Your website is your first handshake with customers. When it speaks their language, it instantly feels familiar. Translating your website helps you connect with people in the languages they trust most.
A well-planned translation process ensures your content remains accurate, consistent, and culturally appropriate, wherever your users come from. You move beyond simply converting text to creating an experience that feels personal and accessible.
In this guide, you’ll explore the complete website translation process, from planning to testing. You’ll also understand how modern translation methods and technologies can help you manage multilingual websites more efficiently while keeping quality intact.
Key Takeaways
- A structured workflow builds clarity. Translating your website strategically ensures consistency, quality, and cultural relevance across every language.
- The right method drives efficiency. Choose between human, machine, or hybrid translation to balance accuracy, speed, and cost effectively.
- Technology makes scaling simple. Tools like Anuvadak automate updates, manage glossaries, and streamline multilingual content management securely.
- Optimisation never stops. Post-launch testing, SEO tracking, and regular updates keep your multilingual website accurate and engaging over time.
What Is Website Translation? Definition and Scope
Website translation means adapting your site’s written and visual content so users in different regions can understand it clearly. Every part of your website, including menus, buttons, product information, and support content, needs to appear in the user’s preferred language.
This process improves accessibility and helps users feel included, no matter where they are. It also builds trust, which often translates into higher engagement and conversions.
Translation vs Localisation
These two terms often overlap, but they mean different things:
| Aspect | Translation | Localisation |
| Focus | Converts text from one language to another | Adapts the entire experience for cultural and regional fit |
| Scope | Language and words | Language, visuals, formats, design, and tone |
| Example | Translating a “Buy Now” button to Hindi | Adjusting visuals, date formats, and currencies for Indian users |
For example, if you’re translating an eCommerce site for Tamil-speaking audiences, localisation may also include showing prices in rupees and using imagery that resonates with South Indian culture.
Also Read: Guide to Improving the Quality of Translation for your Website
Why a Structured Website Translation Process Matters
Translating a website is not a one-time task. It is an organised sequence of steps that ensures every piece of content feels natural and accurate in each language. Without structure, translations often lose meaning, style, or brand tone.
A structured process helps you:
- Maintain accuracy and consistency across languages.
- Reduce manual effort through automation.
- Ensure quality control at every stage.
- Create a repeatable workflow for future updates.
How It Impacts Your Business
When you approach translation strategically, you create stronger connections with your audience. A well-translated website:
- Builds trust by communicating in the user’s native language.
- Improves engagement through relevant and localised messaging.
- Boosts conversions because visitors stay longer and interact more.
For example, a banking app translated into multiple Indian languages can reach millions of first-time digital users who may not be comfortable with English. This not only drives adoption but also strengthens brand credibility.
Enterprise Perspective
For larger organisations, structure brings scalability. When you have multiple websites, products, or departments, a centralised translation process avoids duplication and ensures uniform messaging.
Government platforms, educational portals, and large eCommerce brands benefit from using a consistent framework supported by technology such as Anuvadak, which automates workflows and maintains quality control.
Now that you know why process matters, let’s look at the practical steps that make it successful.
Also Read: The Concept of Translation in the Digital Age: Website Translation Impact
Step-by-Step Website Translation Workflow – Part 1: Planning and Analysis
A successful translation project follows a sequence of clear, repeatable steps. Planning and analysis form the foundation of this process. Without them, even the best translation tools cannot deliver quality or consistency.
This stage helps you identify what needs translation, define objectives, and prepare your resources before you begin.
When you start with a structured plan, your team avoids unnecessary rework and ensures the entire project moves smoothly. Let’s explore the key steps that make up this first phase.
