In India, voice is fast becoming the most natural way for people to interact with technology, especially when language barriers are at play. Voice search queries in the country are growing at a staggering rate of 270% per year, underlining how rapidly enterprises need to adapt.
Yet the multilingual complexity of India, with 24+ languages, hundreds of dialects, and widespread code-switching (think Hinglish), presents a tough challenge for businesses aiming to deliver ideal voice experiences. Without strong translation, voice-led systems in support, IVR, training or e-commerce risk alienating large segments of users.
That’s where speech-to-speech translation comes in: the ability to turn spoken words in one language into speech in another. In this blog, you’ll learn how modern enterprises can utilise this pipeline to build truly inclusive, multilingual voice interfaces tailored for India.
Key Takeaways:
- Speech-to-speech translation enables real-time conversion of spoken input into multiple Indian languages, enhancing communication across workflows.
- Solutions optimised for India handle 24+ languages, regional dialects, and code-switching like Hinglish for accurate interactions.
- Enterprises can use it for customer support, IVR, training, e-learning, automotive voice assistants, and voice bots.
- Choosing the right engine requires evaluating language coverage, domain-specific accuracy, latency, and deployment flexibility for compliance.
- Enterprise-grade systems like Reverie’s improve engagement, reduce operational costs, and scale multilingual voice experiences effectively.
What is Speech-to-Speech Translation in a Modern Enterprise Context?
Speech-to-speech translation is not just converting one language into another; it is a pipeline that transforms spoken words in your customer or employee interactions into accurate, contextual speech in another language. For you as a product leader, support head, or IVR architect, this means enabling real-time multilingual communication without slowing down workflows or frustrating users.
In India’s multilingual markets, this capability is essential for reaching Tier-2 and Tier-3 audiences who may prefer local languages or use mixed-language speech.
Here are key ways you can utilise it in your enterprise:
- Multilingual Customer Support: Deploy voice bots that understand Hindi, Tamil, or Bengali and respond in the customer’s preferred language, improving satisfaction and reducing call handling times.
- Workforce Training Across Languages: Train employees in their native tongue while delivering consistent enterprise messaging across locations.
- Automated Guidance for IVR or Voice Assistants: Guide users in local languages for banking, e-commerce, or government services without manual intervention.
- Voice-Enabled Product Interactions: Let users navigate apps, issue commands, or search for products in their spoken language, including Hinglish or regional code-switching.
