core Features
Deepgram’s speech-to-text platform is built for both real-time streaming and batch transcription workflows, supporting enterprise deployments across call centres, voice applications, and conversational AI systems in India. Its models are optimised for diverse accents, code-switched speech, noisy environments, and number-heavy conversations, making them suitable for BFSI, e-commerce, healthcare, and education use cases.
Key Deepgram capabilities include:
- Nova models: High-performance ASR for production transcription, robust in noisy conditions, with global and Indian language support.
- Low-latency conversational models: Optimised for live voice agents and real-time dialogue handling.
- Industry-tuned configurations: Domain adaptation and custom vocabularies for BFSI, healthcare, and legal workloads.
Increase CSAT and Reduce Costs with Reverie Speech-to-Text
Achieve up to 52% higher CSAT and cut operational costs by up to 62%.
Deepgram supports 36+ languages worldwide, with features such as smart formatting, speaker diarisation, keyword prompting, numeral handling, and redaction for sensitive content. Its streaming API enables low-latency transcription, while batch transcription supports high-volume audio processing.
Google STT in 2026: Platform Overview and Core Features
Google Speech-to-Text is a cloud-based automatic speech recognition API supporting over 125 languages and variants. It provides strong global language coverage, high-quality English transcription, and deep integration with Google Cloud services, enabling developers to embed speech recognition into applications, bots, and analytics pipelines.
Core Google capabilities include:
- Enhanced and domain-tuned models: Default, Video, Command-and-Search, and telephony models designed for different accuracy and latency requirements.
- Streaming and batch transcription: Real-time and offline processing with punctuation and formatting.
- Speaker diarisation and word-level timestamps: Speaker identification and precise word timing for recorded audio.
- Automatic language detection: Multi-language handling, though code-switched Indian speech may require manual model selection.
While Google Speech-to-Text performs well for clear English and major global languages, it is less consistent for Indian telephony audio, regional dialects, and Hinglish speech patterns, which can impact accuracy in call centre and conversational AI workloads.
While we have understood the core capabilities of each platform, let’s explore its key differences and strategic focus for enterprise deployments.
Deepgram vs Google: Key Differences in 2026
Deepgram and Google Speech-to-Text both convert speech into structured text, but they are built with different architectural priorities and enterprise objectives.
Deepgram focuses on high-accuracy transcription for real-world enterprise audio, including noisy call-centre environments, accented speech, and mixed-language conversations commonly found in Indian business workflows.
Google Speech-to-Text is designed for global-scale cloud applications, offering broad language coverage, strong English transcription, and deep integration with Google Cloud services. Its optimisation prioritises global consistency and cloud-native deployment rather than India-specific linguistic patterns.
Below is a practical comparison of their capabilities:
| Feature / Capability | Deepgram | Google Speech-to-Text |
| Primary focus | Enterprise ASR for real-world audio and conversational AI | Global cloud transcription and voice AI |
| Languages supported | 36+ global languages | 125+ global languages |
| Indian code-switching | Strong performance on accented and mixed speech | Limited optimisation for Hinglish and regional mixing |
| Real-time streaming | Ultra-low latency with noise robustness | Strong for English and clean audio |
| Batch transcription | Yes, high-volume enterprise workloads | Yes, cloud-based batch processing |
| Model customisation | Domain vocabularies for BFSI, healthcare, and legal | Phrase hints and speech adaptation |
| Deployment | Cloud and private cloud (VPC) | Cloud only |
| Enterprise tooling | Analytics, API playground, keyword, and profanity filters | Timestamps, diarisation, Google Cloud integration |
| Typical use cases | Call centres, IVR, BFSI, e-commerce, voice agents | Global voice AI, media transcription, bots |
For businesses operating in India with multilingual, code-switched, and telephony-heavy audio, platforms like Reverie offer an India-first approach to real-time and batch transcription. Contact us now to test it in your workflows.
Also Read: 8 Best Speech-to-Text APIs in 2026: A Complete Comparison Guide
Now that we’ve outlined how Deepgram and Google differ, let’s examine which platform is the right fit for your business scenarios.