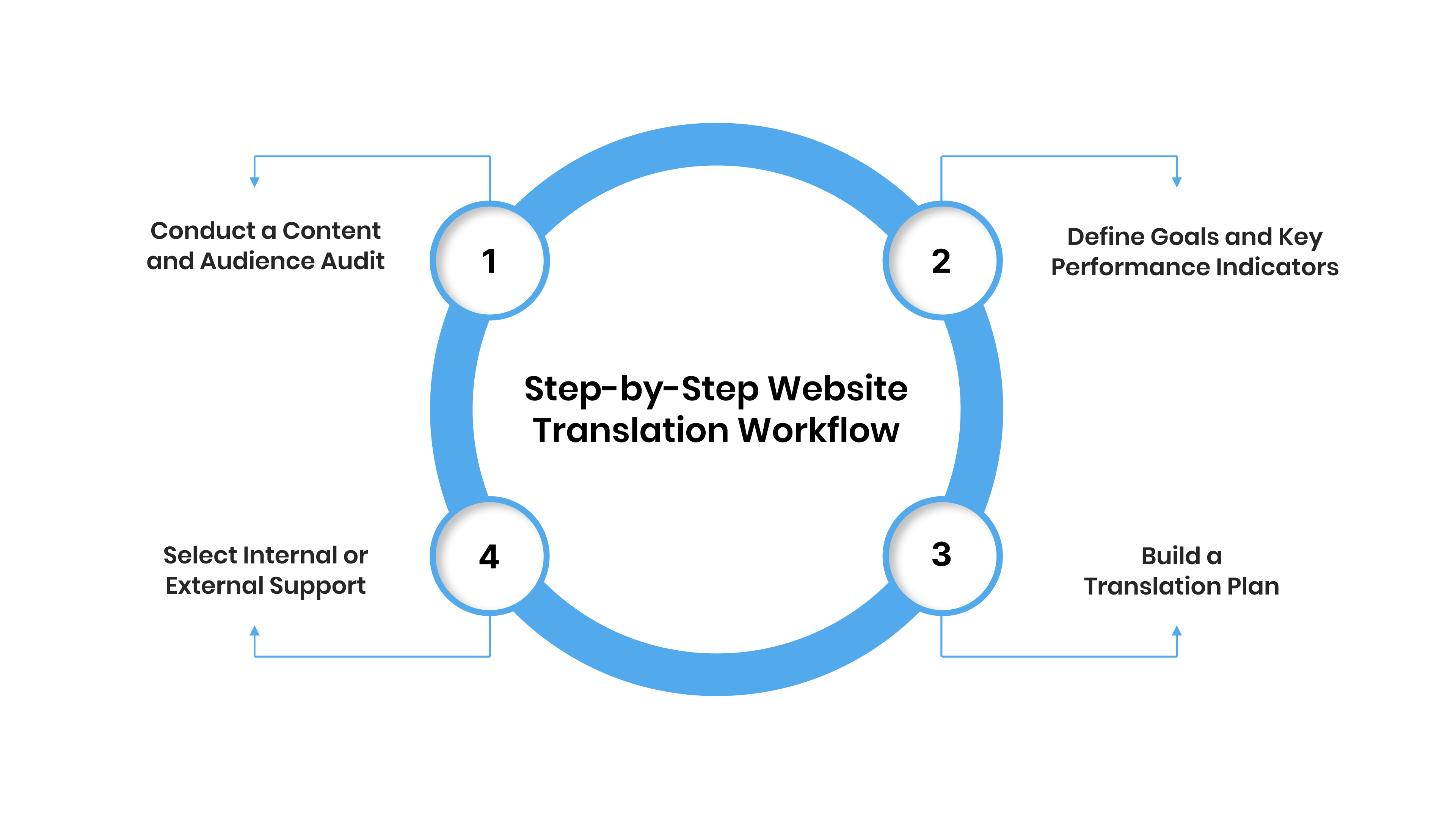
1. Conduct a Content and Audience Audit
Before translating your website, take time to understand what truly needs attention. Translating everything may seem thorough, but it often wastes time and budget.
You can begin by:
- Review your website analytics to find the most visited and highest-converting pages.
- Identifying where your visitors come from and what languages they use.
- Categorising pages by importance:
- Critical: Home page, product pages, pricing, checkout.
- Supporting: Blogs, FAQs, support content.
- Low priority: Archived or low-traffic pages.
This simple analysis ensures you translate content that has real business impact.
2. Define Goals and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Now that you know which pages matter, set measurable goals. A translation project without KPIs lacks direction.
You might aim to:
- Increase organic traffic in specific regions.
- Improve engagement or time spent on translated pages.
- Achieve higher conversion rates in local languages.
These metrics will later help you track success and fine-tune your localisation strategy.
3. Build a Translation Plan
Once your goals are clear, create a plan that connects people, tools, and timelines.
Include:
- Target languages and audience segments.
- Team roles and review responsibilities.
- Content update frequency.
- Chosen translation tools or management platforms.
A defined plan helps your team stay aligned and avoid duplicate work. On the other hand, skipping this step often leads to inconsistent translations and missed deadlines.
4. Select Internal or External Support
Finally, decide who will manage the actual translation. You can:
- Use your internal language or marketing team.
- Hire professional translators for accuracy and cultural depth.
- Partner with a localisation platform such as Anuvadak, which connects your CMS with translation experts and automates the workflow for speed and quality.
Now that your planning stage is complete, the next step is to choose the most suitable translation method for your project.
Part 2: Choosing Translation Methods
Once your translation plan is ready, the next step is to decide how to translate your content. The translation method you choose affects accuracy, cost, speed, and overall quality.
There are three main methods used by businesses today: human translation, machine translation, and hybrid workflows. Each has its place depending on the scale of your project and the level of precision required. Let’s look at each one in detail.