To understand its impact, let’s first explore how speech-to-speech translation actually works in modern enterprise applications.
How Speech-to-Speech Translation Works?
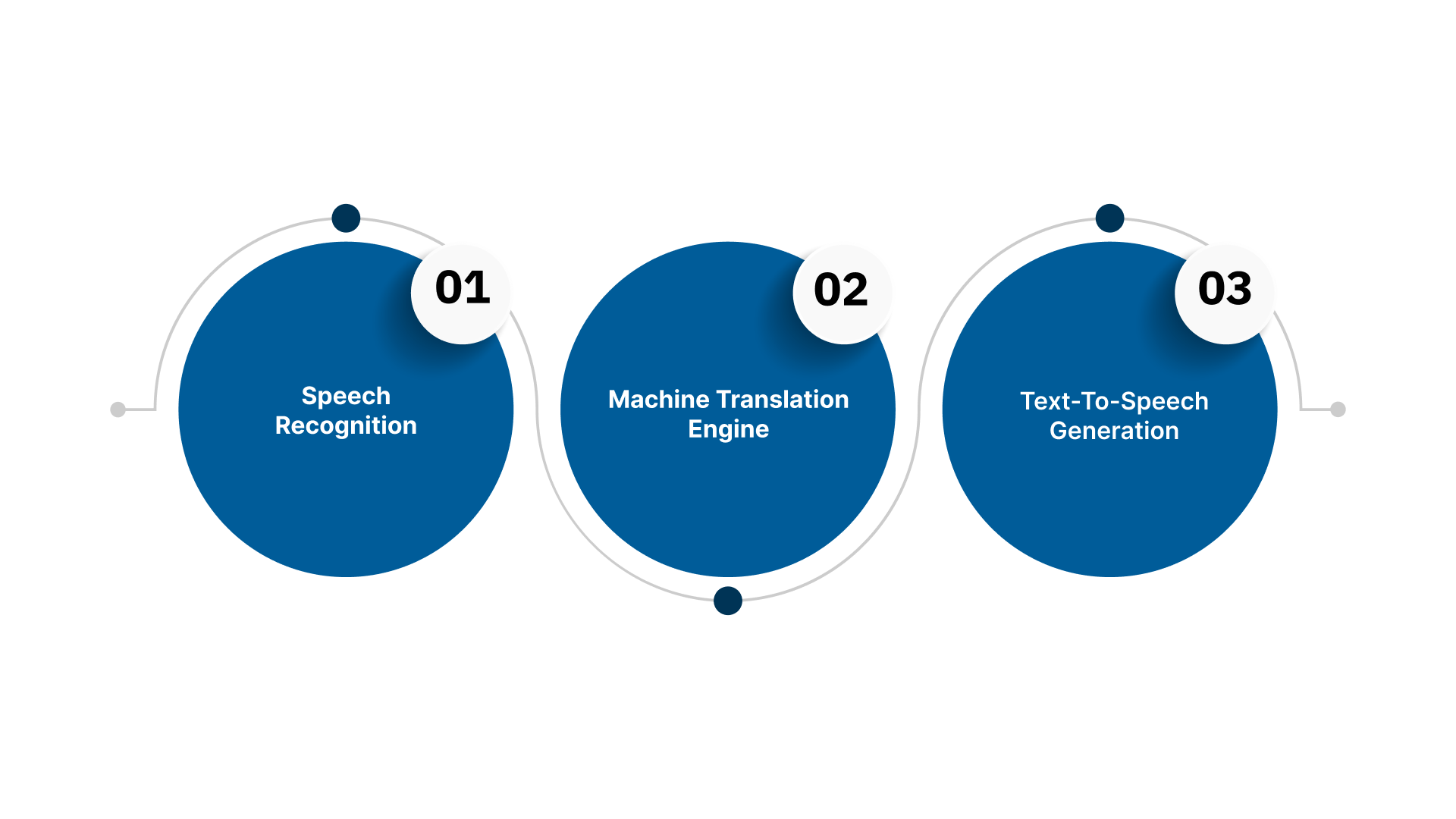
At its core, speech-to-speech translation is a three-step process that turns spoken words in one language into accurate, natural speech in another. First, it recognises what is being said, even in noisy or mixed-language environments. Next, it translates the text while preserving meaning, context, and domain-specific terminology.
Finally, it generates speech that sounds natural and expressive to the listener. For you, understanding this flow is key to choosing the right solution and integrating it into customer support, IVR, training, or automotive voice systems.
Below is a step-by-step breakdown of each stage so you can see exactly how it works.
Step 1: Speech Recognition (ASR)
The first step in speech-to-speech translation is recognising what is being said. You need a system that can accurately capture spoken words from your customers or employees, even when there’s background noise, mixed languages, or regional dialects. In India, this is especially challenging with code-switching like Hinglish or heavy regional accents.
For your business, getting this step right is critical; errors here ripple through translation and speech output, affecting IVR flows and training content. High accuracy ensures smooth workflows, reduces customer frustration, and supports multilingual engagement.
Below are the key aspects to focus on in speech recognition:
- Language Detection: Automatically identify which language or dialect the speaker is using for correct processing.
- Dialect and Accent Handling: Understand regional variations like Bengali vs. Bangla accents or Tamil vs. Chennai Tamil.
- Noise Robustness: Maintain accuracy even in call centres, vehicle cabins, or busy offices.
- Code-Switching Support: Accurately recognise mixed speech, such as Hindi-English sentences, without losing context.
- Flexible Audio Input: Accept live streaming, file uploads, and low-fidelity IVR channels for enterprise scenarios.
If accurate speech recognition is the core of your multilingual workflows, this is the perfect moment to experience it firsthand. See how enterprise-grade ASR handles Indian accents and real call-centre scenarios. Let your team feel the difference high-accuracy STT can make. Get started with the Speech-to-Text API.
Step 2: Machine Translation Engine
Once your system recognises the spoken words, the next step is translating them accurately into the target language. For your business, this means maintaining the meaning, context, and domain-specific terms without confusing your users. In India, where conversations often mix languages and dialects, a generic translation engine can easily misinterpret intent or technical vocabulary.