Choosing the Right Platform for Your Enterprise
Selecting a speech-to-text solution depends on your enterprise’s language requirements, audio quality, and deployment environment. While both Deepgram and Google Speech-to-Text deliver enterprise-grade transcription, each platform is optimised for different scenarios and operational priorities.
When Deepgram STT Excels
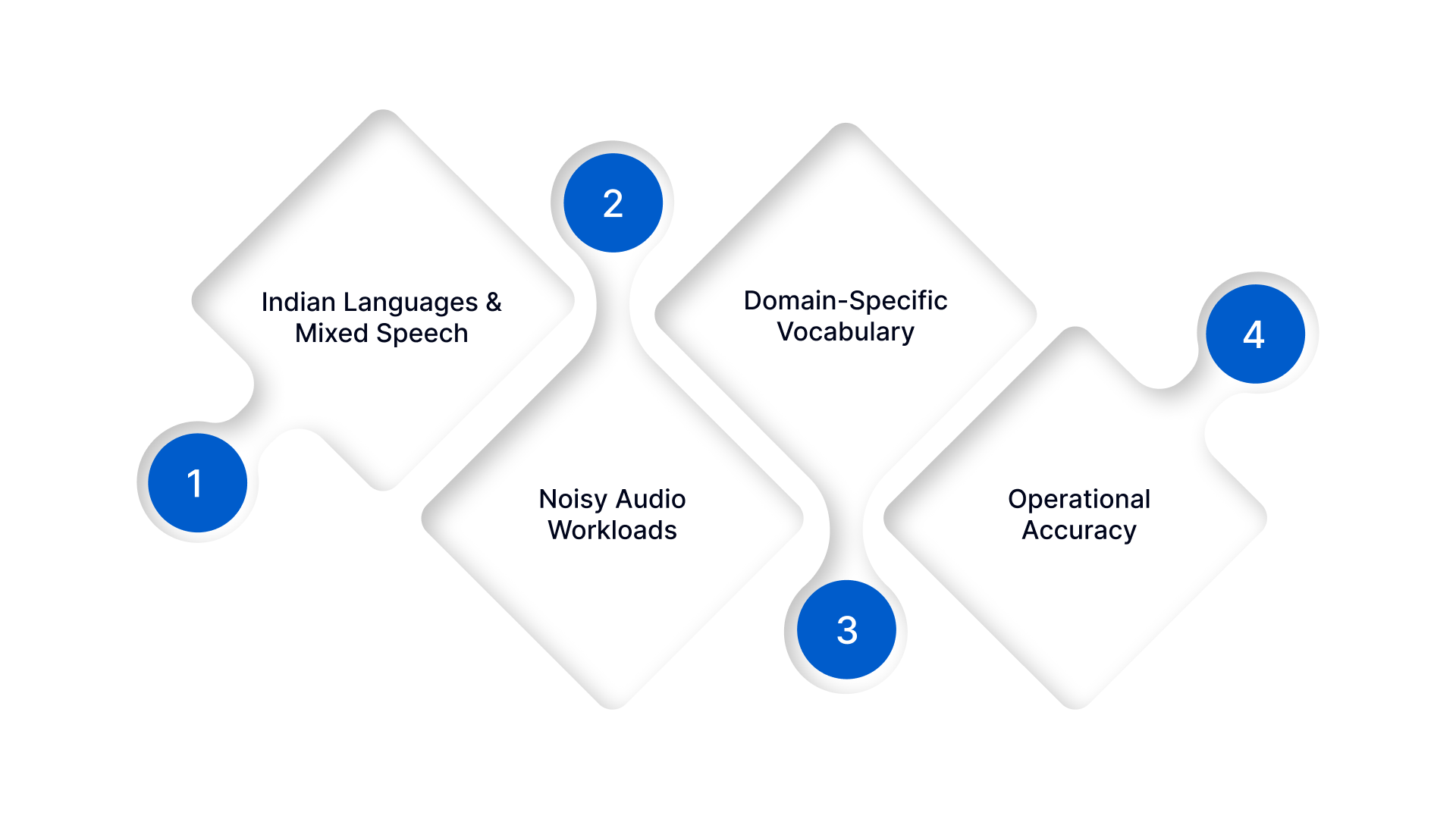
Optimised for Indian enterprises, Deepgram performs reliably on noisy, accented, and code-switched audio.
