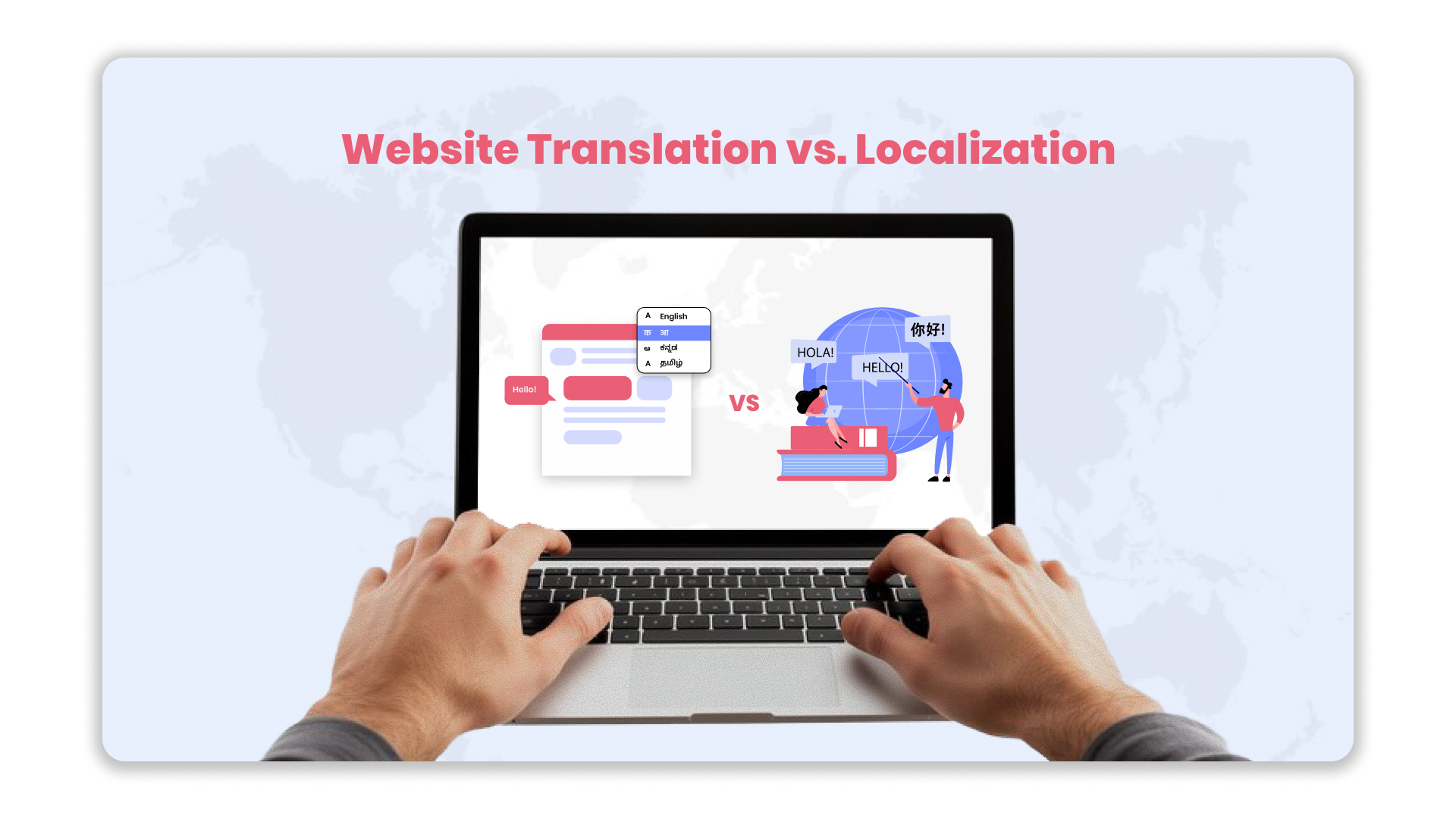
When expanding a business internationally, CTOs, product managers, and localisation managers in the eCommerce, BFSI, or healthcare industries must decide whether to prioritise localisation services over website translation. While both involve adapting your site for different languages, translation focuses on converting text, whereas localisation takes it a step further by ensuring your content aligns with local cultures, user expectations, and legal requirements.