Below are the essential elements to focus on in the translation engine:
- Domain-Specific Tuning: Ensure translations correctly handle industry vocabulary like banking, healthcare, or legal terms.
- Indian-Language Mapping: Map source and target Indian languages accurately, e.g., Hindi to Tamil or Marathi to English.
- Context Preservation: Maintain the meaning of sentences, even with code-switched input like Hinglish.
- Scalable Processing: Handle multiple simultaneous translations in live environments like call centres.
- Error Handling and Corrections: Automatically detect uncertain translations and optimise them for enterprise workflows.
Step 3: Text-to-Speech Generation
After translating the text, the final step is converting it back into natural, expressive speech that your users can understand and engage with. For your business, this is where the experience becomes perfect, whether it is a voice bot answering customer queries, IVR prompts guiding callers, or training modules narrating content in local languages.
Below are the key elements to focus on in text-to-speech generation:
- Natural and Expressive Voices: Use voices that sound human and adapt to Indian tonal nuances.
- Language and Dialect Accuracy: Pronounce words correctly in regional languages like Marathi, Tamil, or Punjabi.
- Real-Time Generation: Deliver instant speech output for live customer support or IVR workflows.
- Domain-Aware Speech: Maintain correct pronunciation for industry-specific terms in banking, healthcare, or automotive.
- Flexible Deployment: Support both streaming and file-based audio output to match enterprise needs.
Example: Multilingual Customer Support in Banking
Imagine a customer in Chennai calls your bank’s IVR system and speaks in Tamil to check their account balance. Here’s how the speech-to-speech translation pipeline works for you:
- Speech Recognition (ASR): The system recognises the Tamil words, correctly handling regional pronunciation and any code-switched words like “balance check” in English.
- Machine Translation: The recognised Tamil text is translated into English for your support agent, or vice versa if the agent speaks another language. Domain-specific banking terms like “overdraft” or “NEFT” are preserved.
- Text-to-Speech Generation: The translated text is converted back into natural, expressive Tamil speech, which the customer hears instantly, making the interaction smooth and accurate.
Also Read: How AI Chatbot for Real Estate Can Transform Lead Generation
This ensures your customer gets real-time support in their preferred language, improves satisfaction, and reduces call-handling time. With the process explained, we can now look at the key business use cases of speech-to-speech translation in India.
Key Business Use Cases for Speech-to-Speech Translation in India
For your enterprise, speech-to-speech translation is more than a technology; it is a tool to expand reach, improve customer experiences, and streamline operations. In India’s multilingual scene, enabling real-time communication across languages can directly impact engagement, satisfaction, and productivity.
Whether you are running call centres, voice-led apps, in-vehicle assistants, or training programmes, having a reliable translation pipeline ensures your users or employees understand and interact without friction. By using this technology, you can reach regional audiences, reduce operational bottlenecks, and deliver consistent messaging across languages.
Below are some practical ways you can apply it in your business:
- Customer Support: Deploy multilingual voice bots that respond to queries in Hindi, Tamil, Bengali, or Hinglish, reducing wait times and increasing satisfaction.
- BFSI IVR Workflows: Convert calls in Hindi to English or Tamil in real-time, allowing smooth banking, insurance, or loan processes.
- Automotive Voice Guidance: Enable drivers to interact with in-car assistants in regional languages for navigation, infotainment, and safety prompts.
- E-Learning and Education: Localise lectures or training modules into multiple Indian languages, ensuring comprehension across your workforce or students.
- Healthcare Consultations: Transcribe and translate doctor-patient conversations in local languages, supporting multilingual medical documentation.
- Government or Public Services: Let citizens interact with IVR or voice portals in their preferred language, improving accessibility and service delivery.
After exploring the use cases, the next step is selecting the right speech-to-speech translation engine for Indian enterprises.