- Indian Languages & Mixed Speech: Your users speak Indian languages, Hinglish, or mixed-accent English.
- Noisy Audio Workloads: You process large volumes of call-centre or IVR audio with background noise.
- Domain-Specific Vocabulary: Critical for BFSI, healthcare, and government sectors.
- Operational Accuracy: Precision on numbers, names, and intent directly impacts business outcomes.
When Google STT Excels
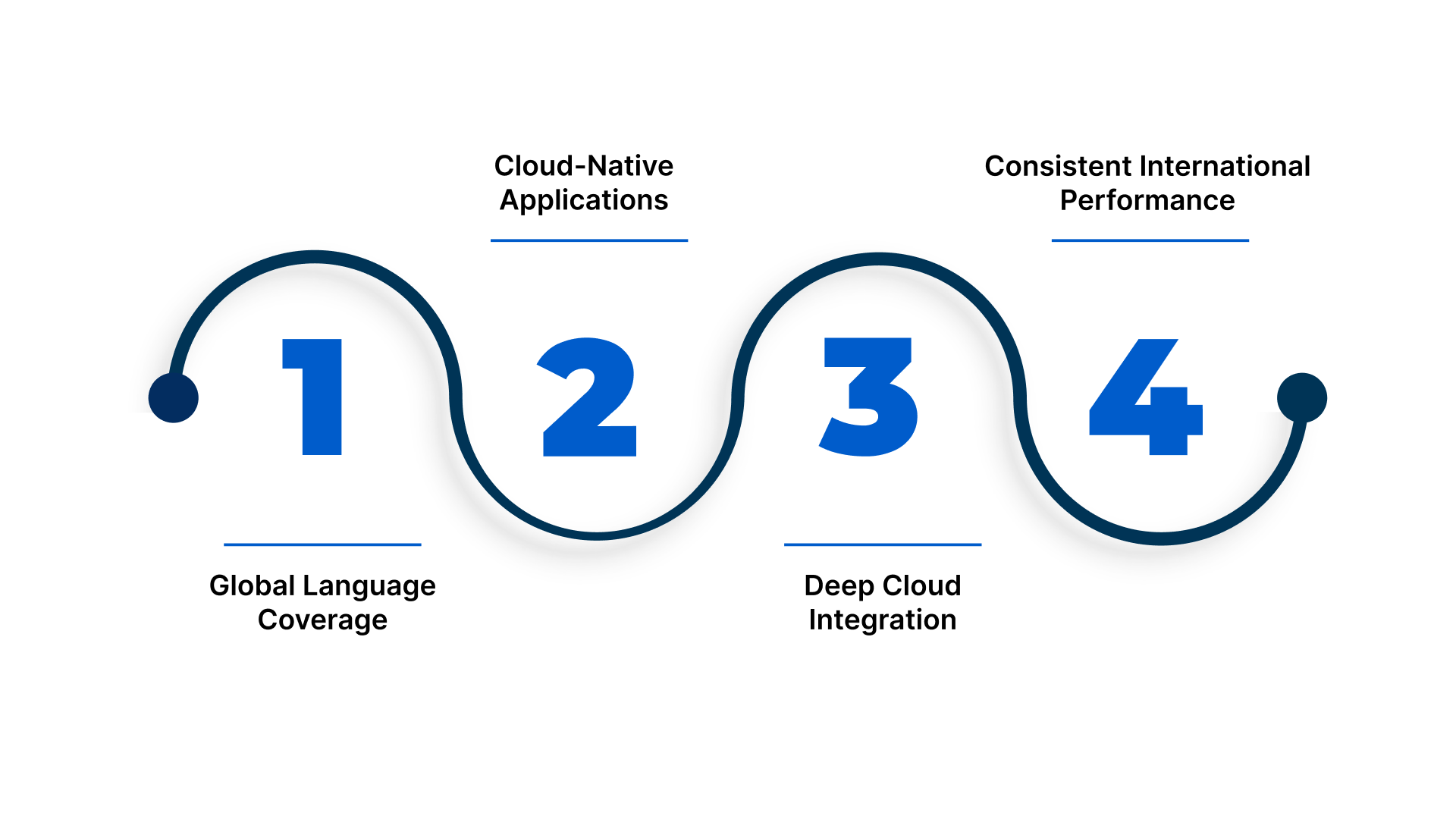
Designed for global applications, Google Speech-to-Text works best in clean audio and cloud-native workflows.