Understanding the difference between website translation vs localization services helps businesses choose the right approach for global expansion, compliance, and user experience.
In this blog, we’ll break down these differences and show you how to implement each approach for maximum impact.
Key Takeaways
- Website translation focuses on converting text into another language, while localisation adjusts content for cultural, legal, and functional relevance in the target market.
- Localisation enhances user engagement by adapting the language and also visuals, user interface, and technical elements.
- For businesses expanding globally, localisation helps reduce risks related to legal compliance and ensures that content meets local regulations, especially for BFSI and Government sectors.
- Multilingual APIs and Translation Management Systems (TMS) facilitate seamless integration of both translation and localisation for a consistent global user experience.
- Website translation is cost-effective for reaching new language-speaking audiences, while localisation is essential for deeper market penetration and ensuring a culturally relevant experience.
Website Translation vs. Localization: 8 Key Differences
Below is a table highlighting the key distinctions between website translation vs localization services for global businesses:
| Aspect | Website Translation | Website localisation |
| 1. Definition | Converts content from one language to another, typically using multilingual APIs or CAT tools. | Adapts content to the cultural, technical, and legal needs of a specific region, adjusting layout, functionality, and design. |
| 2. Focus | Primarily focuses on language accuracy and textual integrity. | Involves cultural context, regional functionality, and technical requirements such as currency formatting, regional legal compliance, and social values. |
| 3. Scope | Involves textual changes such as translating product descriptions, legal terms, and marketing content. | Involves linguistic changes plus technical adjustments like altering payment systems, user interface elements, and regional customer service integration. |
| 4. Objective | Ensures the message is understood by native speakers, using basic linguistic conversion. | Ensures that the content feels culturally relevant and functional in the target region, enhancing user experience (UX) and meeting regional laws. |
| 5. User Experience (UX) | Limited impact on design, as the text is simply translated. | Adjusts images, icons, date formats, and navigation to align with local user habits. |
| 6. Cultural Adaptation | Focuses on ensuring words are accurately translated, regardless of cultural context. | Changes elements like colours, shapes, symbols, and humour to better align with local cultural norms (key for Marketing Heads and CX Leaders). |
| 7. Technical Considerations | Translating static content like text, with minor concerns for code integration. | Adapts technical elements such as regional legal compliance (e.g., GDPR), regional laws for Healthcare, and local accessibility standards. |
| 8. Legal Compliance | Often involves translating legal documents like terms of service. | Ensures that all content adheres to local regulations, including privacy policies, local laws, and sector-specific guidelines. |
Also Read: What is Continuous Localisation?
Now, let’s explore in detail what website localisation is.
What is Website Localisation?
Website localisation is the process of adapting your website to meet the language, cultural, and functional needs of a specific target market. It goes beyond simple translation and involves modifying elements such as design, functionality, and content to ensure relevance in a local context.
For example, a BFSI platform might need to adjust content to comply with local financial regulations, while an eCommerce site might need to change product names and descriptions to align with regional preferences.
Moving ahead, we’ll discuss why website localisation is so important for reaching global markets.
Why is Website Localisation Important?