Choosing the Right Speech-to-Speech Translation Engine for Indian Enterprises
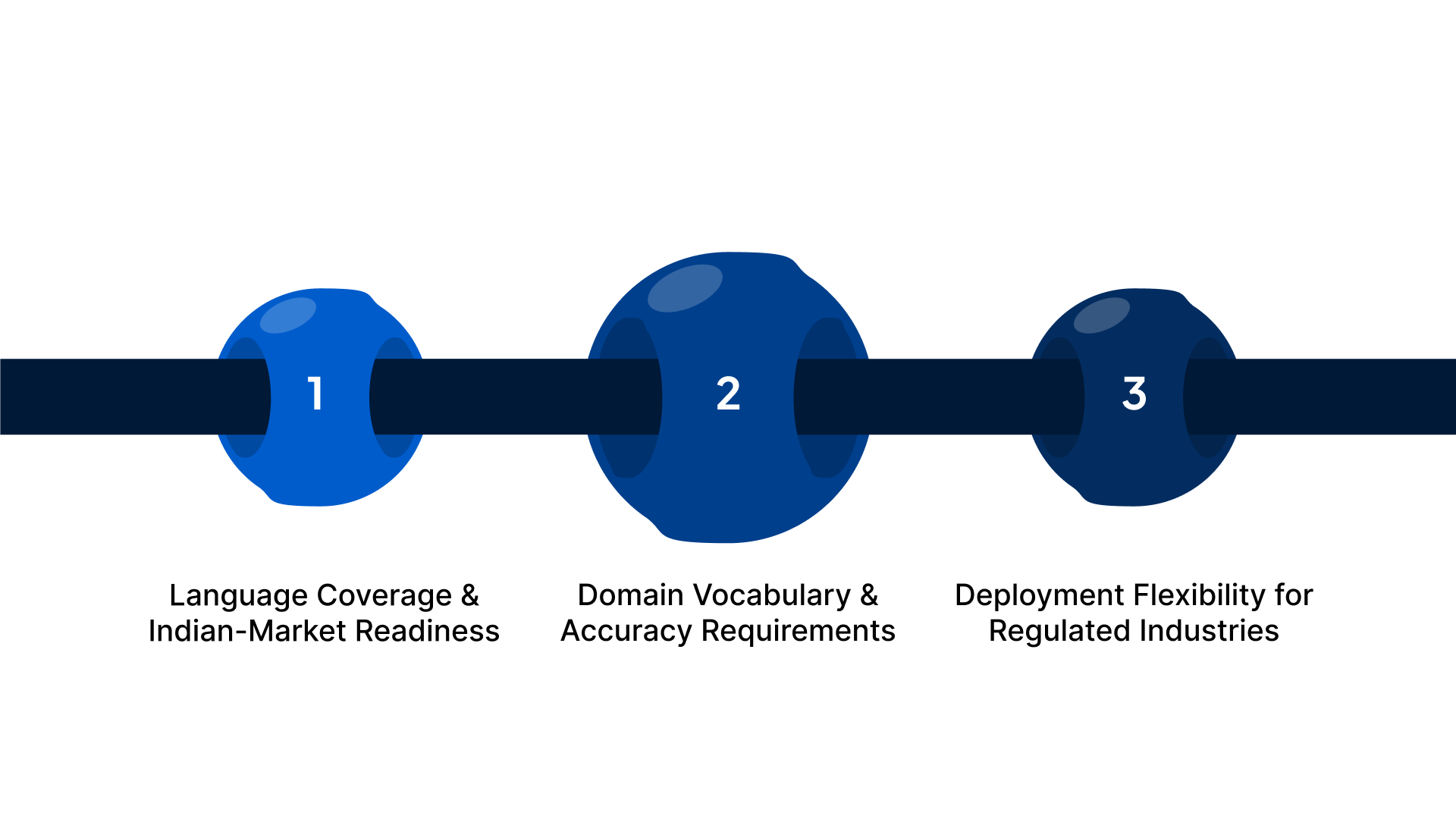
Selecting the right translation engine is critical for your enterprise to deliver consistent, high-quality multilingual voice experiences. You need a solution that not only supports the languages your users speak but also integrates with your existing systems, scales with demand, and meets compliance requirements.
For regulated industries like BFSI or healthcare, deployment flexibility and data privacy are non-negotiable. You also want an engine that can adapt to your domain vocabulary, handle practical audio variations, and maintain performance across live and batch workflows. Making the right choice today saves you time, costs, and user frustration tomorrow.
Below are the key factors to evaluate when choosing a solution for your business:
Language Coverage and Indian-Market Readiness
For your enterprise, it is not enough to support just the major languages. You need a translation engine that understands the diversity of India’s linguistic scene, including regional dialects, code-switching patterns, and pronunciation variations.