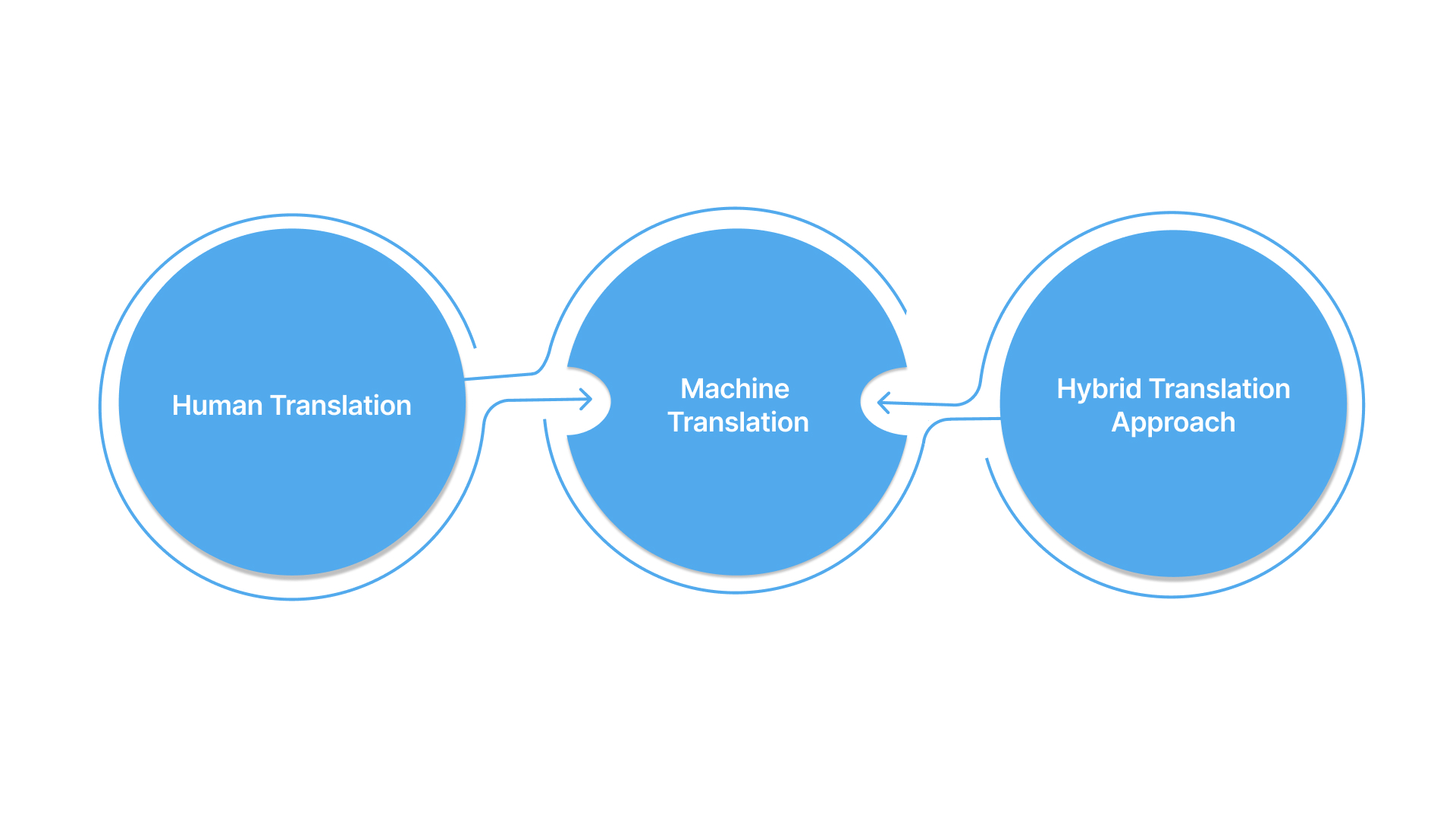
1. Human Translation
Human translation involves professional linguists who translate content manually. They understand cultural nuance, idioms, and tone better than any machine.
Best for:
- Marketing campaigns or brand content.
- Government, healthcare, and financial communication that require accuracy.
- Legal and compliance documents.
Advantages:
- Contextually accurate and culturally sensitive.
- Maintains brand voice and style.
Limitations:
- Slower and more expensive for large-scale projects.
Example: If your brand tagline or slogan needs translation, a human translator ensures the message carries the same emotional weight across languages.
2. Machine Translation
Machine translation uses AI-based systems to convert text automatically. It works best when you need to translate large volumes quickly.
Best for:
- Technical documentation, FAQs, or product catalogues.
- Content that changes frequently, such as user-generated data.
Advantages:
- Fast and scalable for large websites.
- Lower cost compared to manual translation.
Limitations:
- Accuracy may vary depending on language pair and context.
Machine translation tools have improved significantly with AI, but they still benefit from human review for tone and context.