Website localisation is essential for businesses looking to succeed in international markets. Here’s why it’s important:
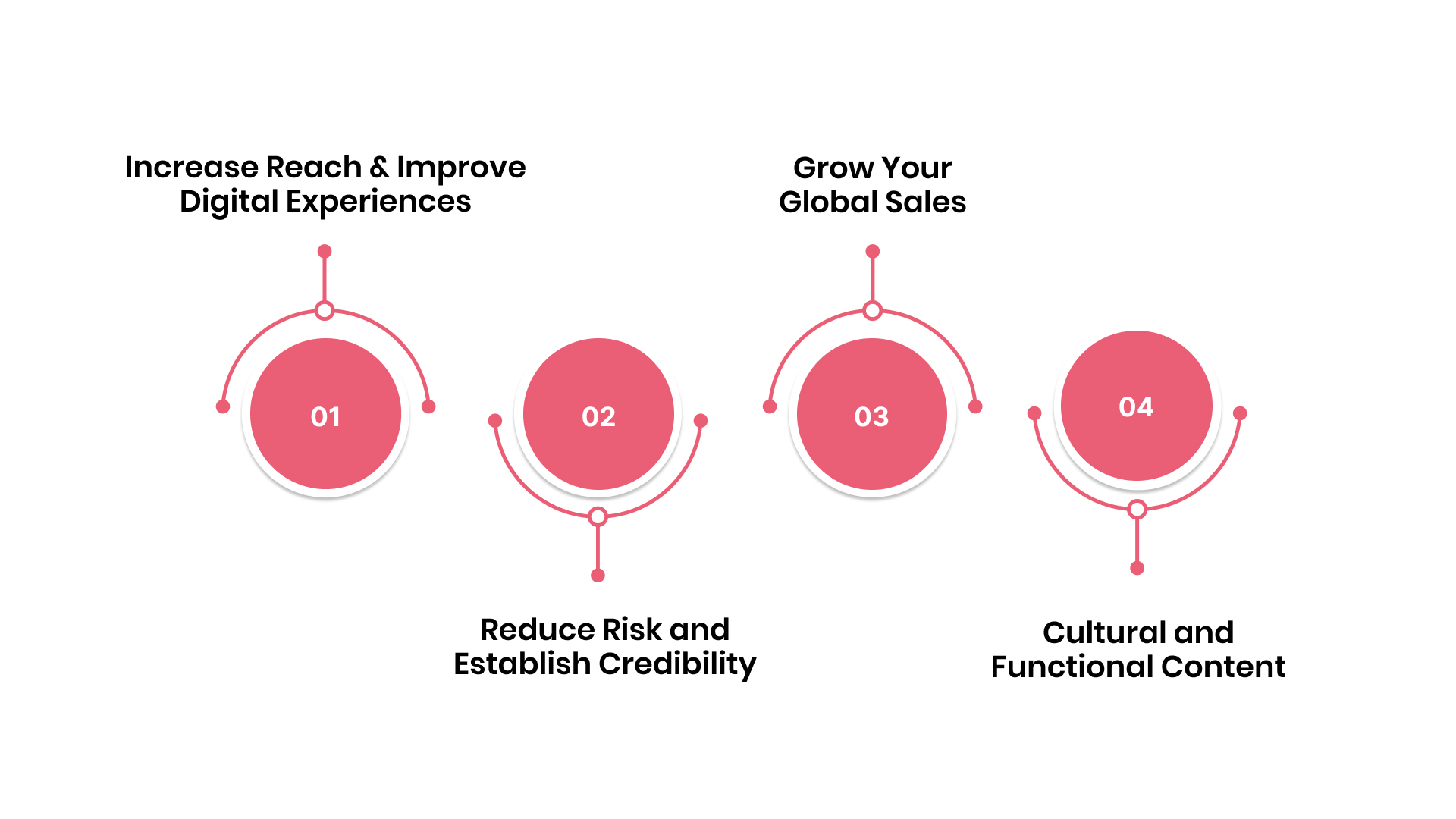
1.Increase Reach and Improve Digital Experiences
Localisation helps businesses reach a wider audience by adapting their content to fit local preferences. If you’re targeting eCommerce shoppers or Healthcare users, localised content creates a better user experience.
2.Reduce Risk and Establish Credibility
By localising content, businesses can ensure they meet local regulations, thereby reducing legal risks. For industries like BFSI and Legal & Compliance, adhering to local rules is essential for avoiding penalties.
3.Grow Your Global Sales
Localisation drives engagement, improving conversion rates by providing content that resonates with the target audience. For eCommerce platforms, this means localised product descriptions and local payment options, increasing the likelihood of purchase.
4.Cultural and Functional Content
Localisation ensures that content is culturally relevant, including adapting imagery, symbols, and social values to fit the target market. This approach is essential for Government services and platforms targeting e-learning audiences.
Also Read: What is ASO Localisation? A Complete Guide for App Growth
Let’s now look into the website localisation process and how to get started.
