Voice technology is no longer a futuristic gimmick; for Indian enterprises, it’s becoming mission-critical. Between multilingual customer support, voice assistants, and IVR automation, companies want to turn speech into structured data. According to a 2025 forecast by Grand View Research, the Indian NLP market, across all types (text, speech etc.), is expected to grow from US $2.728 billion in 2024 to US $28.28 billion by 2030.
Yet developers often face a tough trade-off: off-the-shelf speech APIs may lack support for Indian dialects and domain-specific vocabularies, while building your own recognition system is resource-intensive.
In this blog, you will learn exactly what a speech SDK is, why it matters for enterprise-grade voice applications in India, and how to build powerful, multilingual speech-enabled solutions using Reverie’s SDK.
Key Takeaways
- Speech SDKs give you full control over speech recognition workflows, customisation, and on-device processing, far beyond what a simple API call can offer.
- Accuracy depends on clean audio, the right sampling rate, and using supported formats like WAV/PCM for Indian accents and multi-language requirements.
- Noise reduction techniques matter, especially for India’s high-noise environments, and use DSP filters, beamforming mics, and on-device preprocessing.
- Enterprise-grade security is non-negotiable, with encryption, data minimisation, and regulatory alignment (DPDP, RBI guidelines, sector rules).
- A Speech SDK future-proofs your stack, enabling offline mode, edge deployment, and scalable custom ML models to meet India’s enterprise workloads.
What Is a Speech SDK and Why Do Developers Use It?
When you start building voice-enabled features inside an app, website or IVR system, you need more than a simple API that converts audio to text. You need a toolkit that helps you capture audio, stream it efficiently, manage callbacks, handle errors and fine-tune recognition behaviour.
This is exactly where a speech SDK becomes essential. It gives you a structured way to add real-time or file-based speech recognition without building every layer from scratch, which means you can focus on your product logic rather than low-level audio engineering.
Here are the core reasons developers use a speech SDK in their development workflow:
- Faster Integration: You plug ready-to-use libraries into your Android, iOS, Web or server environment, so you avoid writing audio pipelines or complex networking logic yourself.
- Real Time Handling: Work with live transcription through event listeners, which is ideal when you want instant outputs for use cases such as voice search in retail apps or in call guidance in contact centres.
- Audio Pipeline Control: Manage sample rates, buffer sizes and audio sources, which gives you clarity when building apps that need accurate speech capture even in noisy Indian conditions.
- Developer Friendly APIs: Work with simple classes, functions and callbacks instead of large manual code blocks, which keeps your codebase clean and maintainable.
- Low Latency Performance: Get predictable response times that matter when you build IVR systems, chatbots or in-app commands where users expect the system to react immediately.
- Rapid Prototyping: Validate new voice features quickly, especially when your product team wants to test Indian language commands or mixed language inputs before a full launch.
Also Read: What is a Generative Model Chatbot? A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding a Speech SDK is key to supporting real-time and file-based speech recognition in enterprise workflows.
Understanding Real-Time and File-Based Speech Recognition for Enterprise Workflows
When you build speech features for enterprise localisation systems, the first decision you need to make is whether your workflow needs real-time recognition or file-based processing. Each mode solves a different operational challenge.
Below are the key differences you should consider:
- Live Interactions: Use real-time recognition when your system must respond instantly, such as guiding callers inside an IVR or powering voice search across multilingual product catalogues.
- Post Call Analysis: Choose file-based mode when you want clean transcripts of recorded customer conversations, medical dictations or legal recordings that need structured processing.
- Latency Expectations: Real-time mode gives you millisecond-level responses suitable for interactive tasks, while file-based mode lets you process larger audio files without user wait time.
- Resource Planning: Real-time workflows demand stable network handling and efficient streaming, while file-based workflows allow scheduled processing that fits into your backend load cycle.
- Error Recovery: In real-time mode, you handle transient network issues with graceful fallbacks, while file-based mode lets you retry or reprocess files without affecting user experience.