Example: An online retailer updating thousands of product descriptions daily can rely on MT for initial drafts, followed by human review for accuracy.
3. Hybrid Translation Approach
A hybrid model combines both human and machine translation. Machines handle the bulk of the text, and human editors review and refine it for quality.
Best for:
- Enterprises managing multilingual content at scale.
- Websites require both speed and accuracy.
Advantages:
- Faster than full human translation.
- Higher quality than pure machine translation.
- Balanced cost and output.
Example: Using Anuvadak, you can automate initial translation through APIs and then add human review layers for accuracy. This creates a balanced workflow suitable for enterprise-scale websites.
| Translation Method | Accuracy | Cost | Speed | Best For |
| Human | High | High | Moderate | Branding, compliance |
| Machine | Moderate | Low | High | Large-scale or technical content |
| Hybrid | High | Moderate | High | Balanced enterprise use |
Now that you know the main translation methods, the next step is to explore the tools and technologies that simplify this entire process.
Also Read: The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Best Real-Time Translator for Your Needs
Tools and Technology that Support the Website Translation Process
Technology is at the heart of modern website translation. It helps you automate repetitive tasks, manage multilingual content efficiently, and ensure accuracy across every page. From translation memory systems to APIs, the right tools save time and maintain consistency.
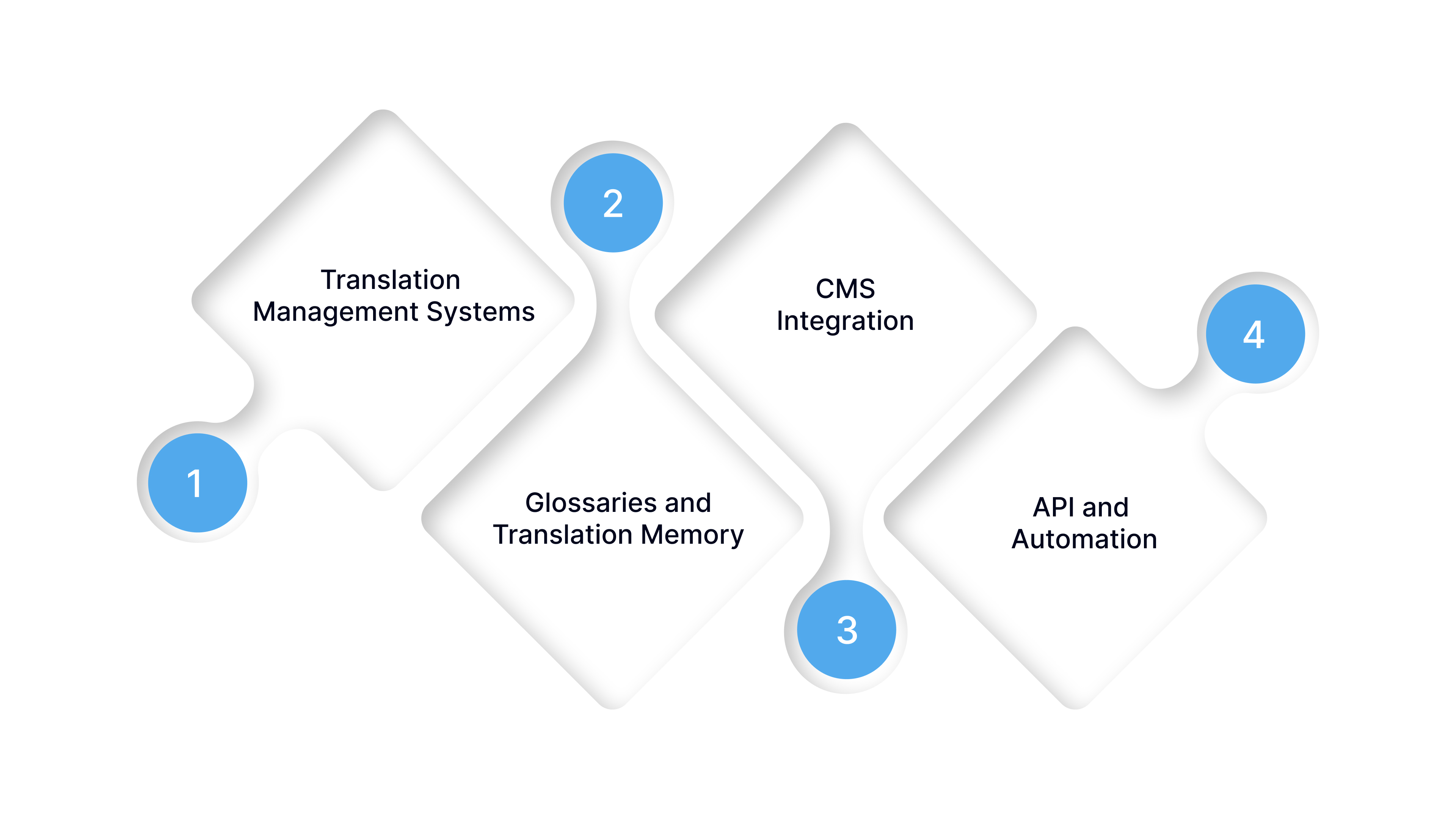
Let’s explore the key technologies that power a smooth translation process.