- Global Language Coverage: You require broad multilingual support for international markets.
- Cloud-Native Applications: You are building voice agents, bots, or media transcription pipelines.
- Deep Cloud Integration: Integration with Google Cloud services is a priority.
- Consistent International Performance: Ensures uniform results across regions.
Enterprises in India face unique challenges with multilingual, code-switched, and noisy audio. Understanding how each platform performs in these contexts can help identify solutions optimised for local workflows.
Cut Development Time with Reverie Speech-to-Text APIs
Reduce dev time by up to 97% and scale multilingual voice workflows across India.
Also Read: Speech-to-Text API Market Trends and Evolution
For enterprises seeking a solution optimised for India’s multilingual, code-switched, and noisy audio environments, Reverie provides an India-first platform that understands local language nuances. Let’s see how Reverie addresses these challenges.
Why Reverie is Better Suited for Indian Businesses
Reverie is designed specifically for India’s multilingual, mixed-language, and high-volume speech environments. Instead of adapting a global speech engine for Indian use cases, Reverie trains and optimises its Speech-to-Text model on how people in India actually speak across regions, accents, and real call conditions.
This India-first approach makes a measurable difference for enterprises working with customer conversations, IVR systems, and voice-led applications where accuracy on numbers, names, and code-switched speech directly impacts outcomes.
What gives Reverie a strong advantage in India:
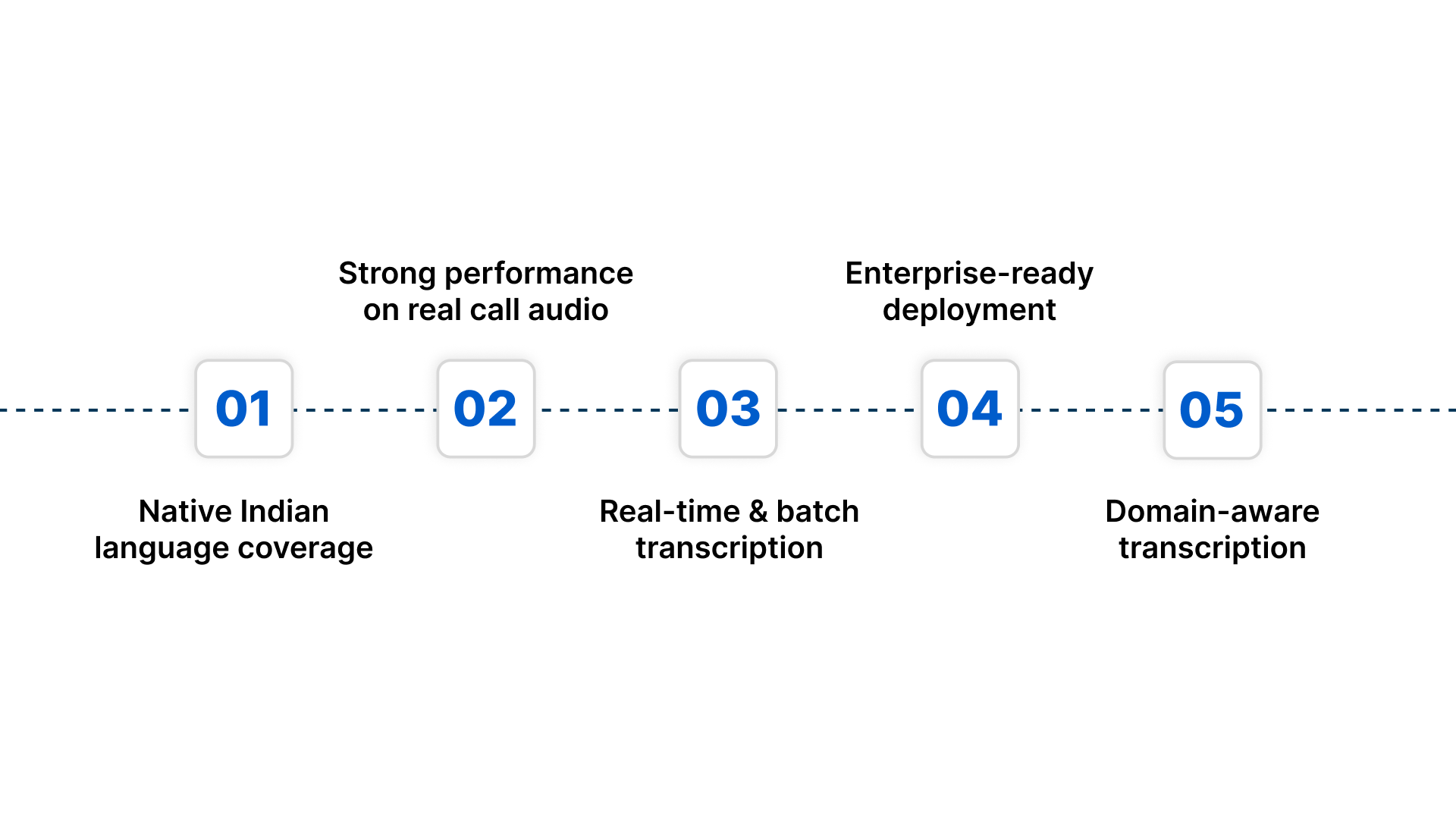
- Native Indian language coverage: Supports 11+ Indian languages with dedicated models, not generic multilingual layers.
- Strong performance on real call audio: Built to handle telephony-grade input, background noise, and mixed Hindi-English or regional speech.
- Real-time and batch transcription: Works equally well for live calls, voice bots, IVR flows, and large volumes of recorded audio.
- Enterprise-ready deployment: Available on cloud or on-premise to meet data residency, compliance, and security requirements common in BFSI.
- Domain-aware transcription: Adapts to industry-specific vocabulary and accurately recognises numbers and Indian names, reducing post-processing effort.