Building real-time or file-based transcription doesn’t have to feel complicated. If you want to experiment with Indian-language STT, test accuracy for your domain, or validate your workflow, try running a quick prototype now. Get started with the Speech-to-Text API.
Test real-time and file-based transcription fast
Validate your workflow on real audio with Reverie Speech-to-Text. Teams report up to 97% reduction in dev time.
With the basics of a Speech SDK in mind, it’s time to explore the essential components that power modern speech applications.
Core Components of a Modern Speech SDK
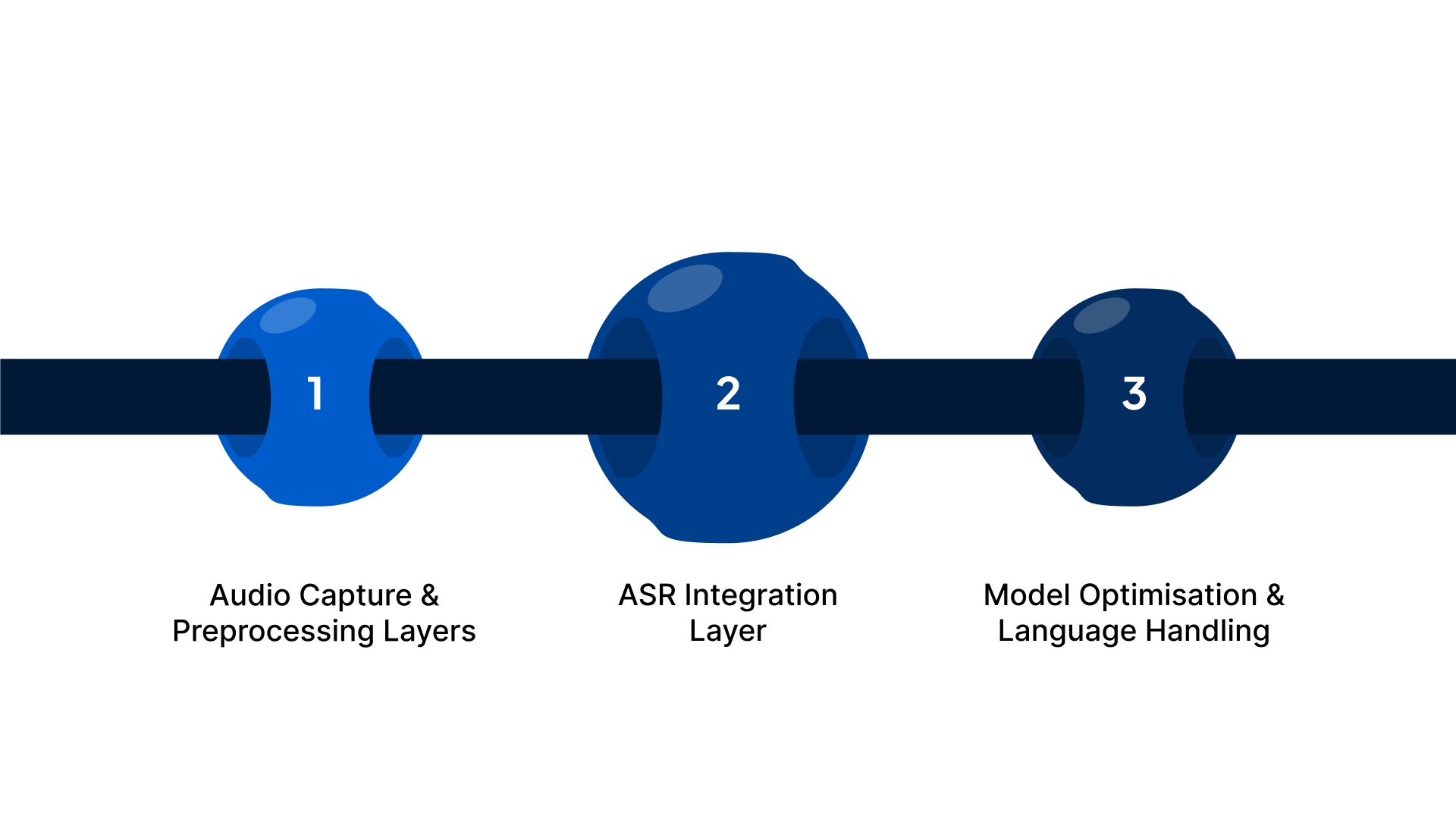
When you work with a mature speech SDK, you rely on a set of internal modules that keep audio capture, recognition and output handling predictable across different platforms. These components shape how reliably your application understands speech, especially when you deal with varied Indian environments such as mobile apps, on-ground service kiosks or IVR systems.