The Website Localisation Process
Understanding the steps in website localisation ensures that your content resonates with local audiences while maintaining consistency across regions. Here’s how to get started.
1. Preparation and Planning
Identify target markets and languages, then prioritise content for localisation. Ensure resources are in place for translation and integration with your CMS to align with your localisation strategy.
2. Content Translation
Translate content accurately using AI tools or professionals. Focus on key elements such as product descriptions and legal disclaimers for industries like BFSI and eCommerce, ensuring cultural sensitivity and SEO compatibility.
3. Adapting Visuals and Design
Modify images, icons, and layouts to reflect local culture and preferences. Ensure support for right-to-left languages and update currency symbols and measurement units based on regional norms.
4. Implementing Local Functionality
Integrate local payment methods and customer support tools. For industries like healthcare, ensure compliance with regional regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA, and secure data integration.
5. Testing and Quality Assurance
Test translations for accuracy and cultural relevance. For government services and legal content, ensure compliance with local regulations and maintain consistency in messaging across languages.
6. Launch and Continuous Updates
Monitor the localised site’s performance and make updates based on user feedback and regional trends. Ensure that localisation processes are adaptable to evolving market needs and new content.
Also Read: Why Magento Localisation is Crucial for Enhancing Customer Experience
Next, we’ll look at when you should implement localisation for maximum impact.
When Should You Implement Localisation?
Localisation adapts your website for regional preferences, culture, and legal needs, ensuring that your content fits the local market’s expectations.
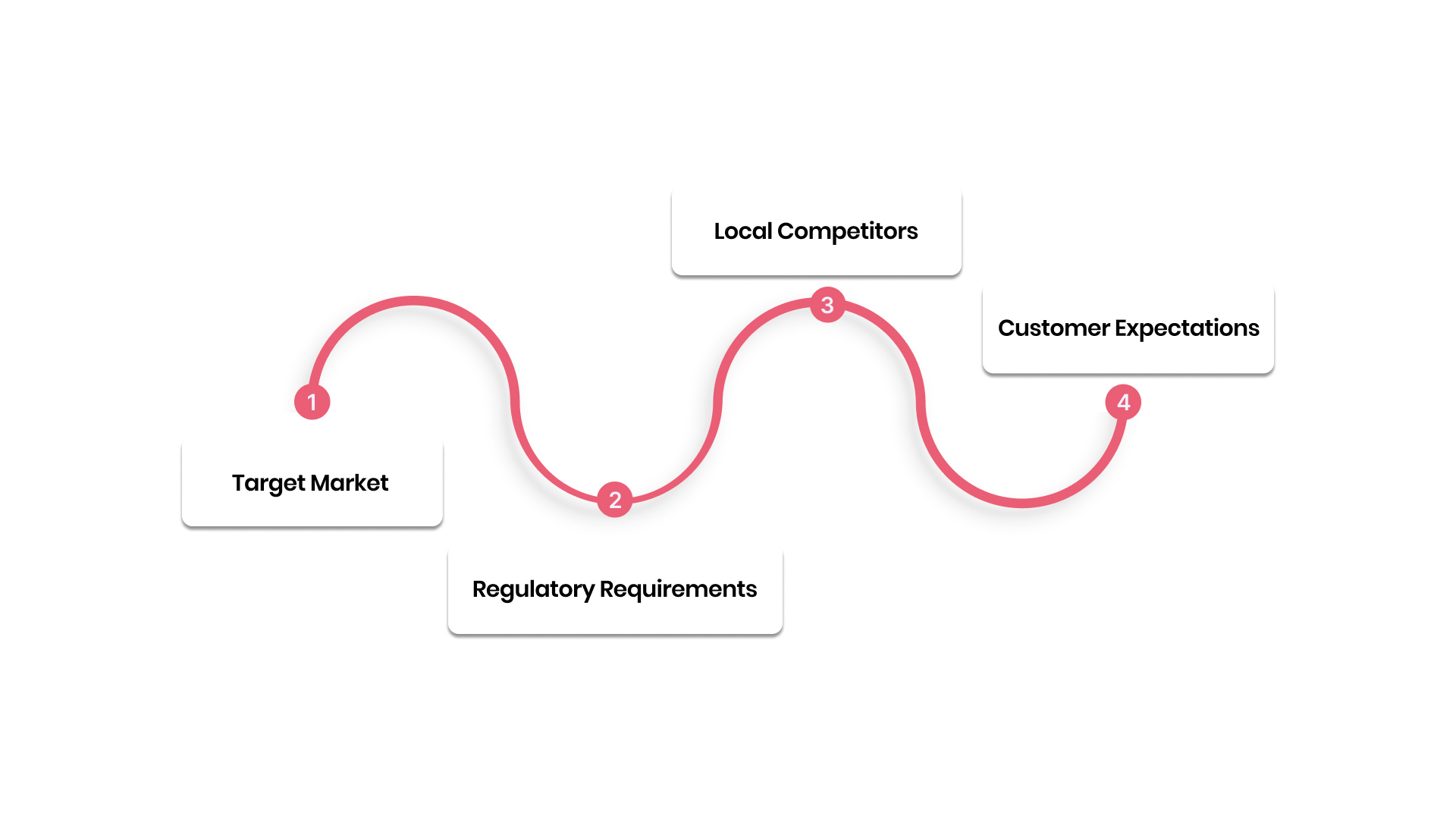
- Target Market: When you have identified a market with distinct cultural norms and expectations that differ from your home country.
- Regulatory Requirements: When entering a market with specific legal or compliance requirements, such as in BFSI or Healthcare.