1. Translation Management Systems (TMS)
A TMS acts as the central hub for managing your translation projects. It allows teams to collaborate, track progress, and maintain translation assets like glossaries and style guides.
Key benefits:
- Centralised project control.
- Version tracking and translation memory reuse.
- Quality assurance checks within the system.
Example: If your company regularly updates product descriptions, a TMS ensures previously translated terms remain consistent across languages.
2. Glossaries and Translation Memory
Glossaries define approved terms and phrases for your brand, while translation memory stores previously translated content for reuse. Together, they ensure linguistic consistency and reduce rework.
Why they matter:
- Faster turnaround for recurring terms.
- Uniform brand tone across markets.
- Reduced translation cost over time.
3. CMS Integration
Integrating translation tools directly with your Content Management System (CMS) allows seamless content updates. When you add or edit content, it automatically passes through the translation workflow.
Benefits:
- No manual file transfers.
- Reduced human error.
- Faster publication cycles.
Example:
Platforms such as Anuvadak connect directly with your CMS, so new content is instantly available for translation and review without switching between tools.
4. API and Automation
APIs enable different systems to communicate and automate translation workflows. This is particularly useful for large organisations managing multiple websites or mobile apps.
Advantages:
- Scalable for high-volume translation.
- Integrates with chatbots, web apps, and customer platforms.
- Ensures real-time content updates.
When combined with secure cloud infrastructure, APIs allow you to maintain both speed and data protection.
Now that you understand the technologies that power website translation, the next section will explain how website translation methods compare in detail and how to choose the right one for your organisation.
Also Read: 10 Best Website Translation Services in 2025
Technical SEO Considerations in the Translation Process
A well-translated website is valuable only if people can find it. That is where technical SEO comes in. Multilingual SEO ensures your translated pages rank correctly in each target market. Without proper optimisation, even high-quality translations may go unseen.
The good news is that a few technical practices can help you achieve consistent visibility across languages.
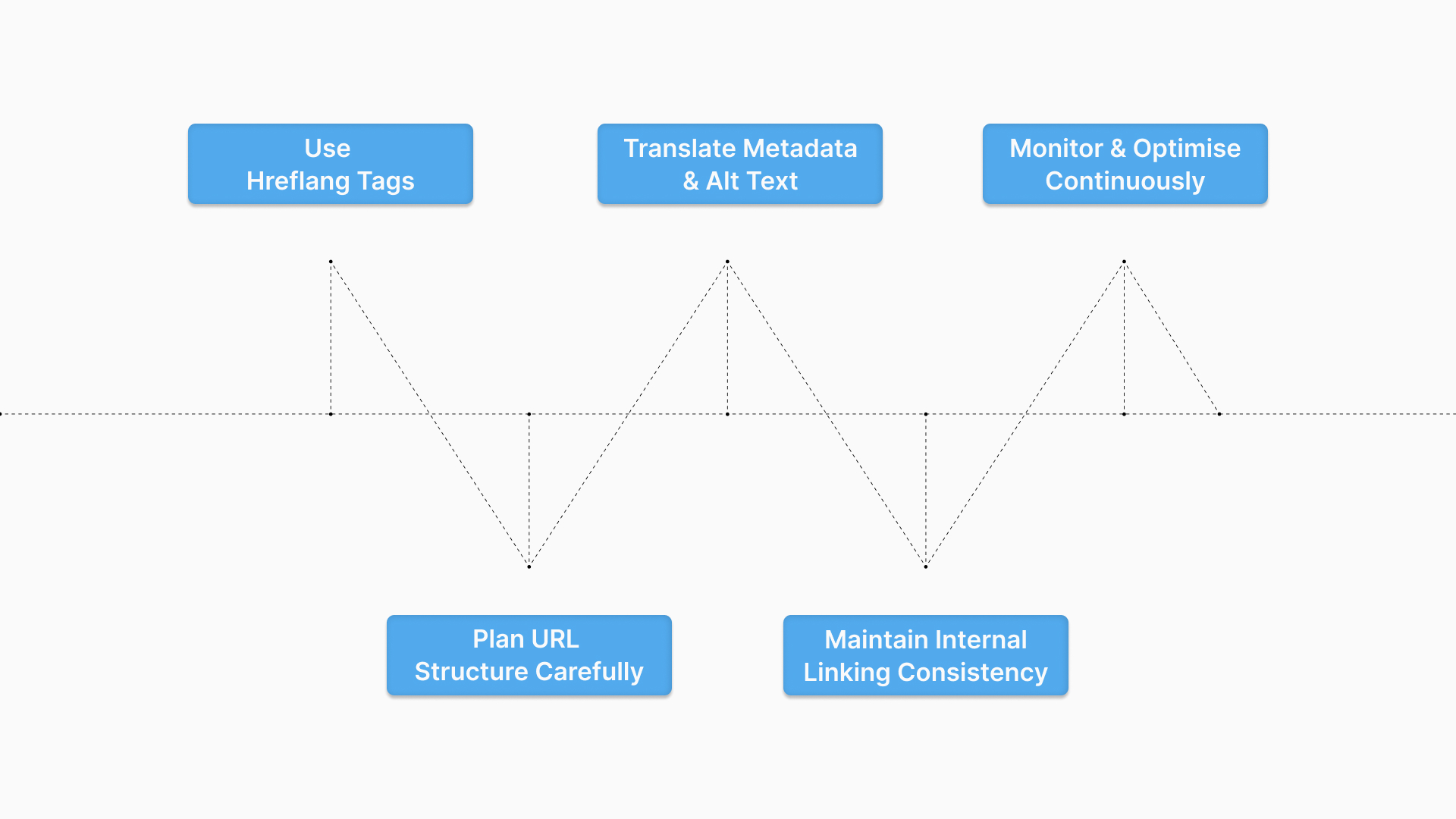
1. Use Hreflang Tags
Hreflang tags tell search engines which language version of a page to show to users based on their location or browser settings.
Best practices:
- Add hreflang tags to all translated versions.
- Reference both the target page and the original version.
- Include regional variations such as “en-gb” or “hi-in”.
Example: If your English site has a Hindi translation, add <link rel=”alternate” hreflang=”hi-in” href=”example.com/hi/”> in your HTML header.
2. Plan URL Structure Carefully
Your URL structure should clearly signal language versions to both users and search engines.
Recommended formats:
- Subdirectories: example.com/fr/ (best for unified domains).
- Subdomains: fr.example.com (useful for regional targeting).