This ensures your users feel understood and reduces friction in voice-led interactions. A system optimised for India can handle Tier-2 and Tier-3 city accents, mixed-language phrases, and emerging vernacular trends.
Below are the aspects to prioritise when evaluating language readiness:
- Regional Dialect Support: Recognise variations within a language, like North vs. South Kannada or Mumbai vs. Pune Marathi.
- Code-Switching Capability: Handle common mixed-language speech patterns, such as Hinglish or Tamil-English phrases.
- Emerging Language Trends: Adapt to evolving local expressions, slang, or business-specific jargon.
- Coverage Beyond Major Cities: Ensure speech translation works well for Tier-2 and Tier-3 audiences.
- Cross-Language Consistency: Maintain meaning and tone across multiple Indian languages simultaneously.
Domain Vocabulary and Accuracy Requirements
For your business, the quality of translation is only as good as its understanding of your domain. Generic engines may misinterpret specialised terms, leading to miscommunication, errors, or frustrated users. You need a solution that can accurately recognise and translate industry-specific vocabulary, whether it is legal terminology, medical phrases, automotive commands, or banking instructions.
High accuracy ensures that your IVR prompts, voice bots, or training modules convey the correct meaning every time. Investing in domain-aware translation not only protects your brand but also improves operational efficiency and user trust.
Below are the key factors to ensure domain accuracy in your enterprise workflows:
- Industry-Specific Vocabulary: Include terms unique to your sector, like “NEFT” in banking or “HIPAA compliance” in healthcare.
- Customisable Glossaries: Update dictionaries to reflect your products, processes, or regional expressions.
- Error Detection and Correction: Flag and correct ambiguous translations automatically.
- Consistency Across Channels: Maintain uniform interpretation in IVR, voice bots, and training modules.
- High Precision in Mixed-Language Input: Correctly handle sentences that combine local language and English technical terms.
Deployment Flexibility for Regulated Industries
For your enterprise, especially in sectors like BFSI, healthcare, or government, how you deploy a speech-to-speech translation engine is as important as its capabilities. You need the freedom to choose between cloud and on-premise deployment depending on compliance requirements, data privacy, and infrastructure constraints.
Flexibility ensures you can scale without compromising sensitive information, integrate with existing systems, and maintain consistent performance across multiple locations.
Below are the key deployment considerations to keep in mind:
- Cloud Deployment: Quickly scale for live customer support, voice bots, or training without heavy infrastructure investment.
- On-Premise Deployment: Keep sensitive data in-house to meet compliance standards for regulated industries.
- Hybrid Models: Combine cloud speed with on-premise security where needed.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Ensure smooth connection with IVR, CRM, or in-vehicle systems.
- Optimised Performance Across Locations: Deliver consistent real-time translation in offices, call centres, or remote branches.
If you want to explore deployment options that balance security, accuracy, and scale, testing the platform hands-on is the best place to begin. Explore the Developer Suite today.
Once you choose the right translation engine, the next step is measuring accuracy and performance to ensure reliable speech-to-speech translation.
Measuring Accuracy and Performance in Speech-to-Speech Translation
For your enterprise, knowing how well your speech-to-speech translation engine performs is crucial. You need to measure not only the correctness of recognised and translated speech but also how efficiently it operates in live workflows. Tracking metrics helps you identify bottlenecks, optimise latency, and maintain high-quality user experiences across languages, regions, and devices.
Below are the key factors to focus on when measuring accuracy and performance:
- Word Error Rate (WER): Track the percentage of words misrecognised to gauge transcription quality.
- Translation Accuracy: Measure how faithfully the translated text reflects the original meaning and intent.
- Latency: Ensure speech-to-speech responses are delivered in real-time for live interactions.
- Speaker Diarisatoin: Verify the engine correctly identifies multiple speakers in a conversation.
- Domain Consistency: Check that industry-specific vocabulary is consistently translated across sessions.
Also Read: How AI Outbound Calling is Transforming Call Centres in 2025
Once accuracy and performance are measured, it’s important to understand the challenges in speech-to-speech translation and how enterprises can overcome them.