- Local Competitors: If competitors in the region are already providing a localised experience that appeals to the local audience.
- Customer Expectations: When your audience expects a more personalised experience, particularly in regions with distinct languages and cultural preferences.
Transform your website with Anuvadak’s seamless translation and localisation tools. Use Context-Aware Translation Memory and Real-Time Multilingual APIs for accurate content delivery across languages.
Now, let’s take a deeper look at website translation.
What is Website Translation?
Website translation is the process of converting your website’s content from one language to another to make it accessible to a broader audience. This is essential for businesses aiming to expand into new regions, like eCommerce and BFSI platforms, ensuring that users can interact with the content in their preferred language.
Let’s continue by exploring the importance of translating your website content.
Why is Website Translation Important?
Website translation is important for businesses looking to reach global markets and improve user engagement. Key benefits include:
- Expanding Market Reach: By translating your website, you make it accessible to new customers in different regions, driving global sales for eCommerce businesses.
- Improved User Experience: Offering content in multiple languages increases customer satisfaction and engagement, especially in Healthcare platforms where clear communication is vital.
- Boosting SEO: Multilingual websites are more likely to rank higher in local search results, enhancing visibility in regions like BFSI and Education & eLearning.
- Legal Compliance: Translation ensures adherence to local regulations, especially in industries like Legal & Compliance or Telehealth, where accurate communication is important.
Also Read: B2B SaaS Content Localisation: What It Is and Why It Matters
Now that we understand why translation matters, let’s explore how the translation process works.
The Website Translation Process
The website translation process involves several steps to ensure that the content is translated accurately and fits the technical and cultural needs of the target audience.