To explore these layers in detail, here is how a modern SDK is structured.
- Audio Capture and Preprocessing: Controls microphone input, filters background noise, normalises formats, stabilises volume and manages interruptions so the recognition engine receives clean, consistent audio.
- ASR Integration: Handles streaming for live use cases, batch routing for recorded files, real-time transcript callbacks, error flow control during network drops and seamless language switching for multilingual speech.
- Model Optimisation and Language Handling: Adapts to regional dialects, supports industry-specific vocabulary, decodes mixed-language speech, tunes acoustics for different environments and applies contextual hints for more accurate intent recognition.
Once you understand the core components, the next step is setting up your development environment to start building with the Speech SDK.
Setting Up Your Development Environment With a Speech SDK
When you begin working with a Speech SDK, your goal is simple: you want an environment that doesn’t break midway, doesn’t confuse you with unnecessary steps, and lets you start experimenting fast. As a developer, your biggest frustration is usually misconfigured paths, missing dependencies, or SDK versions that don’t match your OS requirements.
Here’s exactly how you set it up:
- Choose the Right SDK Build for Your Platform: You need the SDK version that fits your OS: Windows, macOS, or Linux. For example, if you’re on macOS M1, downloading an Intel-only build will lead to architecture errors later. Matching the SDK to your platform saves you hours of debugging.
- Install the Required Runtime Dependencies: Before running any sample, make sure your system libraries or frameworks (like .NET, Python, or Node.js versions) are installed. If you choose Python, you should confirm with python3 –version that you’re using a supported version to avoid “unsupported interpreter” errors.
- Set Up Your Project Folder Structure: Organise your workspace from the start, keep your credentials file, audio samples, and SDK scripts separate. For example:
/project-root/sdk/ for library files,
/project-root/samples/ for WAV files,
/project-root/config/ for keys and endpoints.
This helps you locate everything instantly when testing. - Configure Environment Variables Properly: Your Speech SDK won’t work until your API key and region are added to environment variables. For your security, store them using commands like:
export SPEECH_KEY=”yourkey”
This keeps your secrets out of your codebase and prevents accidental commits. - Run a Sample Script to Verify Installation: Once everything is installed, run a quick sample from the SDK docs, such as a short audio transcription test. If the script successfully prints text output, your setup is verified and ready for custom development.
- Use a Virtual Environment for Cleaner Management: If you’re using Python or Node.js, create a virtual environment so dependency conflicts never affect your global system. For example, run python3 -m venv venv and activate it before installing SDK packages.
- Keep a Test Audio File Ready: You’ll need a sample WAV or MP3 file to test your setup. Use a clean, short clip, even a 5-second voice note recorded on your phone, works well for initial validation.
Also Read: AI Ticketing Systems: Complete Guide
After setting up the environment, you’re ready to start implementing speech recognition with the Speech SDK.
Implementing Speech Recognition Using a Speech SDK
When you start implementing speech recognition, your focus shifts from setup to real interaction, turning raw audio into accurate, usable text. At this stage, you’re not just “running an SDK”; you’re shaping how your application listens, responds, and behaves in real time.
Below are the core implementation areas you focus on at this stage:
- SDK Initialisation and Configuration: Load API credentials securely, reuse SDK instances for stable performance, select the right ASR model for your use case, define audio formats (sample rate, channels, encoding), set silence timeouts, choose between streaming or batch modes, enable real-time callbacks, and apply environment-level security controls.