- ccTLDs: example.fr (best for country-specific branding).
Tip: Keep URLs short, lowercase, and avoid machine-translated slugs.
3. Translate Metadata and Alt Text
Translation should extend beyond visible content. Search engines index metadata, image alt text, and even structured data.
Checklist:
- Translate title tags, meta descriptions, and headings.
- Add keywords in each language naturally.
- Localise image names and captions.
This improves search relevance and accessibility for multilingual audiences.
4. Maintain Internal Linking Consistency
Ensure your translated pages link correctly within their language versions. Broken or mixed-language links can confuse users and harm SEO performance.
Good practice: Create separate navigation structures per language and update all internal links accordingly.
5. Monitor and Optimise Continuously
SEO is not static. Track rankings, impressions, and traffic for each language regularly. Tools like Google Search Console and analytics dashboards can reveal how each region performs.
Metrics to watch:
- Organic sessions by language.
- Click-through rate (CTR) for translated pages.
- Bounce rate and time on page.
For larger sites, automation platforms such as Anuvadak help maintain metadata consistency and streamline multilingual SEO updates without manual effort.
Now that your technical foundation is in place, the next section will explore how to ensure quality and accuracy through effective testing and quality assurance practices.
Also Read: Top 10 Multilingual SEO Best Practices for Expanding Your Business in India
Quality Assurance and Testing of the Translation Process
Once your translated content is ready, the next essential step is quality assurance (QA). This process ensures that every translated page is accurate, functional, and culturally appropriate. Skipping QA can lead to errors that affect both user experience and brand reputation.
Let’s look at how to review your website for linguistic quality, functionality, and overall usability.
1. Linguistic Quality Assurance
Linguistic QA checks whether translations are correct, natural, and consistent with your brand’s tone.
Key actions:
- Compare translated pages with the source content for meaning accuracy.
- Check terminology against your approved glossary.
- Review punctuation, spelling, and grammar in each target language.
- Confirm that translation memory entries have been applied correctly.
Tip: Always involve native speakers during this stage. They can identify subtle phrasing issues that automated tools may overlook.
2. Functional Testing
This phase ensures that translated elements work correctly on your website. It includes checking how text appears across devices, browsers, and layouts.
Checklist:
- Verify that text fits correctly within buttons, menus, and forms.
- Test date, currency, and number formats for regional accuracy.
- Confirm that all links, forms, and scripts work after translation.
Example: A long word in German may overflow a button or layout. Functional testing ensures that the design remains consistent in every language.
3. Usability and Cultural Review
Cultural relevance enhances user comfort. Review imagery, colour choices, and idioms to make sure they align with the audience’s expectations.