Challenges in Speech-to-Speech Translation and How Enterprises Can Overcome Them
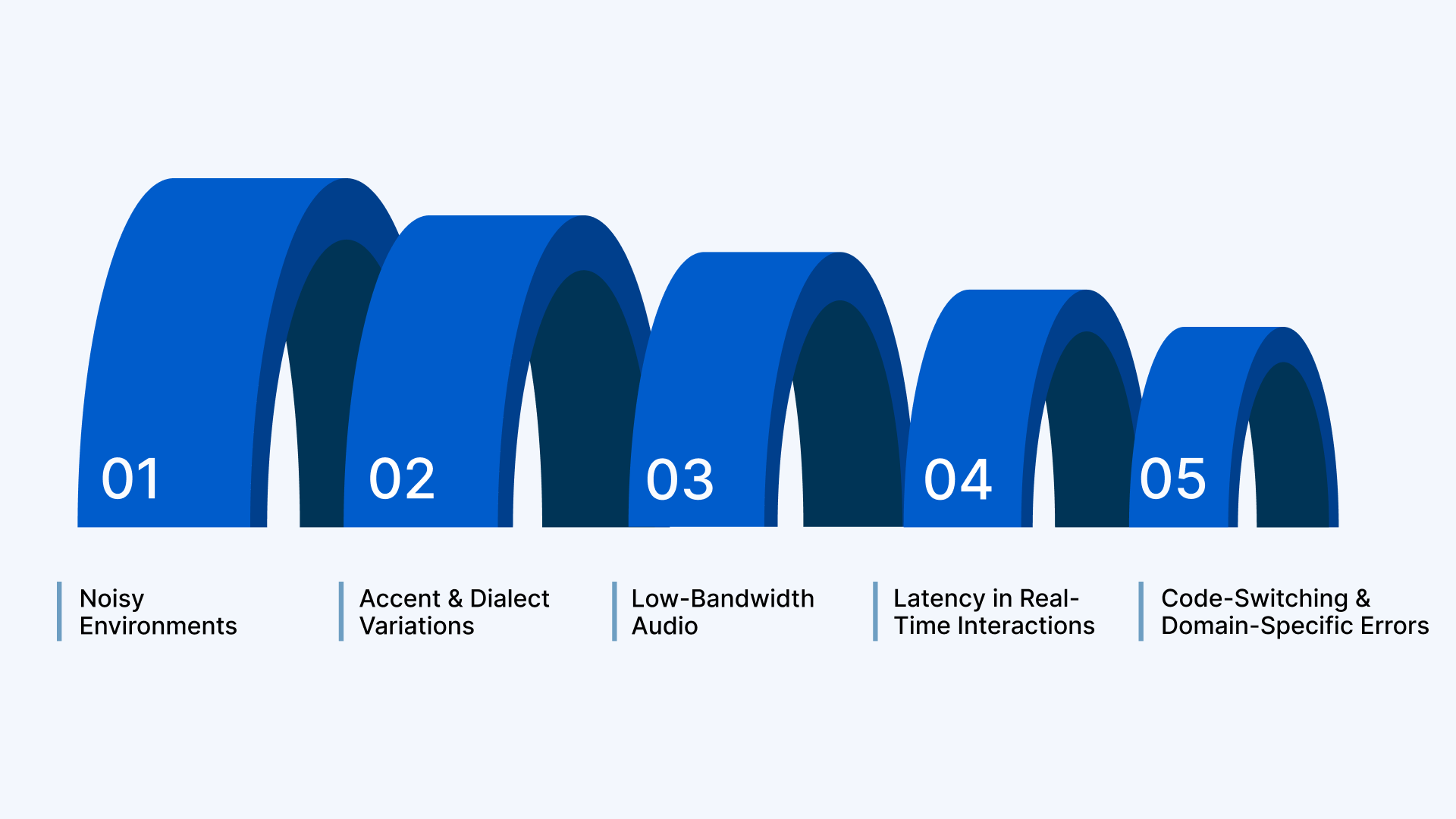
Implementing speech-to-speech translation in your enterprise comes with unique challenges that can impact user experience and operational efficiency. Issues like background noise, regional accents, low-quality audio channels, and latency can disrupt real-time communication. You may also face errors from code-switched speech or highly domain-specific terminology.
Addressing these challenges proactively ensures your IVR, voice bots, and training platforms deliver a reliable multilingual website.