- Real-Time Transcription Handling: Detect speech start for UI triggers, process partial transcripts for live feedback, capture final transcripts for storage and processing, respond to silence automatically in IVR flows, manage network or audio errors gracefully, and monitor connection stability for live agent environments.
- Transcription Output Processing: Normalise raw text, apply timestamps, extract entities like names and amounts, classify intent for smart routing, add punctuation for readability, detect keywords for instant alerts, and push structured output into CRMs, analytics tools, and AI ticketing systems.
Also Read: B2B SaaS Content Localisation: What It Is and Why It Matters
Once basic speech recognition is in place, following best practices ensures your speech-enabled applications are scalable and reliable.
Best Practices for Building Scalable and Reliable Speech-Enabled Applications
As your speech workloads grow, the challenge is keeping everything fast, accurate and stable across devices, locations and traffic spikes. Your application should perform consistently during low usage and peak demand, across metros and tier 2 cities, and on both high-end and mid-range devices.
Below are the core practices that help you scale reliably:
- Edge and Cloud Balance: Offload simple processing to the device and reserve heavy tasks for the cloud to keep latency low for fast-paced mobile and agent workflows.
- Adaptive Buffer Management: Adjust buffer sizes dynamically based on network quality to handle unstable mobile data in tier 2 and tier 3 regions.
- Language-Specific Routing: Direct each request to the right model when users switch between Hindi, Tamil, Marathi or English to improve accuracy without backend overhead.
- Graceful Failure Handling: Use retries and temporary text prompts when audio quality drops to prevent user frustration during outages or noisy situations.
- Performance Monitoring Hooks: Track accuracy, error types and latency with real-time metrics and alerts for location-based spikes.
If you’re building for a regulated sector, speech recognition has to be secure, compliant and deployment-flexible. Explore tools that help developers build confidently without worrying about data exposure or regulatory friction. Explore the Developer Suite today.
Alongside scalability and reliability, addressing security and compliance is essential for handling speech data in Indian enterprises.
Security and Compliance Considerations for Speech Data in Indian Enterprises
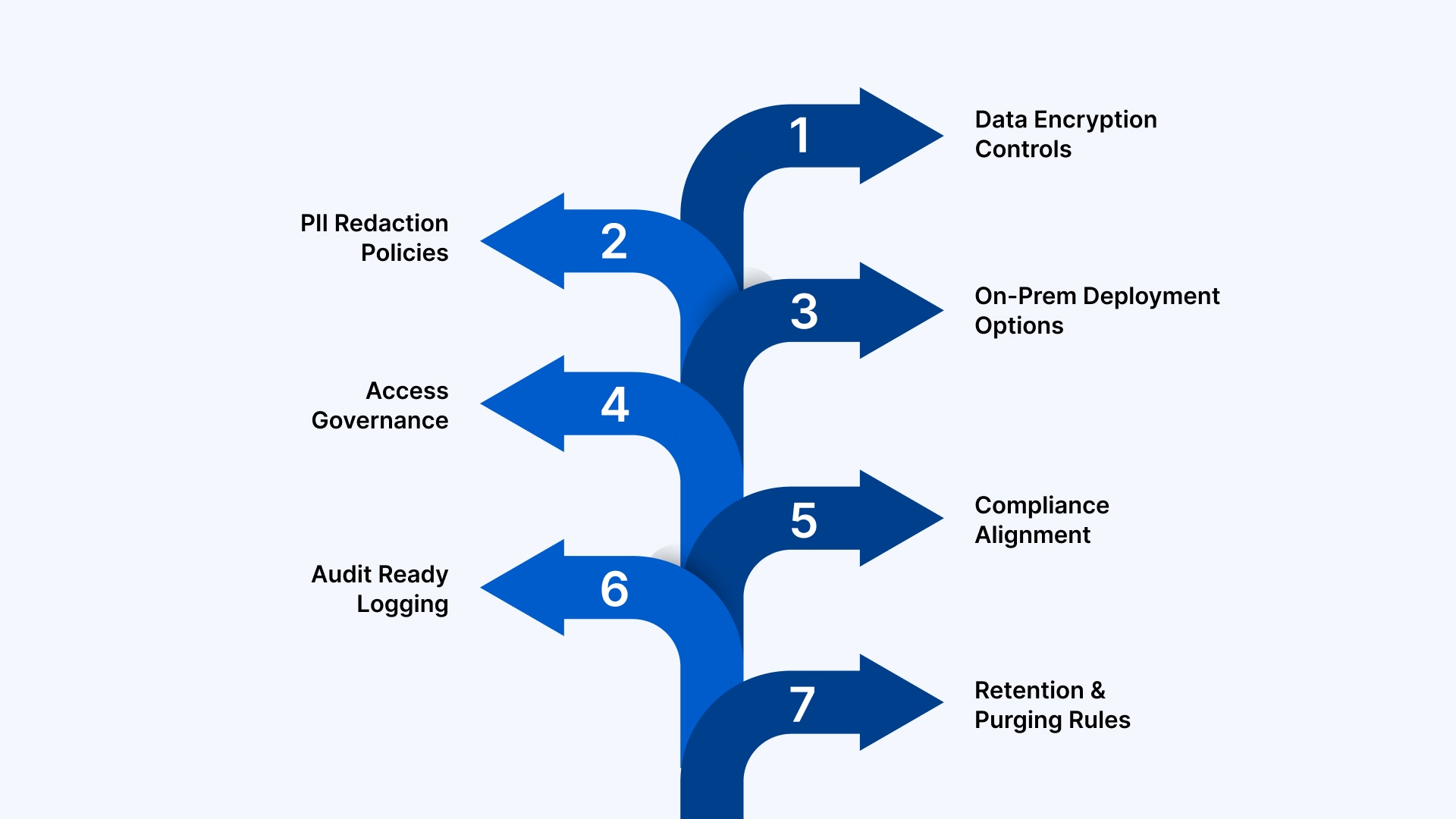