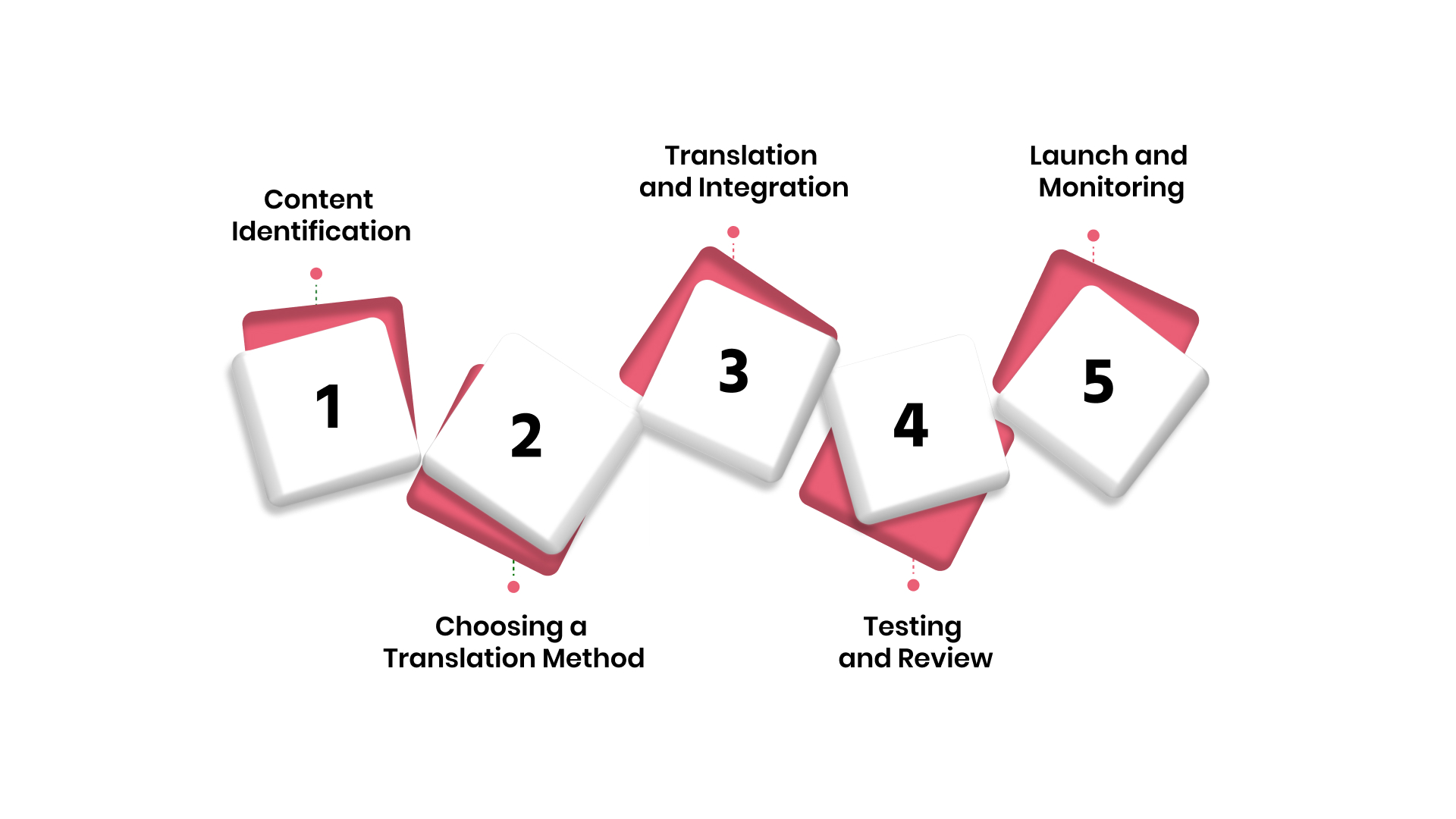
1. Content Identification: Identify all content on the website that needs to be translated, including text, images, and multimedia. For eCommerce, this would include product descriptions, reviews, and pricing information.
2. Choosing a Translation Method: Decide if to use human translators, machine translation, or a combination (MTPE). This depends on the complexity and scale of the project, especially for industries like BFSI and Healthcare, where precision is important.
3. Translation and Integration: Translate the content and integrate it into the website. Ensure that it’s formatted correctly and properly embedded within the website’s CMS, using multilingual APIs for seamless integration.
4. Testing and Review: Conduct QA testing to ensure that the translated content displays correctly and aligns with the cultural norms of the target audience. This step is critical for sectors like Legal & Compliance and Telehealth.
5. Launch and Monitoring: Once the website is translated and tested, launch it for the new audience. Continuously monitor the site for issues related to user experience and functionality, ensuring it meets local expectations.
By following these steps, localisation Managers, Marketing Heads, and Product Managers can ensure that their BFSI, eCommerce, or Healthcare websites are effectively translated and ready for a global audience.