For Indian enterprises evaluating speech-to-text platforms, Reverie stands apart by delivering consistent accuracy across multilingual, code-switched, and telephony-heavy environments where global speech engines often struggle.
Conclusion
Selecting a Speech-to-Text API is ultimately a business decision. The right choice depends on how well the system handles your users’ languages, your audio conditions, and production-scale workflows.
For Indian enterprises, Reverie provides consistent transcription accuracy across multilingual, code-switched, and noisy audio, while supporting both real-time and high-volume batch workflows with enterprise-ready deployment options. Its design ensures numbers, names, and mixed-language speech are reliably captured for operational use.
If you are exploring speech-to-text solutions for India-focused applications, Reverie offers a practical, enterprise-ready platform. Sign up now to evaluate its capabilities through a trial or pilot deployment.
FAQs
1. Can Deepgram handle mixed-language Indian speech better than Google?
Yes. Deepgram’s India-optimised models are trained on Hinglish and regional dialects, enabling accurate recognition of code-switched sentences, numbers, and proper nouns, while Google may require manual model selection for mixed-language Indian audio.
2. How does telephony-grade audio affect Deepgram vs Google accuracy?
Deepgram is optimised for low-fidelity, noisy call-center audio common in Indian BFSI and e-commerce workflows. Google performs well on clean audio but may have reduced accuracy on compressed, multi-speaker telephony recordings.
3. Is model customisation possible for domain-specific vocabulary?
Deepgram allows tuning for BFSI, healthcare, and legal terms, improving recognition of industry-specific words and phrases. Google primarily relies on pre-trained general-purpose models, limiting fine-tuning for domain adaptation.
4. Which platform is faster for real-time enterprise workflows?
Deepgram’s streaming API offers ultra-low latency and robust noise handling, enabling faster transcription of live calls. Google provides reliable real-time streaming but is optimised more for global cloud workloads than regional telephony speed.
5. Can both platforms support high-volume batch transcription?
Yes. Deepgram handles large volumes with enterprise-grade batch processing suitable for call centres and e-commerce analytics. Google supports cloud-based batch transcription but may be less optimised for Indian multilingual or mixed-accent data.