When you handle speech data inside an Indian enterprise, you work under strict regulatory expectations and high user sensitivity. Every audio clip, transcript and metadata packet carries potential risk if it is not protected properly. Whether you operate in BFSI, healthcare, insurance, mobility or government-linked workflows, you want strong safeguards so your speech features stay compliant without slowing down development.
Below are the considerations you typically focus on:
- Data Encryption Controls: Protects audio and transcript flows during transit and storage. For instance, TLS for streaming audio ensures that call centre recordings travelling from the browser or mobile device remain unreadable to outsiders.
- PII Redaction Policies: Removes sensitive terms such as Aadhaar numbers, phone numbers or account details before storing transcripts. This helps you stay compliant with internal governance rules while reducing exposure risk.
- On-Prem Deployment Options: Keeps speech processing within your data centre when cloud usage is restricted. BFSI teams often use this model for KYC calls, loan verification audio and dispute recordings.
- Access Governance: Restricts transcript visibility based on roles. For example, an operations manager may review call summaries while analysts only view anonymised text.
- Compliance Alignment: Supports frameworks relevant to Indian enterprises, such as RBI guidelines, HIPAA for health data or ISO 27001 for internal audits. This avoids friction during compliance checks and vendor assessments.
- Audit Ready Logging: Records who accessed what transcript, when and from where. This is especially important when your organisation handles dispute resolution or stores conversational data for regulatory review.
- Retention and Purging Rules: Manages how long audio and transcripts stay in storage. Some teams keep call summaries for support quality assessment, but purge raw audio after predefined durations.
Deploy secure speech recognition for regulated workflows
Build for BFSI, healthcare, and government use cases with enterprise deployment options. Businesses report up to 62% reduction in operational costs.
With security and compliance in mind, let’s explore how Reverie’s Speech SDK empowers developers to build robust speech applications.
How Reverie’s Speech SDK Supports Developers Building Speech Applications?
Building Indian language speech features is never as simple as plugging in a generic ASR API. You work with mixed-language speech, unpredictable accents, varied audio quality and specialised domain terms that typical global engines are not tuned for. This is where Reverie’s Speech SDK gives you a practical enhancement. It is engineered for India’s linguistic diversity, enterprise scale and regulatory needs.