Next, let’s look at when website translation should be implemented in your business strategy.
When Should You Implement Translation?
Translation is ideal for making content accessible in a new language without requiring cultural adjustments. It’s the first step for regions where localisation isn’t necessary.
- Targeting new language-speaking regions: When entering regions with minimal cultural differences, translation ensures accessibility, such as BFSI platforms expanding to other European markets.
- Expanding content for broader reach: Add translations for widely spoken languages, like Mandarin or Spanish, to reach larger markets, ideal for eCommerce and Healthcare.
- Localising legal or product documents: Translate content such as contracts or product descriptions for Legal & Compliance firms, where cultural adaptation isn’t required, but accuracy is vital.
Also Read: A Complete Guide to WordPress Localization: Make Your Website Multilingual
Now, let’s take a look at some real-world examples of translation and localisation.
3 Real-World Examples of Translation and Localisation
Real-world examples highlight the difference between translation and localisation, showcasing how businesses successfully adapt content for global markets and cultural relevance.
1. KitKat
When KitKat entered the Japanese market, the company’s iconic slogan “Have a break, have a KitKat” would not resonate culturally. Instead of translating it literally, KitKat adapted the slogan to “Kitto Katsu,” meaning “Surely Win,” which aligned with Japan’s cultural emphasis on success. This localisation strategy was extended further with unique chocolate flavours tailored to Japanese tastes, ensuring the brand resonated with local preferences. KitKat’s success in Japan highlights the power of cultural adaptation beyond simple translation.
2. Coca-Cola
Coca-Cola maintains a unified global brand but tailors its messaging and marketing to different markets. In China, the company localised its name from “Coca-Cola” to “Kekou Kele,” meaning “delicious happiness,” which resonated more with local consumers. Coca-Cola’s ability to adapt its product names and campaigns based on cultural context has contributed to its success worldwide, demonstrating the importance of localisation in maintaining brand identity while connecting with regional markets.
3. Intel’s Slogan in Brazil
Intel’s global slogan “Intel: Sponsors of Tomorrow” didn’t translate well into Brazilian Portuguese, where it implied the company wouldn’t deliver until tomorrow, a message that suggested delay and unreliability. In Brazil, Intel localised the slogan to “Intel: In Love with the Future,” which conveyed the original optimism without the negative connotations. This case emphasises how localisation (or transcreation) is often more effective than direct translation, particularly when addressing cultural nuances and maintaining brand integrity.
Also Read: What is Cultural Localization? A Complete Guide
Let’s explore how Anuvadak can simplify your website’s translation and localisation process.
Translation vs Localization: Which Should I Choose?
When deciding between website translation vs. localization services, it’s important to evaluate key factors that impact user experience, functionality, and compliance. Below are the essential elements to consider for different industries.
1. Language and Regionalism
Translation focuses on linguistic accuracy, while localisation adapts content for regional dialects and cultural nuances. For BFSI platforms, this means translating financial terms accurately, while for eCommerce, regional preferences and language variations are key for effective communication.
2. Ease of Navigation
In translation, the website’s structure remains intact, but localisation ensures that navigation is culturally relevant. For Healthcare or Government services, this can involve adjusting content for easier access to key information, like patient forms or local public services.
3. Cultural Elements
Localisation goes beyond translation, adapting colours, sizes, and imagery to local expectations. For eLearning platforms, this might include modifying icons or graphics to align with regional cultural symbols, while for eCommerce, adapting marketing materials to local humour or etiquette is essential.
- Colors, shapes, sizes, and styles: Tailor the visuals to match regional aesthetics.
- Images, icons, and graphics: Modify imagery to fit cultural preferences, particularly in eCommerce.
- Societal codes: Adapt humour, etiquette, and symbols for regional relevance, particularly for BFSI or Marketing Heads.
4. Transactional Elements
Localisation adjusts date/time formats, telephone numbers, and currency for local use. This is especially important for eCommerce where product descriptions and reviews need to be tailored to the local market, ensuring that users feel at home navigating the site.
- Date and time formats, telephone numbers, and contact information: Ensure that these details are regionally compliant, particularly in Healthcare and Government services.