Questions to consider:
- Do visuals reflect local culture and values?
- Are tone and phrasing appropriate for the region?
- Does navigation remain intuitive in the target language?
Platforms such as Anuvadak simplify QA by providing a centralised dashboard for language reviewers and automated error checks.
Once your QA is complete, your multilingual website is ready to launch, but your work does not end there. Continuous optimisation is the next crucial step.
Also Read: Strategies for Implementing Dynamic Content Translation on Your Website
Post-Launch Maintenance and Continuous Optimisation
After your translated website goes live, maintaining its quality and performance becomes an ongoing process.
Languages evolve, products change, and user preferences shift. Continuous optimisation ensures your multilingual website remains accurate, updated, and engaging.
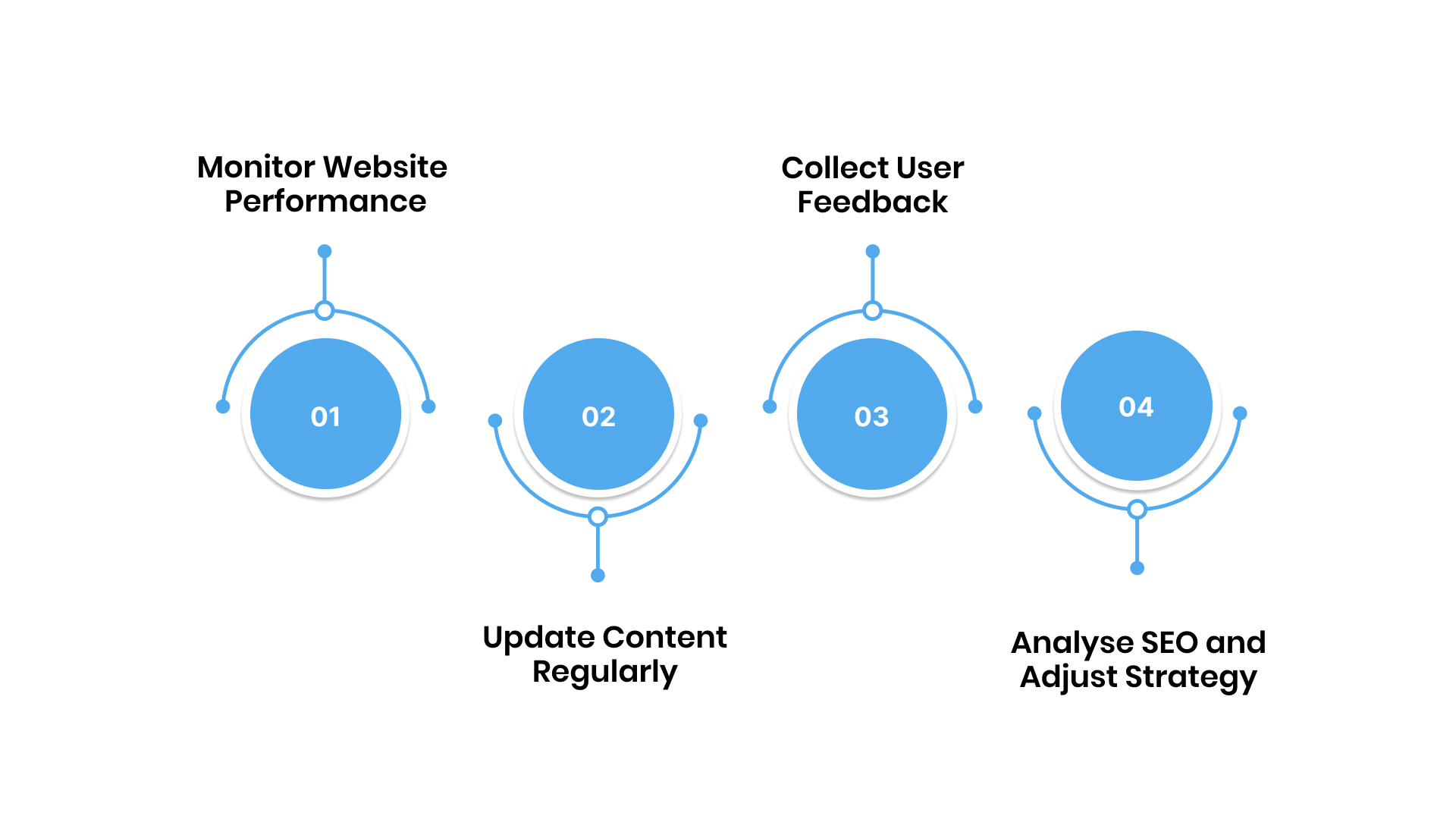
1. Monitor Website Performance
Regularly track how your translated pages perform. Use analytics to see which languages bring the most visitors and conversions.