Below are the capabilities you depend on when you build with Reverie:
- Indian Language First: Covers Hindi, Bengali, Marathi, Tamil, Telugu, Kannada, Gujarati, Malayalam, Odia, Assamese, Punjabi and English in real-time and file-based formats. For example, you can power multilingual voice search in your e-commerce app without routing users to English-only queries.
- Real Time and Batch Ready: Supports live transcription for IVR and bot workflows, along with file-based processing for meetings, call recordings or compliance archives. This flexibility helps you manage both high traffic and long-form audio.
- Domain Tuned Models: Adapts to vertical-specific vocabulary in sectors such as automotive, healthcare, legal and BFSI. For instance, a finance app can accurately capture phrases like overdue EMI or UPI mandate without manual correction.
- Keyword Spotting Tools: Flags moments where users mention specific terms such as refund, cancellation or complaint, which is helpful in contact centre automation and analytics.
- Profanity and Brand Safety Filters: Remove inappropriate language from transcripts to maintain brand reputation across customer support or bot-driven journeys.
- Speaker Identification: Separates speakers in multi-participant conversations. This is effective when you capture doctor-patient interactions or multi-agent sales calls.
- Flexible Audio Input: Handles various formats, including low-fidelity telephony audio that normally reduces accuracy. Perfect for IVR-based journeys in government services or banks.
- Cloud and On-Prem Choice: Gives you deployment flexibility for strict compliance environments such as insurance and healthcare, where audio cannot leave your internal infrastructure.
- Developer Ready SDKs: Offers Android, iOS, Web and REST options with clear code samples so you can reduce integration time and build proof of concepts quickly.
Also Read: Top Use Cases for AI Voice Agents in Retail and E-Commerce
Having seen how Reverie’s Speech SDK aids developers, we can now wrap up with key takeaways. Explore the STT Developers Page for technical documentation and code snippets.
Conclusion
As India moves deeper into voice-led interactions, your applications need speech recognition that handles real user behaviour, multilingual marketing inputs and enterprise scale without compromising accuracy. Reverie’s Indian language optimised engine simplifies this journey by giving you real-time transcription, domain customisation, analytics and deployment flexibility in a single developer-friendly stack.
If you are exploring voice features for apps, bots, IVR or customer workflows, you can start immediately with Free Speech-to-Text API credits that include 10 hours of Speech to Text and 10,000 Text to Speech characters, along with a playground for rapid proof of concepts.
Many teams report strong outcomes such as 37 per cent improvement in sales and 62 per cent reduction in operational costs, making the business case even stronger. Ready to build with Indian language speech? Sign up now!
FAQs
1. How does a Speech SDK differ from a Speech API?
A Speech SDK gives you prebuilt libraries, event handlers and client-side controls that simplify integration, while a Speech API is just a server endpoint. With an SDK, you manage audio, callbacks and performance far more efficiently.
2. What is the ideal audio format for high accuracy in speech recognition?
For most enterprise use cases, uncompressed audio such as WAV with 16-bit PCM at 16 kHz delivers the best accuracy. Clean input with minimal compression helps the ASR engine capture frequencies needed for Indian language clarity.
3. How does background noise impact STT accuracy, and how can you minimise it?
Noise masks key speech frequencies, reducing word clarity and increasing substitution errors. You improve accuracy by using directional microphones, applying noise suppression, capturing audio closer to the speaker and avoiding environments with traffic, fans or cross conversations.
4. Can speech recognition work offline on mobile applications?
Yes, if the SDK supports on device models optimised for mobile hardware. These models are lighter than cloud ASR and suit voice commands, shortcuts or car mode features where connectivity is weak or unavailable.
5. What is the role of sampling rate in speech recognition accuracy?
A higher sampling rate captures more speech detail, helping the ASR engine recognise phonetic variations accurately. Most enterprise use cases work best at 16 kHz, which balances audio clarity with bandwidth and processing efficiency.