- Weights, measurements, and geographical references: For Automotive and Manufacturing, adjusting technical specifications to regional units is key.
- Language and linguistic content, product descriptions, and reviews: Localise descriptions and reviews to match the expectations and language of the region.
5. Communication Elements
Localisation extends to the customer service and legal information provided on the website. For Compliance Officers in Legal & Compliance industries, ensuring that legal disclaimers and terms of service are localised to comply with regional laws is important.
- Local customer service information: Adapt customer support channels and information to the local language and norms, vital for CX Leaders in eCommerce.
- Legal information: Ensure that Privacy Policies, Terms of Service, and other legal documentation are fully compliant with local regulations.
The decision between website translation vs localization services depends on regulatory requirements, cultural expectations, and the depth of market penetration you aim to achieve.
Also Read: A Complete Guide to iOS Localization
Now, let’s explore what Anuvadakk’s automatic translation solutions can do for your website.
Simplify Website Translation and Localisation with Anuvadak
Translation is only effective when it feels native to the audience. Anuvadak helps businesses manage both translation and localisation together, ensuring content aligns with regional language preferences and cultural context. Designed for sectors like eCommerce, BFSI, and healthcare, it supports scale while maintaining accuracy and user trust.
- Website & App Localisation: Automates both translation and localisation, ensuring your content is culturally relevant and accurate for diverse global markets. Perfect for eCommerce and Healthcare.
- Real-Time Multilingual APIs: Supports API-based translation and content delivery, ensuring real-time updates to multilingual content across web and mobile applications, especially for fast-paced industries like eCommerce and BFSI.
- Seamless CMS Integration: Easily integrates with platforms, simplifying the management of multilingual content across websites and apps, reducing manual translation workflows.
- Context-Aware Translation Memory: Utilises AI-powered translation memory to maintain consistency across languages, ensuring accuracy and reducing redundancy in your content.
- Cultural Relevance: Automatically adapts content to meet local cultural norms, ensuring your brand’s message resonates with each region and customer segment.
- Enterprise-Grade Security & Compliance: Ensures secure, encrypted translations, meeting the highest data protection and regulatory standards for industries such as BFSI and Healthcare.
- Scalable for Global Expansion: Scales with your business as you grow, providing enterprise-level solutions for websites and apps across multiple languages without compromising quality.
With Anuvadak, expanding your business globally becomes a smooth process. Automate website translation and localisation, ensuring your content is consistent, culturally relevant, and secure across all regions, so you can engage users wherever they are.
Conclusion
Understanding the distinctions between website translation vs localization services is essential for B2B professionals, especially CTOs, Product Managers, and Marketing Heads. localisation offers a more comprehensive solution for adapting content culturally and functionally, making it ideal for businesses looking to engage with global audiences effectively.
With Anuvadak, you can automate the translation and localisation of your website and adapt it to local markets effortlessly. Multilingual APIs and Seamless CMS Integration ensure that your content remains consistent and relevant across regions, all while enhancing user engagement.
Contact us to see how Anuvadak can automate your website’s translation and localisation for global consistency and engagement.
FAQs
1. How can I ensure legal compliance when localising my website for different regions?
For Legal & Compliance industries, work with local legal experts to ensure privacy policies and terms of service comply with region-specific laws like GDPR.
2. How does localisation impact user engagement on a multilingual eCommerce platform?
Localised product descriptions and customer support options improve user engagement, increase conversion rates, and build brand trust, especially for eCommerce businesses targeting global markets.
3. What tools can I use to integrate both website translation and localisation seamlessly?
Multilingual APIs and TMS platforms, such as WordPress plugins, allow seamless integration of website translation and localisation, ensuring consistency across markets.
4. How do translation and localisation differ in terms of SEO for a multilingual site?
Localisation adapts SEO strategies for specific regions using local keywords and SEO tactics. Translation focuses on converting existing content, which may not always be SEO-optimised.
5. What is the cost difference between translation and full website localisation?
Translation is typically more affordable, as it involves text conversion only, while localisation requires cultural, functional, and legal adjustments, increasing both time and cost.