Below are common challenges and ways to overcome them:
- Noisy Environments: Use noise-robust recognition models to handle call centres, vehicles, or crowded spaces.
- Accent and Dialect Variations: Employ Indian-context tuned engines to accurately interpret regional speech patterns.
- Low-Bandwidth Audio: Optimise for IVR and remote connections to maintain real-time performance.
- Latency in Real-Time Interactions: Choose engines with low-latency streaming for seamless conversational experiences.
- Code-Switching and Domain-Specific Errors: Implement domain-tuned translation and code-switch handling to maintain accuracy in mixed-language conversations.
Also Read: Contact Centre Quality Assurance: 10 Best Practices for 2025
After exploring the challenges, let’s see how Reverie’s speech and translation stack can support enterprises in addressing them effectively.
How Can Reverie’s Speech and Translation Stack Support Enterprises?
Reverie provides a comprehensive Speech-to-Text, Machine Translation, and Text-to-Speech solution built for Indian enterprises. You can convert spoken input into accurate text, translate it across multiple Indian languages, and generate natural, expressive speech for real-time or batch workflows.
This empowers your business to deliver ideal multilingual experiences across customer support, IVR, training, e-learning, and automotive applications.
Below are the ways Reverie helps your enterprise achieve results:
- Real-Time and File-Based Transcription: Capture speech instantly from live calls or uploaded recordings.
- Domain-Aware Translation: Maintain accuracy for BFSI, healthcare, legal, and automotive workflows.
- Expressive Indian Voices: Deliver natural speech output in Hindi, Tamil, Bengali, and more.
- Flexible Deployment Options: Cloud or on-premise models for compliance-heavy sectors.
- Developer-Ready APIs and SDKs: Easily integrate into Android, iOS, Web, and REST platforms.
- Analytics and Optimisation: Track usage, monitor performance, and continuously improve accuracy.
- Rapid Proofs-of-Concept: Free API credits (10 hours STT + 10,000 TTS characters) and a playground for testing.
With Reverie, you can expand multilingual reach, streamline operations, and deliver consistent voice experiences.
Conclusion
In India’s multilingual market, enabling speech-to-speech translation is key to driving engagement, reducing costs, and improving user satisfaction. Reverie equips you with enterprise-grade accuracy, domain-specific vocabulary, and Indian-language optimisation so that your IVR, voice bots, training, and in-app voice experiences perform flawlessly.
With real-time transcription, translation, and expressive speech generation, you can scale quickly and connect with users in their preferred language.
Take the next step today: start your multilingual journey with Speech-to-Text API for technical integration and enhance adoption by signing up with Reverie. With proven metrics like 37% higher sales and 62% lower operational costs, Reverie makes the business case clear and helps you deliver voice experiences that truly resonate with every Indian user.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between direct speech-to-speech translation and cascade (text‑based) translation?
Direct translation converts spoken input straight into speech in another language, skipping text. Cascade translation first transcribes speech into text, translates the text, and then generates speech. Direct reduces latency, while cascade allows easier editing, logging, and domain tuning.
2. Can speech-to-speech translation systems work for unwritten or oral-only languages?
Yes, but it’s challenging. Systems rely on audio patterns and phonemes instead of text corpora. With sufficient recorded speech data and language modelling, they can recognise, translate, and synthesise oral-only languages, enabling inclusion for communities without written scripts.
3. Is speech-to-speech translation possible without transcribing into text first?
Yes, end-to-end models can directly map input speech to output speech, skipping text. This reduces latency and preserves prosody but requires large amounts of parallel speech data for training. Accuracy improves with domain and language-specific tuning.
4. What are the privacy risks when using speech translation in sensitive domains like banking or healthcare?
Voice data can contain personal information. Risks include unauthorised access, data leaks, or improper storage. Enterprises must use encryption, secure storage, access controls, and compliance with local regulations to protect sensitive conversations in real-time and batch translation.
5. How much latency (delay) is introduced when translating speech in real time?
Latency varies by model, language complexity, and network. Real-time enterprise-grade systems typically aim for 300–800 milliseconds per segment, ensuring smooth conversation. Optimised streaming, edge processing, and low-bandwidth handling reduce delays for IVR, voice bots, and live support.