Metrics to monitor:
- Organic traffic growth by language.
- User engagement metrics such as time on page and scroll depth.
- Conversion rates and exit pages.
If certain pages underperform, review their translation and localisation strategy.
2. Update Content Regularly
Keep your multilingual content aligned with your original site. Whenever you publish new pages or promotions, ensure they are translated promptly.
Recommended practices:
- Schedule quarterly audits for all language versions.
- Refresh translated pages when source content changes.
- Maintain a single source of truth using a translation management system.
A platform like Anuvadak automatically detects new content on your CMS and routes it for translation, helping you stay current across languages.
3. Collect User Feedback
Multilingual users can offer valuable insights about clarity, tone, or navigation. Collect feedback through surveys or chat support to identify pain points.
Use this feedback to refine translations and improve regional user experience.
4. Analyse SEO and Adjust Strategy
Monitor keyword rankings and localised search performance. Add new region-specific keywords as user behaviour evolves.
Example: If Hindi-speaking users search for different phrases than English users, adapt your translated metadata accordingly.
Regular analysis keeps your website competitive and visible in each market.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Even with a strong plan, website translation can present challenges. Knowing these early helps you avoid delays, maintain quality, and control costs.
Here are the most common obstacles and ways to solve them.
| Challenge | Impact | Solution |
| Managing large volumes of content | Slows delivery and increases manual effort | Use translation automation tools with workflow management. |
| Maintaining consistency across languages | Brand tone may vary | Build glossaries and translation memory within a central system. |
| Cultural mismatch | Reduces engagement | Involve native linguists for review and localisation feedback. |
| SEO gaps | Poor visibility in target regions | Apply hreflang tags and localised metadata for each page. |
| Data security | Risk of exposure with third-party tools | Choose enterprise-grade platforms like Anuvadak with encryption and compliance controls. |
Tip: Regular reviews and clear communication between your content, marketing, and technical teams can prevent most of these challenges.
When supported by the right technology, managing multilingual websites becomes smoother and more predictable.
Choosing the Right Partner or Platform
Choosing the right translation partner or platform determines how efficiently you can manage multilingual operations. The right partner should combine linguistic expertise with advanced technology and strong data security.
Let’s look at what to consider before making your choice.
1. Key Evaluation Criteria
When comparing providers, consider these factors:
- Accuracy: Proven expertise in your industry and target languages.
- Technology: Ability to integrate with your CMS or digital ecosystem.
- Scalability: Support for multiple websites, products, and regional versions.
- Security: Compliance with enterprise and government data standards.
- Support: Dedicated account management and technical assistance.
2. Benefits of Using an Integrated Platform
A unified platform allows you to handle translation, localisation, and updates from one place.
Advantages include:
- Centralised project management and version control.
- Automated workflows that reduce manual effort.
- Translation memory and glossary management for consistency.
- Real-time updates between CMS and translated sites.
With Anuvadak, you can manage website translation, API integrations, and voice or text localisation from a single dashboard. This creates efficiency, scalability, and reliability for large organisations.
3. Collaboration Between Humans and Technology
The most effective results come from combining skilled linguists with powerful technology. Human translators bring nuance, while automation tools maintain speed and consistency.
This balanced approach helps enterprises achieve high-quality translations without losing efficiency.
Conclusion
A structured website translation process turns your digital presence into a multilingual gateway for new audiences. From careful planning to post-launch optimisation, every step adds clarity, trust, and inclusivity to your online experience.
Choosing the right translation method and technology determines how effectively you can scale. With the right workflow, you not only translate words but also communicate your brand’s message to people in a way that feels personal and relevant.
For organisations that manage content across multiple Indian languages, Anuvadak offers an integrated localisation solution. It automates translation, maintains consistency, and ensures cultural accuracy across every digital touchpoint.
Start creating meaningful connections with your audience today by making your website accessible in the languages they value most.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between translation and localisation?
Translation changes text into another language. Localisation adapts the whole experience, words, visuals, dates, and formats, so it feels natural for each audience.
2. Do I need to translate my entire website?
No, you can start small. Focus on pages that bring traffic or sales, such as your homepage, product listings, or key landing pages. Translate other content later as demand grows.
3. Is automatic translation good enough?
Automatic tools are quick but often inaccurate. They miss the tone and cultural meaning. A mix of machine translation and human review usually gives better results.
4. How long does website translation take?
Timing depends on content size and language count. A small site might take weeks, while large projects can take months. Good planning and tools make it faster.
5. Does translation affect SEO?
Yes. Each translated version needs proper keywords, metadata, and hreflang tags. This helps search engines show the right language to the right audience.
6. What are common mistakes to avoid in website translation?
Common errors include translating everything at once, relying only on machine tools, or ignoring visuals and SEO. The best approach is structured, prioritised, and reviewed by experts.